Abstract
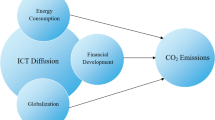
This study intends to examine the impact of ICTs (i.e., internet usage and mobile cellular subscriptions), globalization, electricity consumption, financial development, and economic growth on environmental quality by using 1994–2014 panel data of BRICS economies. This study employed a second-generation panel unit root test accounting for the presence of cross-sectional dependence and indicated that carbon dioxide emissions, electricity consumption, financial development, internet usage, mobile usage, globalization, and economic growth have integration of order one. The results from Westerlund panel co-integration test confirms that the variables are co-integrated and revealed that ICT-finance-globalization-electricity-GDP-CO2 nexus has long-run equilibrium relationship. The results from dynamic seemingly unrelated regression (DSUR) indicate that internet usage and mobile cellular subscriptions (ICTs) have significant, adverse impact on carbon dioxide emissions. To put it simply, ICT positively contributes towards environmental quality. Similarly, economic growth also has an adverse effect on carbon dioxide emissions. On the other hand, electricity consumption, globalization, and financial development have a significant positive effect on carbon emissions. In addition, Granger causality test results show the presence of a bidirectional causal relationship between internet usage and environmental quality, financial development and electricity consumption, ICT and financial development, mobile cellular subscription and globalization, economic growth and environmental quality, and internet usage and economic growth. A unidirectional causal link is detected running from mobile cellular subscriptions towards environmental quality, ICT towards electricity consumption, financial development towards environmental quality, globalization towards environmental quality, and globalization towards economic growth. Moreover, time series analysis has also been done in this study to analyze the findings for each of BRICS countries which are directed towards important policy implications. For instance, ICT policy can play an integral part in improving environmental quality policy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This time period has been chosen due to restrictions on availability of data. Moreover, we have used those panel techniques, which is the best for this available data, i.e., time period is greater than cross sections. These techniques give unbiased and consistent results.
References
Ahmed K (2017) Revisiting the role of financial development for energy-growth-trade nexus in BRICS economies. Energy 128:487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.04.055
Aktas AZ (2018) Could energy hamper future developments in information and communication technologies (ICT) and knowledge engineering ? Renew Sust Energ Rev 82:2613–2617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.087
Al-Mulali U, Sheau-Ting L, Ozturk I (2015a) The global move toward internet shopping and its influence on pollution: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9717–9727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4142-2
Al-mulali U, Weng-wai C, Sheau-ting L, Hakim A (2015b) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.029
Amri F (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions, total factor productivity, ICT, trade, financial development, and energy consumption: testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Tunisia, pp 33691–33701
Añón Higón D, Gholami R, Shirazi F (2017) ICT and environmental sustainability: a global perspective. Telematics Inform 34:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.01.001
Asongu S, Governance A, Roux S (2017a) Enhancing ICT for inclusive human development in sub-Saharan Africa. AGDI Work Pap 118:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.01.026
Asongu SA, Le Roux S, Biekpe N (2017b) Enhancing ICT for environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 127:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.022
Belkhir L, Elmeligi A (2018) Assessing ICT global emissions footprint : trends to 2040 & recommendations. J Clean Prod 177:448–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.239
Biryukova OV, Matiukhina AI (2018) ICT services trade in the BRICS countries : special and common features. J Knowl Econ:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1313
Bölük G, Mert M (2015) The renewable energy, growth and environmental Kuznets curve in Turkey: an ARDL approach. Renew Sust Energ Rev 52:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.138
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47:239. https://doi.org/10.2307/2297111
Chavanne X, Schinella S, Marquet D, Frangi JP, le Masson S (2015) Electricity consumption of telecommunication equipment to achieve a telemeeting. Appl Energy 137:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.10.027
Coroama VC, Hilty LM, Birtel M (2012) Effects of internet-based multiple-site conferences on greenhouse gas emissions. Telematics Inform 29:362–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2011.11.006
Danish KN, Baloch MA et al (2018) The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: does the level of income matters? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:22850–22860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2379-2
Demidov O (2014) ICT in the Brics agenda before the 2015 summit: Installing the missing pillar? Secur Index A Russ J Int Secur 20(2):127–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/19934270.2014.965968
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1981) Likelihood ratio statistics for autoregressive time series with a unit root. Econometrica 49:1057–1072
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:1074–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.02.006
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5323-8
Dreher A (2006) Does globalization affect growth? Evidence from a new index of globalization. Appl Econ 38:1091–1110. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036840500392078
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29:1450–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
EITO (2011) Special Report, BRIC countries' ICT markets, 2007-2011, January 3, 2011. http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC92241/jrc92241.pdf. Accessed 29 November 2018.
Erumban AA, Kusum D (2016) Information and communication technology and economic growth in India. Telecommun Policy 40:412–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2015.08.006
Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Causal relationship between CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15663–15676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4767-1
Frankel JA, Romer DH (1999) Does trade cause growth? Am Econ Rev 89:379–399
Gonel F, Akinci A (2018) How does ICT-use improve the environment? The case of Turkey. World J Sci Technol Sustain Dev 15:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1108/WJSTSD-03-2017-0007
Hafeez M, Chunhui Y, Strohmaier D, Ahmed M, Jie L (2018) Does finance affect environmental degradation: evidence from One Belt and One Road Initiative region? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:9579–9592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1317-7
Hamdi H, Sbia R, Shahbaz M (2014) The nexus between electricity consumption and economic growth in Bahrain. Econ Model 38:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2013.12.012
Haseeb M, Hassan S, Azam M (2017) Rural – urban transformation, energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emissions using STRIPAT model for BRICS countries. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 36:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12461
Haseeb A, Xia E, Danish et al (2018) Financial development, globalization, and CO2 emission in the presence of EKC: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:31283–31296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3034-7
Hofman A, Aravena C, Aliaga V (2016) Information and communication technologies and their impact in the economic growth of Latin America, 1990–2013 $. Telecommun Policy 40:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2016.02.002
Houghton J (2010) ICT and the environment in developing countries: opportunities and developments. Dev Dimens ICTs Dev Improv Policy Coherence 6:149. file:///C:/Users/hp/Downloads/SSRN-id1659765.pdf
Hsueh S, Hu Y, Tu C (2013) Economic growth and financial development in Asian countries: a bootstrap panel Granger causality analysis. Econ Model 32:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2013.02.027
Ishida H (2014) The effect of ICT development on economic growth and energy consumption in Japan. Telematics Inform 32:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2014.04.003
Javid M, Sharif F (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve and financial development in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:406–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.019
Kasman A, Duman YS (2015) CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption, trade and urbanization in new EU member and candidate countries: a panel data analysis. Econ Model 44:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2014.10.022
Khan MTI, Yaseen MR, Ali Q (2017) Dynamic relationship between financial development, energy consumption, trade and greenhouse gas: comparison of upper middle income countries from Asia, Europe, Africa and America. J Clean Prod 161:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.129
Latif Z, Jianqiu Z, Salam S et al (2017) FDI and ‘political’ violence in Pakistan’ s telecommunications. Hum Syst Manag 36:341–352. https://doi.org/10.3233/HSM-17154
Latif Z, Mengke Y, Danish, Latif S, Ximei L, Pathan ZH, Salam S, Jianqiu Z (2018) The dynamics of ICT, foreign direct investment, globalization and economic growth: panel estimation robust to heterogeneity and cross-sectional dependence. Telematics Inform 35:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.12.006
Luo Y, Bu J (2016) How valuable is information and communication technology? A study of emerging economy enterprises. J World Bus 51:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2015.06.001
Mahalik MK, Babu MS, Loganathan N, Shahbaz M (2017) Does financial development intensify energy consumption in Saudi Arabia? Renew Sust Energ Rev 75:1022–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.081
Mark NC, Ogaki M, Sul D (2005) Dynamic seemingly unrelated cointegrating regressions. Rev Econ Stud 72:797–820
Mathiesen BV, Lund H, Connolly D, Wenzel H, Østergaard PA, Möller B, Nielsen S, Ridjan I, Karnøe P, Sperling K, Hvelplund FK (2015) Smart energy systems for coherent 100% renewable energy and transport solutions. Appl Energy 145:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.075
Moyer JD, Hughes BB (2012) ICTs: do they contribute to increased carbon emissions? Technol Forecast Soc Chang 79:919–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2011.12.005
Naser M, Afzal I, Gow J (2016) Electricity consumption and information and communication technology in the next eleven emerging economies. Int J Energy Econ Policy 6:381–388
Nassani AA, Aldakhil AM, Qazi Abro MM, Zaman K (2017) Environmental Kuznets curve among BRICS countries: spot lightening finance, transport, energy and growth factors. J Clean Prod 154:474–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.025
Osorio BB, Dutta S, Geiger T, Lanvin B (2013) The networked readiness index 2013: benchmarking ICT uptake and support for growth and jobs in a hyperconnected worlde. In: The global information technology report 2013: growth and jobs in a hyperconnected world. World Economic Forum, Geneva, pp 3–33
Ozatac N, Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N (2017) Testing the EKC hypothesis by considering trade openness, urbanization, and financial development: the case of Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:16690–16701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9317-6
Ozcan B, Apergis N (2017) The impact of internet use on air pollution: evidence from emerging countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0825-1
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2013) The long-run and causal analysis of energy, growth, openness and financial development on carbon emissions in Turkey. Energy Econ 36:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2012.08.025
Palvia P, Baqir N, Nemati H (2017) ICT for socio-economic development: a citizens perspective. Inf Manag 55:1–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2017.05.003
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross-section dependence in panels. CESifo working paper series no. 1229; IZA discussion paper no. 1240. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=572504
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22:265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Phillips PC, Hansen BE (1990) Statistical inference in instrumental variables regression with I (1) processes. Rev Econ Stud 57:99–125. https://doi.org/10.2307/2297545
Phillips PC, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 75:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/75.2.335
Plepys A (2002) The grey side of ICT. Environ Impact Assess Rev 22:509–523
Pradhan RP, Arvin MB, Norman NR (2015) The dynamics of information and communications technologies infrastructure, economic growth, and financial development: evidence from Asian countries. Technol Soc 42:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2015.04.002
Pradhan RP, Arvin M, Nair M, Bennett S, Bahmani S (2017) ICT-finance-growth nexus: empirical evidence from the next-11 countries. Cuad Econ 40:115–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cesjef.2016.02.003
Profaizer P, Zapater MH, Valdavida MA, Bribian IZ (2016) Information and communications technologies (ICTs) for energy efficiency in buildings: review and analysis of results from EU pilot projects. Energy Build 1–38:128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.05.064
Rohman IK (2013) The globalization and stagnation of the ICT sectors in European countries: an input-output analysis. Telecommun Policy 37:387–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2012.05.00
Sadorsky P (2010) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 38:2528–2535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.12.048
Salahuddin M, Alam K (2015) Internet usage, electricity consumption and economic growth in Australia: a time series evidence. Telematics Inform 32:862–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2015.04.011
Salahuddin M, Alam K (2016) Information and communication technology, electricity consumption and economic growth in OECD countries: a panel data analysis. Electr Power Energy Syst 76:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.11.005
Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I (2016) The effects of internet usage and economic growth on CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a panel investigation. Renew Sust Energ Rev 62:1226–1235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.018
Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I, Sohag K (2017) The effects of electricity consumption, economic growth, financial development and foreign direct investment on CO2 emissions in Kuwait. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.009
Sassi S, Goaied M (2013) Financial development, ICT diffusion and economic growth: lessons from MENA region. Telecommun Policy 37:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2012.12.004
Saud S, Danish, Chen S (2018) An empirical analysis of financial development and energy demand: establishing the role of globalization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:24326–24337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2488-y
Saud S, Chen S, Danish, Haseeb A (2019) Impact of financial development and economic growth on environmental quality : an empirical analysis from Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2253–2269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3688-1
Seker F, Ertugrul HM, Cetin M (2015) The impact of foreign direct investment on environmental quality: a bounds testing and causality analysis for Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 52:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.118
Shahbaz M, Hye QMA, Tiwari AK, Leitão NC (2013a) Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.04.009
Shahbaz M, Ozturk I, Afza T, Ali A (2013b) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in a global economy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.021
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Mahmood H, Arouri M (2013c) Does financial development reduce CO2 emissions in Malaysian economy? A time series analysis. Econ Model 35:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2013.06.037
Shahbaz M, Khraief N, Uddin GS, Ozturk I (2014) Environmental Kuznets curve in an open economy: a bounds testing and causality analysis for Tunisia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 34:325–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.03.022
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Indic 52:379–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.12.025
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis and the role of globalization in selected African countries. Ecol Indic 67:623–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.03.024
Shahbaz M, Jawad S, Shahzad H (2017a) Does globalisation worsen environmental quality in developed economies? Environ Model Assess 23:141–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9574-2
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017b) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62:929–957. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217590817400331
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Kumar M (2017c) Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New threshold analysis. Environ Model Assess 23:557–568
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Alam S, Apergis N (2018) Globalisation, economic growth and energy consumption in the BRICS region: the importance of asymmetries. J Int Trade Econ Dev 8199:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638199.2018.1481991
Simon JP (2014) The ICT landscape in Brazil, India, and China. Eur Comm Jt Res Cent Inst Prospect Technol Stud Luxemb 1–110. https://doi.org/10.2791/503714
Stern DI (2010) Between estimates of the environmental Kuznets curve. CAMA Working Paper No. 4/2010. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1668123
Tamazian A, Rao BB (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation ? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ 32:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2009.04.004
Tamazian A, Chousa JP, Vadlamannati KC (2009) Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy 37:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.08.025
Tang CF, Tan BW (2014) The linkages among energy consumption, economic growth, relative price, foreign direct investment, and financial development in Malaysia. Qual Quant 48:781–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-012-9802-4
Tang CF, Tan BW (2015) The impact of energy consumption, income and foreign direct investment on carbon dioxide emissions in Vietnam. Energy 79:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.11.033
Van Heddeghem W, Lambert S, Lannoo B et al (2014) Trends in worldwide ICT electricity consumption from 2007 to 2012. Comput Commun 50:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2014.02.008
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69:709–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.2007.00477.x
Xu Z, Baloch MA, Danish et al (2018) Nexus between financial development and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia: analyzing the role of globalization. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2876-3
Yao X, Liu J (2011) The potential of economic growth and technology. In: International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics
Yi L, Thomas HR (2007) A review of research on the environmental impact of e-business and ICT. Environ Int 33:841–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.03.015
Zhang Y (2011) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: an empirical analysis in China. Energy Policy 39:2197–2203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.02.026
Zhang L, Gao J (2016) Exploring the effects of international tourism on China’s economic growth, energy consumption and environmental pollution: evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew Sust Energ Rev 53:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.08.040
Zhang C, Liu C (2015) The impact of ICT industry on CO2 emissions: a regional analysis in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 44:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.12.011
Zhu H, Xia H, Guo Y, Peng C (2018) The heterogeneous effects of urbanization and income inequality on CO 2 emissions in BRICS economies: evidence from panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(17):17176–17193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haseeb, A., Xia, E., Saud, S. et al. Does information and communication technologies improve environmental quality in the era of globalization? An empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 8594–8608 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04296-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04296-x