Abstract
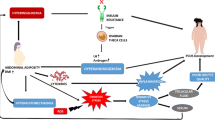
This study was conducted to investigate the effects of maternal exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) on testis development of F1 male mice. The BPA exposure model of pregnant mice was prepared by intragastric administration of BPA at the doses of 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg/day at gestation day (GD) 0.5–17.5. The testis index of the offspring mice was calculated at postnatal day (PND) 21 and PND 56. The results showed that maternal exposure to 20 mg/kg BPA during pregnancy significantly increased the testicular index of F1 males at PND 21, and 40 mg/kg BPA significantly decreased the testicular index of F1 males at PND 56 (P < 0.01). BPA significantly reduced serum testosterone (T) and estradiol (E2) levels, and improved testicular ERα and ERβ levels in F1 males at both PND 21 and PND 56. BPA exposure also upregulated transcription of testicular Dnmt1 and inhibited the transcription of testicular Dnmt3A and Dnmt3B in F1 mice at PND 21. BPA reduced the transcriptional level of testicular DNA methyltransferase (Dnmt), increased the expression of testicular caspase-7, caspase-9, and bax, and decreased the expression of bcl-2 in F1 mice at PND 56. Consistent with that, BPA improved the apoptosis rate in the testis at PND 56 (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05). Our study indicates that BPA disrupts the secretion of testosterone, estradiol, and estrogen receptors by interfering with the transcription of testicular DNA methyltransferase (Dnmt) in offspring males, which damages testicular tissues and affects the potential reproductive function.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi J (2018) Scientists call FDA statement on bisphenol a safety premature. JAMA 319:1644–1646
Abilmona SM, Sumrell RM, Gill RS, Adler RA, Gorgey AS (2018) Serum testosterone levels may influence body composition and cardiometabolic health in men with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 57:229–239.
Armstrong CM, Allred KF, Weeks BR, Chapkin RS, Allred CD (2017) Estradiol has differential effects on acute colonic inflammation in the presence and absence of estrogen receptor beta expression. Dig Dis Sci 62:1977–1984
Banerjee A, Anjum S, Verma R, Krishna A (2012) Alteration in expression of estrogen receptor isoforms alpha and beta, and aromatase in the testis and its relation with changes in nitric oxide during aging in mice. Steroids 77:609–620
Beal JA (2018) Baby bottles and bisphenol A (BPA): still a parental concern. MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs 43:349
Canovas S, Ross PJ, Kelsey G, Coy P (2017) DNA methylation in embryo development: epigenetic impact of ART (assisted reproductive technologies). Bioessays 39:1700106.
Comeglio P, Cellai I, Filippi S, Corno C, Corcetto F, Morelli A, Maneschi E, Maseroli E, Mannucci E, Fambrini M, Maggi M, Vignozzi L (2016) Differential effects of testosterone and estradiol on clitoral function: an experimental study in rats. J Sex Med 13:1858–1871
Delbes G, Levacher C, Pairault C, Racine C, Duquenne C, Krust A, Habert R (2004) Estrogen receptor beta-mediated inhibition of male germ cell line development in mice by endogenous estrogens during perinatal life. Endocrinology 145:3395–3403
D'Errico F, Goverse G, Dai Y, Wu W, Stakenborg M, Labeeuw E, De Simone V, Verstockt B, Gomez-Pinilla PJ, Warner M, Di Leo A, Matteoli G, Gustafsson JA (2018) Estrogen receptor beta controls proliferation of enteric glia and differentiation of neurons in the myenteric plexus after damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:5798–5803
Fagin D (2012) Toxicology: the learning curve. Nature 490:462–465
Fenichel P, Chevalier N (2017) Environmental endocrine disruptors: new diabetogens? C R Biol 340:446–452
Gupta S, Guha P, Majumder S, Pal P, Sen K, Chowdhury P, Chakraborty A, Panigrahi AK, Mukherjee D (2018) Effects of bisphenol A (BPA) on brain-specific expression of cyp19a1b gene in swim-up fry of Labeo rohita. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 209:63–71
Huang YQ, Wong CK, Zheng JS, Bouwman H, Barra R, Wahlstrom B, Neretin L, Wong MH (2012) Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: a review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ Int 42:91–99
Imao M, Nagaki M, Imose M, Moriwaki H (2006) Differential caspase-9-dependent signaling pathway between tumor necrosis factor receptor- and Fas-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis in mice. Liver Int 26:137–146
Ji Y, Hu B, Li J, Traub RJ (2018) Opposing roles of estradiol and testosterone on stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats. J Pain 19:764–776
Jiang X, Yin L, Zhang N, Han F, Liu WB, Zhang X, Chen HQ, Cao J, Liu JY (2018) Bisphenol A induced male germ cell apoptosis via IFNbeta-XAF1-XIAP pathway in adult mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 355:247–256
Jin H, Zhu L (2016) Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 103:343–351
Jurek A, Leitner E (2018) Analytical determination of bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol analogues in paper products by LC-MS/MS. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 34:1225–1238
Kundakovic M, Champagne FA (2011) Epigenetic perspective on the developmental effects of bisphenol A. Brain Behav Immun 25:1084–1093
Laing LV, Viana J, Dempster EL, Uren Webster TM, van Aerle R, Mill J, Santos EM (2018) Sex-specific transcription and DNA methylation profiles of reproductive and epigenetic associated genes in the gonads and livers of breeding zebrafish. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 222:16–25
Li Y, Duan F, Zhou X, Pan H, Li R (2018) Differential responses of GC1 spermatogonia cells to high and low doses of bisphenol A. Mol Med Rep 18:3034–3040
Ma S, Shi W, Wang X, Song P, Zhong X (2017) Bisphenol A exposure during pregnancy alters the mortality and levels of reproductive hormones and genes in offspring mice. Biomed Res Int 2017:3585809
Meng Y, Lin R, Wu F, Sun Q, Jia L (2018) Decreased capacity for sperm production induced by perinatal bisphenol A exposure is associated with an increased inflammatory response in the offspring of C57BL/6 male mice. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15.pii: E2158.
Muhamad MS, Salim MR, Lau WJ, Yusop Z (2016) A review on bisphenol A occurrences, health effects and treatment process via membrane technology for drinking water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:11549–11567
Negev M, Berman T, Reicher S, Balan S, Soehl A, Goulden S, Ardi R, Shammai Y, Hadar L, Blum A, Diamond ML (2018) Regulation of chemicals in children’s products: how U.S. and EU regulation impacts small markets. Sci Total Environ 616-617:462–471
Owczarek K, Kubica P, Kudlak B, Rutkowska A, Konieczna A, Rachon D, Namiesnik J, Wasik A (2018) Determination of trace levels of eleven bisphenol A analogues in human blood serum by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Sci Total Environ 628–629:1362–1368
Passouant-Fontaine T, Flandre C (1968) Influence of neonatal estrogens on testis development and compensating hypertrophy after hemicastration in rats. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 162:2175–2178
Petrie B, Lopardo L, Proctor K, Youdan J, Barden R, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2019) Assessment of bisphenol-A in the urban water cycle. Sci Total Environ 650:900–907
Pirard C, Compere S, Firquet K, Charlier C (2018) The current environmental levels of endocrine disruptors (mercury, cadmium, organochlorine pesticides and PCBs) in a Belgian adult population and their predictors of exposure. Int J Hyg Environ Health 221:211–222
Potter C, McKay J, Groom A, Ford D, Coneyworth L, Mathers JC, Relton CL (2013) Influence of DNMT genotype on global and site specific DNA methylation patterns in neonates and pregnant women. PLoS One 8:e76506
Quan C, Wang C, Duan P, Huang W, Yang K (2017) Prenatal bisphenol a exposure leads to reproductive hazards on male offspring via the Akt/mTOR and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. Environ Toxicol 32:1007–1023
Rahmani S, Pour Khalili N, Khan F, Hassani S, Ghafour-Boroujerdi E, Abdollahi M (2018) Bisphenol A: what lies beneath its induced diabetes and the epigenetic modulation? Life Sci 214:136–144
Ricci PF (2015) Endocrine disruptors: improving regulatory science policy. Dose-Response 13:1559325815611903
Robinson JL, Gupta V, Soria P, Clanaman E, Gurbarg S, Xu M, Chen J, Wadhwa S (2017) Estrogen receptor alpha mediates mandibular condylar cartilage growth in male mice. Orthod Craniofacial Res 20(Suppl 1):167–171
Roset R, Ortet L, Gil-Gomez G (2007) Role of Bcl-2 family members on apoptosis: what we have learned from knock-out mice. Front Biosci 12:4722–4730
Sano K, Morimoto C, Nataka M, Musatov S, Tsuda MC, Yamaguchi N, Sakamoto T, Ogawa S (2018) The role of estrogen receptor beta in the dorsal raphe nucleus on the expression of female sexual behavior in C57BL/6J mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:243
Takahashi O, Oishi S (2006) Male reproductive toxicity of four bisphenol antioxidants in mice and rats and their estrogenic effect. Arch Toxicol 80:225–241
Toro-Velez AF, Madera-Parra CA, Pena-Varon MR, Lee WY, Bezares-Cruz JC, Walker WS, Cardenas-Henao H, Quesada-Calderon S, Garcia-Hernandez H, Lens PN (2016) BPA and NP removal from municipal wastewater by tropical horizontal subsurface constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 542:93–101
Urriola-Munoz P, Lagos-Cabre R, Moreno RD (2014) A mechanism of male germ cell apoptosis induced by bisphenol-A and nonylphenol involving ADAM17 and p38 MAPK activation. PLoS One 9:e113793
Vasquez YM (2018) Estrogen-regulated transcription: mammary gland and uterus. Steroids 133:82–86
Wang DH, Hu JR, Wang LY, Hu YJ, Tan FQ, Zhou H, Shao JZ, Yang WX (2012) The apoptotic function analysis of p53, Apaf1, Caspase3 and Caspase7 during the spermatogenesis of the Chinese fire-bellied newt Cynops orientalis. PLoS One 7:e39920.
Wei Q, Luo Q, Liu H, Chen L, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2018) The mitochondrial pathway is involved in sodium fluoride (NaF)-induced renal apoptosis in mice. Toxicol Res (Camb) 7:792–808
Wirbisky-Hershberger SE, Sanchez OF, Horzmann KA, Thanki D, Yuan C, Freeman JL (2017) Atrazine exposure decreases the activity of DNMTs, global DNA methylation levels, and dnmt expression. Food Chem Toxicol 109:727–734
Xia W, Jiang Y, Li Y, Wan Y, Liu J, Ma Y, Mao Z, Chang H, Li G, Xu B, Chen X, Xu S (2014) Early-life exposure to bisphenol a induces liver injury in rats involvement of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. PLoS One 9:e90443
Xu W, Guo G, Li J, Ding Z, Sheng J, Li J, Tan W (2016) Activation of Bcl-2-Caspase-9 apoptosis pathway in the testis of asthmatic mice. PLoS One 11:e0149353
Xue J, Venkatesan AK, Wu Q, Halden RU, Kannan K (2015) Occurrence of bisphenol A Diglycidyl ethers (BADGEs) and Novolac Glycidyl ethers (NOGEs) in archived biosolids from the U.S. EPA’s targeted National Sewage Sludge Survey. Environ Sci Technol 49:6538–6544
Ye Y, Tang Y, Xiong Y, Feng L, Li X (2019) Bisphenol A exposure alters placentation and causes preeclampsia-like features in pregnant mice involved in reprogramming of DNA methylation of WNT2. FASEB J 33:2732–2742
Yin C, Kang L, Lai C, Zhou J, Shi B, Zhang L, Chen H (2017) Effects of 17beta-estradiol on leptin signaling in anterior pituitary of ovariectomized rats. Exp Anim 66:159–166
Zhang S, Tang B, Fan C, Shi L, Zhang X, Sun L, Li Z (2015) Effect of DNMT inhibitor on bovine parthenogenetic embryo development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 466:505–511
Zhang W, Schmull S, Du M, Liu J, Lu Z, Zhu H, Xue S, Lian F (2016) Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in mouse: adipose-derived stem cell proliferation, migration, and brown adipogenesis in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem 38:2285–2299
Zhang Y, Han L, Yang H, Pang J, Li P, Zhang G, Li F, Wang F (2017) Bisphenol A affects cell viability involved in autophagy and apoptosis in goat testis sertoli cell. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 55:137–147
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no.31872506).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The protocols using animals in our study were approved by the Council for Animal Care in Hebei province.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Han, C., Geng, Y. et al. Maternal exposure to bisphenol A during pregnancy interferes testis development of F1 male mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 23491–23504 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05579-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05579-z