Abstract
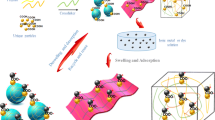
This research focuses on the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads as a potential sorbent. Highly porous magnetic chitosan hydrogel (PMCH) beads were prepared by a combination of in situ co-precipitation and sodium citrate cross-linking. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy indicated that the high sorption efficiency of metal cations is attributable to the hydroxyl, amino, and carboxyl groups in PMCH beads. Thermogravimetric analysis demonstrated that introducing Fe3O4 nanoparticles increases the thermal stability of the adsorbent. Laser confocal microscopy revealed highly uniform porous structure of the resultant PMCH beads, which contained a high moisture content (93%). Transmission electron microscopy micrographs showed that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles, with a mean diameter of 5 ± 2 nm, were well dispersed inside the chitosan beads. Batch adsorption experiments and adsorption kinetic analysis revealed that the adsorption process obeys a pseudo-second-order model. Isotherm data were satisfactorily described by the Langmuir equation, and the maximum adsorption capacity of the adsorbent was 84.02 mg/g. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectra analyses were performed to confirm the adsorption of Pb2+ and to identify the adsorption mechanism.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou El Fadl FI (2014) Radiation grafting of ionically crosslinked alginate/chitosan beads with acrylic acid for lead sorption. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301:529–535
Bulut Y, Gözübenli N, Aydın H (2007) Equilibrium and kinetics studies for adsorption of direct blue 71 from aqueous solution by wheat shells. J Hazard Mater 144:300–306
Chang YC, Chen DH (2005) Preparation and adsorption properties of monodisperse chitosan-bound Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Cu(II) ions. J Colloid Interface Sci 283:446–451
Chen A-H, Liu S-C, Chen C-Y, Chen C-Y (2008) Comparative adsorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Pb(II) ions in aqueous solution on the crosslinked chitosan with epichlorohydrin. J Hazard Mater 154:184–191
Chen J, Hao Y, Chen M (2014) Rapid and efficient removal of Ni 2+ from aqueous solution by the one-pot synthesized EDTA-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1671–1679
Dinu MV, Dragan ES (2010) Evaluation of Cu2+, Co2+ and Ni2+ ions removal from aqueous solution using a novel chitosan/clinoptilolite composite: kinetics and isotherms. Chem Eng J 160:157–163
Galhoum AA, Mahfouz MG, Atia AA, Abdel-Rehem ST, Gomaa NA, Vincent T, Guibal E (2015) Amino acid functionalized chitosan magnetic nanobased particles for uranyl sorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:12374–12385
Ge H, Hua T, Chen X (2016) Selective adsorption of lead on grafted and crosslinked chitosan nanoparticles prepared by using Pb 2+ as template. J Hazard Mater 308:225–232
Giacometti JA, Job AE, Ferreira FC (2005) Thermal analysis of chitosan based networks. Carbohydr Polym 62:97–103
Guibal E, Guzman J, Navarro R, Ruiz M, Sastre A (2004) Influence of the speciation of metal ions on their sorption on chitosan
He J, Lu Y, Luo G (2014) Ca(II) imprinted chitosan microspheres: an effective and green adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 244:202–208
Hosseini F, Sadighian S, Hosseini-Monfared H, Mahmoodi NM (2016) Dye removal and kinetics of adsorption by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles. Desalin Water Treat 57:24378–24386
Hritcu D, Dodi G, Silion M, Popa N, Popa MI (2011) Composite magnetic chitosan microspheres: in situ preparation and characterization. Polym Bull 67:177–186
Hu X-J, Wang J-S, Liu Y-G, Li X, Zeng G-M, Bao Z-L, Zeng X-X, Chen A-W, Long F (2011) Adsorption of chromium (VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 185:306–314
Huang L, Yuan S, Lv L, Tan G, Liang B, Pehkonen SO (2013) Poly(methacrylic acid)-grafted chitosan microspheres via surface-initiated ATRP for enhanced removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 405:171–182
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Jeon BH, Dempsey BA, Burgos WD, Royer RA, Roden EE (2004) Modeling the sorption kinetics of divalent metal ions to hematite. Water Res 38:2499–2504
Jiang W, Wang W, Pan B, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Lv L (2014) Facile fabrication of magnetic chitosan beads of fast kinetics and high capacity for copper removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3421–3426
Kharissova OV, Dias HVR, Kharisov BI (2015) Magnetic adsorbents based on micro- and nano-structured materials. RSC Adv 5:6695–6719
Kim HR, Jang JW, Park JW (2016) Carboxymethyl chitosan-modified magnetic-cored dendrimer as an amphoteric adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 317:608–616
Li B, Jia D, Zhou Y, Hu Q, Cai W (2006) In situ hybridization to chitosan/magnetite nanocomposite induced by the magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 306:223–227
Li A, Lin R, Lin C, He B, Zheng T, Lu L, Cao Y (2016a) An environment-friendly and multi-functional absorbent from chitosan for organic pollutants and heavy metal ion. Carbohydr Polym 148:272–280
Li R, Li P, Cai J, Xiao SJ, Yang H, Li AM (2016b) Efficient adsorption of both methyl orange and chromium from their aqueous mixtures using a quaternary ammonium salt modified chitosan magnetic composite adsorbent. Chemosphere 154:310–318
Lin HY, Sun T, Xue SF, Jiang XL (2016) Heavy metal spatial variation, bioaccumulation, and risk assessment of Zostera japonica habitat in the Yellow River estuary, China. Sci Total Environ 541:435–443
Lin CY, Li SX, Chen M, Jiang R (2017) Removal of Congo red dye by gemini surfactant C-12-4-C-12 center dot 2Br-modified chitosan hydrogel beads. J Dispers Sci Technol 38:46–57
Liu Y, Zheng YA, Wang AQ (2010) Enhanced adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/vermiculite hydrogel composites. J Environ Sci 22:486–493
Lu S, Li HP, Zhang FR, Du N, Hou WG (2016) Sorption of Pb(II) on carboxymethyl chitosan-conjugated magnetite nanoparticles: application of sorbent dosage-dependent isotherms. Colloid Polym Sci 294:1369–1379
Luo X, Zeng J, Liu S, Zhang L (2015) An effective and recyclable adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system: magnetic chitosan/cellulose microspheres. Bioresour Technol 194:403–406
Men HF, Liu HQ, Zhang ZL, Huang J, Zhang J, Zhai YY, Li L (2012) Synthesis, properties and application research of atrazine Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2271–2280
Mi FL, Wu SJ, Chen YC (2015) Combination of carboxymethyl chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles and chitosan-citrate complex gel beads as a novel magnetic adsorbent. Carbohydr Polym 131:255–263
Ngah WSW, Fatinathan S (2010) Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Manag 91:958–969
Peng S, Meng H, Ouyang Y, Chang J (2014) Nanoporous magnetic cellulose–chitosan composite microspheres: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:2106–2113
Podzus PE, Daraio ME, Jacobo SE (2009) Chitosan magnetic microspheres for technological applications: preparation and characterization. Phys B Condens Matter 404:2710–2712
Prakash N, Sudha PN, Renganathan NG (2012) Copper and cadmium removal from synthetic industrial wastewater using chitosan and nylon 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2930–2941
Reddy DH, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 201-202:68–93
Ruthven DM (1984) Principles of adsorption & adsorption processes. Wiley
Singh KP, Mohan D, Sinha S, Tondon GS, Gosh D (2003) Color removal from wastewater using low-cost activated carbon derived from agricultural waste material. Ind Eng Chem Res 42:1965–1976
Varma AJ, Deshpande SV, Kennedy JF (2004) Metal complexation by chitosan and its derivatives: a review. Carbohydr Polym 55:77–93
Wang JL, Chen C (2014) Chitosan-based biosorbents: modification and application for biosorption of heavy metals and radionuclides. Bioresour Technol 160:129–141
Wang Y, Li B, Zhou Y, Jia D (2008) Chitosan-induced synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles via iron ions assembly. Polym Adv Technol 19:1256–1261
Wang Y, Li B, Zhou Y, Jia D (2009) In situ mineralization of magnetite nanoparticles in chitosan hydrogel. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:1041–1046
Wang Y, Li B, Zhou Y, Jia D, Song Y (2011) CS-Fe(II,III) complex as precursor for magnetite nanocrystal. Polym Adv Technol 22:1681–1684
Wang J, Xu W, Chen L, Huang X, Liu J (2014) Preparation and evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles impregnated chitosan beads for arsenic removal from water. Chem Eng J 251:25–34
Yuwei C, Jianlong W (2011) Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan nanoparticles and its application for Cu(II) removal. Chem Eng J 168:286–292
Zhou L, Wang Y, Liu Z, Huang Q (2009) Characteristics of equilibrium, kinetics studies for adsorption of Hg(II), Cu(II), and Ni(II) ions by thiourea-modified magnetic chitosan microspheres. J Hazard Mater 161:995–1002
Zhu Y, Hu J, Wang J (2014) Removal of Co2+ from radioactive wastewater by polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/chitosan magnetic composite. Prog Nucl Energy 71:172–178
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51408074) and the Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (Nos. SKLGP2015Z007, SKLGP2017Z009). Dr. Shengyan PU is grateful for the support from the Hong Kong Scholars Program (No. XJ2015005 and G-YZ80) and the Project Funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015T80966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 782 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, S., Ma, H., Zinchenko, A. et al. Novel highly porous magnetic hydrogel beads composed of chitosan and sodium citrate: an effective adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 16520–16530 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9213-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9213-0