Abstract
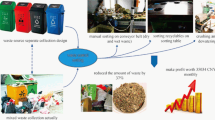
Municipal solid waste (MSW) management and recycling has become an emerging issue in developing countries. Shanghai, the largest megacity in China, is well-known nationwide due to leading China’s MSW separation and recycling. Therefore, this paper introduces the Shanghai mode for MSW management and its current situation to enrich existing MSW management studies. Results show that the total generation volume of MSW and amount of MSW generation per capita were 9.00 million tons and 372.16 kg in 2017, increased approximately eight-fold and four-fold compared with the data in 1978, respectively. The MSW treatment rate reached 100% since 2014, with incineration rate increased to 48.56% in 2017. The cost of MSW management after implementing MSW sorting regulation is increased to 985 CNY/ton, including 390 CNY/ton of MSW sorting cost. Then three key features and innovative MSW management modes, namely, mandatory MSW sorting legislation, Green Account program, and the Combined Network program are introduced. Meanwhile, two main challenges are urgent to be responded, including inadequate collecting vehicles and limited wet waste treatment capacity. Finally, policy recommendations on strengthening MSW recycling process, constructing complete terminal treatment industry, and making systematic policies were provided to respond existing challenges.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batool SA, Chuadhry MN (2009) The impact of municipal solid waste treatment methods on greenhouse gas emissions in Lahore, Pakistan. Waste Manag 29:63–69
Bovea M, Ibáñez-Forés V, Gallardo A, Colomer-Mendoza F (2010) Environmental assessment of alternative municipal solid waste management strategies. A Spanish case study. Waste Manag 30:2383–2395
Chen S (2018) MSW sorting, what is the function of the Green Account? Youth Daily, Shanghai
Cheng J, Dong X (2017) Physical and chemical characteristics of municipal solid waste in Shanghai. Environ Sani Eng 4:36–40
Dong H, Geng Y, Yu X, Li J (2018) Uncovering energy saving and carbon reduction potential from recycling wastes: a case of Shanghai in China. J Clean Prod 205:27–35
Geng Y, Sarkis J, Ulgiati S, Zhang P (2013) Measuring China’s circular economy. Science 339:1526–1527
Giusti L (2009) A review of waste management practices and their impact on human health. Waste Manag 29:2227–2239
Hamer G (2003) Solid waste treatment and disposal: effects on public health and environmental safety. Biotechnol Adv 22:71–79
Han Z, Ye C, Zhang Y, Dan Z, Zou Z, Liu D, Shi G (2019) Characteristics and management modes of domestic waste in rural areas of developing countries: a case study of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8485–8501
Haupt M, Vadenbo C, Hellweg S (2016) Do we have the right performance indicators for the circular economy?: Insight into the Swiss Waste Management System. J Ind Ecol 21(3):615–627
Iimedia (2019) Data analysis of waste sorting industry: recyclable wastes would research 5960 tons per day in October 2019, Shanghai, http://huanbao.bjx.com.cn/news/20191223/1030685.shtml
Ji S (2016) Shanghai sorting waste “Green Account” points recording unstrict, no punishment by related bureau, http://www.cn-hw.net/html/china/201612/56391.html
Jiefang Daily (2017) Shanghai: promote to combine municipal solid waste sorting collection and transportation system and Shanghai
Kaza S, Yao L, Perinaz B-T, Van Woerden F (2018) What A Waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. The World Bank
Kokkinos K, Karayannis V, Lakioti E, Moustakas K (2019) Exploring social determinants of municipal solid waste management: survey processing with fuzzy logic and self-organized maps. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:35288–35304
Li ZS, Yang L, Qu XY, Sui YM (2009) Municipal solid waste management in Beijing City. Waste Manag 29:2596–2599
Liu F, Chen J, Xi D, Shen J (2005) Study on disposal and pollution prevention strategies of municipal household waste in Shanghai. China Resour Compr Util 5:13–17 (In Chinese)
Liu XY, Fu HZ, Jiang HL, Shao Y, Wu XY, Li ZS (2019) A survey of municipal solid waste landfills in Beijing during 2009-2011. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20286–20296
Liu JG, Yu SY, Shang YX (2020) Toward separation at source evolution of municipal solid waste management in China. Front Environ Sci Eng 14:3
Ma J, Hipel KW, Hanson ML, Cai X, Liu Y (2018) An analysis of influencing factors on municipal solid waste source-separated collection behavior in Guilin, China by using the theory of planned behavior. Sustain Cities Soc 37:336–343
Miezah K, Obiri-Danso K, Kádár Z, Fei-Baffoe B, Mensah MY (2015) Municipal solid waste characterization and quantification as a measure towards effective waste management in Ghana. Waste Manag 46:15–27
Ministry of Civil Affairs of the People’s Repiblic of China (2019) National Administrative Division Information Inquiry Platform, http://xzqh.mca.gov.cn/defaultQuery?shengji=%C9%CF%BA%A3%CA%D0%28%BB%A6%29&diji=%C9%CF%BA%A3%CA%D0&xianji=-1
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (2009) Sampling and analysis methods for domestic waste, Beijing
National Bureau of Statistics (2018) China Statistical Yearbook China Statistics Press, Beijing
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2018) China Statistical Yearbook 2018. China Statistics Press, Beijing
National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (2017) Implementation plan of household waste classification system, http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-03/30/content_5182124.htm
Oguntoke O, Emoruwa FO, Taiwo MA (2019) Assessment of air pollution and health hazard associated with sawmill and municipal waste burning in Abeokuta Metropolis, Nigeria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:32708–32722
Qi Y (2012) Comparison of characteristics and treatment technoques of municipal solid waste between Shanghai and other cities in the world, http://www.cn-hw.net/html/32/201201/31505.html
Shanghai Municipal Greening and Appearance Administration Bureau (2018a) Notification of 2017 Shanghai Municipal Solid Waste Sorting Situation, Shanghai, pp 8
Shanghai Municipal Greening and Appearance Administration Bureau (2018b) Green Account, https://www.greenfortune.sh.cn/dist/index.html#/
Shanghai Municipal Greening and Appearance Administration Bureau (2018c) Guidelines for the construction of Combined Network recycling system in Shanghai (Trial Version), http://lhsr.sh.gov.cn/sites/wuzhangai_lhsr/zhengcefagui_content.aspx?infoId=5792a0e4-cea7-4a90-b9e8-46b145d30c8a&ctgId=1ff94abf-7efb-44d8-bb4b-8bc87fdf397d
Shanghai Municipal Greening and Appearance Administration Bureau (2018d) Action plan of construction of the whole system of municipal solid waste classification in Shanghai (2018-2020), http://www.shanghai.gov.cn/nw2/nw2314/nw2315/nw4411/u21aw1304805.html
Shanghai Municipal People’s Congress (2019) Regulation of Shanghai municipal solid waste management. In: Shanghai Municipal People’s Congress (Hrsg.), Shanghai
Shanghai Municipal People’s Congress (2019a) Regulation of Shanghai Municipal Solid Waste Management, Shanghai
Shanghai Municipal People’s Congress (2019b) First month report of Shanghai MSW new regulation, Shanghai
Shanghai Municipal People’s Government (2018a) Implementation plan of establishing and perfecting the whole system of municipal solid waste classification, Shanghai
Shanghai Municipal People’s Government (2018b) Shanghai Master Plan (2017-2035), Shanghai
Shanghai Songjiang (2018) Exchanging difficulty with Green Account, Shanghai
Shenzhen Special Zone Daily (2018) The ranks of MSW sorting in the second season among 46 pilot cities. Shenzhen Special Zone Daily, Shenzhen
Sinolink Securities (2019) The whole cost is 985 CNY/Year? Take Shanghai as example, calculating the cost of MSW treatment
The People’s Government of Beijing Municipality (2019) Regulation of Beijing municipal solid waste management. In: Beijing Municipal People’s Congress (Hrsg.), Beijing
Troschinetz AM, Mihelcic JR (2009) Sustainable recycling of municipal solid waste in developing countries. Waste Manag 29:915–923
United Nations Development Programme (2015) Sustainable development goals. United Nations Development Programme
Wei Y, Li J, Shi D, Liu G, Zhao Y, Shimaoka T (2017) Environmental challenges impeding the composting of biodegradable municipal solid waste: a critical review. Resour Conserv Recycl 122:51–65
Xiao S, Dong H, Geng Y, Brander M (2018) An overview of China’s recyclable waste recycling and recommendations for integrated solutions. Resour Conserv Recycl 134:112–120
Xiao S, Dong H, Geng Y, Tian X, Liu C, Li H (2020) Policy impacts on Municipal Solid Waste management in Shanghai: a system dynamics model analysis. J Clean Prod 262:121366
Yadav P, Samadder SR (2018) Environmental impact assessment of municipal solid waste management options using life cycle assessment: a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:838–854
Ye J (2017) Shanghai: make waste-sorted residents have sensual acquisiton
Zhang H, Wen Z (2014) The consumption and recycling collection system of PET bottles: a case study of Beijing, China. Waste Manag 34:987–998
Zhang DQ, Tan SK, Gersberg RM (2010) Municipal solid waste management in China: status, problems and challenges. J Environ Manag 91:1623–1633
Zhang H, Liu J, Wen Z, Chen Y (2017) College students’ municipal solid waste source separation behavior and its influential factors: a case study in Beijing, China. J Clean Prod 164:444–454
Zhang M, Gao M, Yue S, Zheng T, Gao Z, Ma X, Wang Q (2018) Global trends and future prospects of food waste research: a bibliometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:24600–24610
Zhao S (2013) Privatization, FDI inflow and economic growth: evidence from China’s provinces, 1978-2008. Appl Econ 45:2127–2139
Zhuang Y, Wu S, Wang Y, Wu W, Chen Y (2008) Source separation of household waste: a case study in China. Waste Manag 28:2022–2030
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 71974126, and 71690241). We would also like to thank the support of Shanghai Environmental Key Lab of Environmental Data and Intelligence.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, S., Dong, H., Geng, Y. et al. An overview of the municipal solid waste management modes and innovations in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 29943–29953 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09398-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09398-5