Abstract
Purpose
Harbor sediments normally accumulate the pollutants from municipal and industrial activities in the estuarine zone. This work aimed to characterize the fractionation change of heavy metals in harbor sediments before and after chemical washing. Since the annual dredging around the Kaohsiung Harbor has increased over time, the influence of ex-situ acid washing on sediment quality needs to be evaluated.
Materials and methods
Experimental parameters of acid washing included the solid loading (4–20%) and types (HCl, HNO3, and citric acid) and concentrations (0.01–1 M) of acids. The fractionation of Cu, Zn, Ni, Cd, Cr, and Pb in the sediments at three estuaries, the Chienchen River, Canon River (Dock No.5), and Yanshui River, before and after washing processes were determined through sequential extraction.
Results and discussion
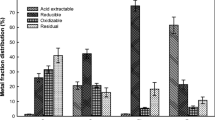
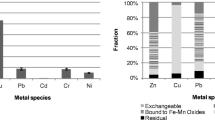
The washing efficiencies of HCl, HNO3, and citric acid were similar, being 80.1–83.7%, 27.6–30.9%, 20.7–23.9%, and 97.2–98.8% for Zn, Ni, Cr, and Cd, respectively. After 15 min of washing, HCl was found as a suitable washing agent, and particularly, more effective for Cu (65.3%) and Pb (79.4%) than other acids. The extraction process suggested that the acid washing of carbonate, the Fe-Mn oxide composite, and organic phases were highly correlated to their quantities in the sediments. However, the removal efficiency was inversely related to the metals in the residual phase.
Conclusions
Knowing the mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals based on fractionation of metals benefits the assessment of the potential risk of dredged harbor sediment after the washing procedure. This study provided evidence that acid washing, as a remediation method, could be versatile in removing heavy metals from mobile phases without causing mineralogical changes to the contaminated sediments of the harbor area.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alan M, Kara D (2019) Comparison of a new sequential extraction method and the BCR sequential extraction method for mobility assessment of elements around boron mines in Turkey. Talanta 194:189–198
Baba Y, Shimoyama I, Hirao N (2016) Chemical state analysis of trace-level alkali metals sorbed in micaceous oxide by total reflection X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl Surf Sci 384:511–516
Bacon JR, Davidson CM (2008) Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction? Analyst 133:25–46
Bárcena JF, Claramunt I, García-Alba J, Pérez ML, García A (2017) A method to assess the evolution and recovery of heavy metal pollution in estuarine sediments: past history, present situation and future perspectives. Mar Pollut Bull 124:421–434
Batjargal T, Otgonjargal E, Baek K, Yang JS (2010) Assessment of metals contamination of soils in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. J Hazard Mater 184:872–876
Bjerrum MJ, Bjerrum J (1990) Estimation of small stability constants in aqueous solution. The chromium(III) chloride system. Acta Chem Scand 44:353–357
Brady JP, Kinaev I, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2016) Comparison of partial extraction reagents for assessing potential bioavailability of heavy metals in sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 106:329–334
Chen CW, Chen CF, Hung CM, Dong CD (2014) Evaluating the leachable metals in Kaohsiung Harbor sediment using the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). Desalin Water Treat 21:1–10
Chen CF, Ju YR, Chen CW, Dong CD (2016) Vertical profile, contamination assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediment cores of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 165:67–79
Chen CF, Chen CW, Ju YR, Dong CD (2017) Determination and assessment of phthalate esters content in sediments from Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 124:767–774
Chen CF, Chen CW, Ju YR, Kao CM, Dong CD (2018a) Impact of disposal of dredged material on sediment quality in the Kaohsiung Ocean dredged material disposal site, Taiwan. Chemosphere 191:555–565
Chen CF, Chen CW, Ju YR, Kao CM, Dong CD (2018b) Impact of disposal of dredged material on sediment quality in the Kaohsiung Ocean dredged material disposal site, Taiwan. Chemosphere 191:555–565
Cissoko N, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Xu X (2009) Removal of Cr(VI) from simulative contaminated groundwater by iron metal. Process Saf Environ Prot 87:395–400
Dahrazma B, Mulligan CN (2007) Investigation of the removal of heavy metals from sediments using rhamnolipid in a continuous flow configuration. Chemosphere 69:705–711
D'Amore JJ, Al-Abed SR, Ryan JA (2005) Methods for speciation of metals in soils: a review. J Environ Qual 34:1707–1745
Dermont G, Bergeron M, Mercier G, Richer-Laflèche M (2008a) Metal-contaminated soils: remediation practices and treatment technologies. Pract Period Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste Manage 12:188–209
Dermont G, Bergeron M, Mercier G, Richer-Lafleche M (2008b) Soil washing for metal removal: a review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications. J Hazard Mater 152:1–31
Dermont G, Bergeron M, Richer-Laflèche M, Mercier G (2010) Remediation of metal-contaminated urban soil using flotation technique. Sci Total Environ 408:1199–1211
Di Palma L, Mecozzi R (2007) Heavy metals mobilization from harbour sediments using EDTA and citric acid as chelating agents. J Hazard Mater 147:768–775
Dong CD, Chen CW, Chen CF (2015) Seasonal and spatial distribution of 4-nonylphenol and 4-tert-octylphenol in the sediment of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 134:588–597
Drahota P, Grösslová Z, Kindlová H (2014) Selectivity assessment of an arsenic sequential extraction procedure for evaluating mobility in mine wastes. Anal Chim Acta 839:34–43
Filgueiras AV, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2002) Chemical sequential extraction for metal partitioning in environmental solid samples. J Environ Monit 4:823–857
Gallardo V, Navarro R, Saucedo I, A’vila M, Guibal E (2008) Zinc(II) extraction from hydrochloric acid solutions using Amberlite XAD-7 impregnated with Cyphos IL 101 (Tetradecyl(trihexyl)phosphonium chloride). Sep Sci Technol 43:2434–2459
Gleyzes C, Tellier S, Astruc M (2002) Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: a review of sequential extraction procedures. Trends Anal Chem 2:451–467
Gómez-Ariza JL, Giráldez I, Sánchez-Rodas D, Morales E (1999) Metal readsorption and redistribution during the analytical fractionation of trace elements in oxic estuarine sediments. Anal Chim Acta 399:295–307
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Hasan M, Kausar D, Akhter G, Shah MH (2018) Evaluation of the mobility and pollution index of selected essential/toxic metals in paddy soil by sequential extraction method. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:283–291
Hei P, Zhang Y, Shang Y, Lei X, Quan J, Zhang M (2017) An approach to minimizing the uncertainty caused by sediment washing pretreatment in phosphorus adsorption experiments. Ecol Eng 107:244–251
Hlavay J, Prohaska T, Weisz M, Wenzel WW, Stingeder GJ (2004) Determination of trace elements bound to soils and sediment fractions. Pure Appl Chem 7:415–420
Hu C, Yang X, Dong J, Zhang X (2018) Heavy metal concentrations and chemical fractions in sediment from swan lagoon, China: their relation to the physiochemical properties of sediment. Chemosphere 209:848–856
Huang YJ, Lee CL, Fang MD (2011) Distribution and source differentiation of PAHs and PCBs among size and density fractions in contaminated harbor sediment particles and their implications in toxicological assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 62:432–439
Jean-Soro L, Bordas F, Bollinger JC (2012) Column leaching of chromium and nickel from a contaminated soil using EDTA and citric acid. Environ Pollut 164:175–181
Kaasalainen M, Yli-Halla M (2003) Use of sequential extraction to assess metal partitioning in soils. Environ Pollut 126:225–233
Kang M, Tian Y, Peng S, Wang M (2019) Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci Total Environ 648:861–870
Kim B, McBride MB (2006) A test of sequential extractions for determining metal speciation in sewage sludge-amended soils. Environ Pollut 144:475–482
Kim KJ, Kim DH, Yoo JC, Baek K (2011) Electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from dredged marine sediment. Sep Purif Technol 79:164–169
Kim EJ, Lee JC, Baek K (2015) Abiotic reductive extraction of arsenic from contaminated soils enhanced by complexation: arsenic extraction by reducing agents and combination of reducing and chelating agents. J Hazard Mater 283:454–461
Lee PK, Kang MJ, Yu S, Ko KS, Ha K, Shin SC, Park JH (2017) Enrichment and geochemical mobility of heavy metals in bottom sediment of the Hoedong reservoir, Korea and their source apportionment. Chemosphere 184:74–85
Li G, Yang X, Liang L, Guo S (2017) Evaluation of the potential redistribution of chromium fractionation in contaminated soil by citric acid/sodium citrate washing. Arab J Chem 10:S539–S545
Liu CC, Lin YC (2013) Reclamation of copper-contaminated soil using EDTA or citric acid coupled with dissolved organic matter solution extracted from distillery sludge. Environ Pollut 178:97–101
Loring DH, Rantala RTT (1992) Manual for the geochemical analyses of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth Sci Rev 32:235–283
Löser C, Zehnsdorf A, Hoffmann P, Seidel H (2007) Remediation of heavy metal polluted sediment by suspension and solid-bed leaching: estimate of metal removal efficiency. Chemosphere 66:1699–1705
Mester Z, Cremisini C, Ghiara E, Morabito R (1998) Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for metal fractionation in sediment samples. Anal Chim Acta 359:133–142
Min X, Xie X, Chai L, Liang Y, Li M, Ke Y (2013) Environmental availability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in zinc leaching residue. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 23:208–218
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60:193–207
Ortega LM, Lebrun R, Blais JF, Hausler R, Drogui P (2008) Effectiveness of soil washing, nanofiltration and electrochemical treatment for the recovery of metal ions coming from a contaminated soil. Water Res 42:1943–1952
Peng JF, Song YH, Yuan P, Cui XY, Qiu GL (2009) The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J Hazard Mater 161:633–640
Peng W, Li X, Xiao S, Fan W (2018) Review of remediation technologies for sediments contaminated by heavy metals. J Soils Sediments 18:1701–1719
Ramette RW, Fan G (1983) Copper(II) chloride complex equilibrium constants. Inorg Chem 22:3323–3326
Rodella I, Vaccaro C, Melchiorre M, Simeoni U, Campisi T, Corbau C (2018) Textural changes and heavy metal distribution in sediments after decontamination treatment by soil washing and attrition scrubber. J Soils Sediments 18:1780–1793
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Akhter G, Shah MH (2018) Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. J Geochem Explor 184:199–208
Shih YJ, Binh NT, Chen CW, Chen CF, Dong CD (2016) Treatability assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated marine sediments using permanganate, persulfate and Fenton oxidation processes. Chemosphere 150:294–303
Suanon F, Sun Q, Dimon B, Mama D, Yu CP (2016) Heavy metal removal from sludge with organic chelators: comparative study of N, N-bis(carboxymethyl) glutamic acid and citric acid. J Environ Manag 166:341–347
Swietlik R, Trojanowska M, Strzelecka M, Bocho-Janiszewska A (2015) Fractionation and mobility of Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb and Zn in the road dust retained on noise barriers along expressway - a potential tool for determining the effects of driving conditions on speciation of emitted particulate metals. Environ Pollut 196:404–413
Templeton D, Ariese F, Cornelis R, Danielsson L, Muntau H, Van Leeuwen H, Lobinski R (2000) Guidelines for terms related to chemical speciation and fractionation of elements. Definitions, structural aspects, and methodological approaches (IUPAC recommendations 2000). Pure Appl Chem 72:1453–1470
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace-metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Vanthuyne M, Maes A (2007) The removal of heavy metals from dredged sediments by mechanical Denver flotation: the contribution of true flotation and entrainment. Land Contam Reclam 15:15–30
Vanthuyne M, Maes A, Cauwenberg P (2003) The use of flotation techniques in the remediation of heavy metal contaminated sediments and soils: an overview of controlling factors. Miner Eng 16:1131–1141
von Gunten K, Alam MS, Hubmann M, Ok YS, Konhauser KO, Alessi DS (2017) Modified sequential extraction for biochar and petroleum coke: metal release potential and its environmental implications. Bioresour Technol 236:106–110
Wang X, Plackowski CA, Nguyen AV (2016) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic investigation into the surface effects of sulphuric acid treated natural zeolite. Powder Technol 295:27–34
Wang H, Liu T, Tsang DCW, Feng S (2017) Transformation of heavy metal fraction distribution in contaminated river sediment treated by chemical-enhanced washing. J Soils Sediments 17:1208–1218
Wang G, Zhang S, Zhong Q, Xu X, Li T, Ji Y, Zhang Y, Peijnenburg WJGM, Vijver MG (2018) Effect of soil washing with biodegradable chelators on the toxicity of residual metals and soil biological properties. Sci Total Environ 625:1021–1029
Wawrzkiewicz M, Wisniewska M, Wołowicz A, Gun'ko VM, Zarko VI (2017) Mixed silica-alumina oxide as sorbent for dyes and metal ions removal from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 250:128–147
Wei M, Chen J, Wang X (2016) Removal of arsenic and cadmium with sequential soil washing techniques using Na2EDTA, oxalic and phosphoric acid: optimization conditions, removal effectiveness and ecological risks. Chemosphere 156:252–261
Wen J, Yi Y, Zeng G (2016) Effects of modified zeolite on the removal and stabilization of heavy metals in contaminated lake sediment using BCR sequential extraction. J Environ Manag 178:63–69
Westrich B, Förstner U (2007) Sediment dynamics and pollutant mobility in rivers: an interdisciplinary approach. Springer, pp 430. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34785-9
Xia B, Guo P, Lei Y, Zhang T, Qiu R, Knorr KH (2016) Investigating speciation and toxicity of heavy metals in anoxic marine sediments—a case study from a mariculture bay in southern China. J Soils Sediments 16:665–676
Xu YH, Huang JH, Brandl H (2017) An optimised sequential extraction scheme for the evaluation of vanadium mobility in soils. J Environ Sci 53:173–183
Yang HJ, Lee CY, Chiang YJ, Jean JS, Shau YH, Takazawa E, Jiang WT (2016) Distribution and hosts of arsenic in a sediment core from the Chianan Plain in SW Taiwan: implications on arsenic primary source and release mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 569–570:212–222
Yoo JC, Lee CD, Yang JS, Baek K (2013) Extraction characteristics of heavy metals from marine sediments. Chem Eng J 228:688–699
Zhang W, Huang H, Tan F, Wang H, Qiu R (2010) Influence of EDTA washing on the species and mobility of heavy metals residual in soils. J Hazard Mater 173:369–376
Zhang C, Yu Z, Zeng G, Jiang M, Yang Z, Cui F, Zhu M, Shen L, Hu L (2014) Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ Int 73:270–281
Zhipeng T, Bingru Z, Chengjun H, Rongzhi T, Huangpu Z, Fengting L (2015) The physiochemical properties and heavy metal pollution of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Process Saf Environ Prot 98:333–341
Funding
The authors would like to thank the National Sun Yat-sen University and National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology, Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. 107-P07.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jos Brils
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 368 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shih, YJ., Syu, SY., Chen, CW. et al. Assessment of ex-situ chemical washing of heavy metals from estuarine sediments around an industrial harbor in Southern Taiwan. J Soils Sediments 19, 3108–3122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02321-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02321-7