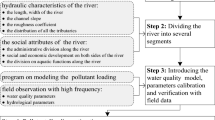
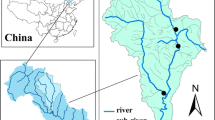
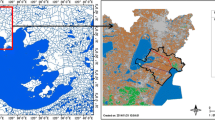
Abstract
The deterioration of water quality in Taihu Lake, China, has caused widespread concern in recent years. The primary pollution sources of Taihu Lake are its inflow rivers. Effective environmental water management strategies need to be implemented in these rivers to improve the water quality of Taihu Lake and to promote sustainable development in the region. In this study, the QUAL2K model is used in conjunction with the trial and error approach to assess permissible load capacities for the Wujin River (a major tributary of Taihu Lake) in terms of COD, NH3-N, TN, and TP. Results show that permissible annual loads for these pollutants are 5216.31, 491.71, 948.53, and 104.38 t, respectively. This suggests that COD, NH3-N, TN, and TP loads in the Wujin River catchment need to be reduced by 13.35, 27.26, 47.75, and 37.08 %, respectively, to satisfy national water quality objectives. Total amount control measures are proposed to control and reduce pollution loads of the Wujin River catchment. The method applied in this study should provide a sound basis for water environmental management decision-making.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anh DT, Bonnet MP, Vachaud G, Minh CV, Prieur N, Duc LV, Anh LL (2006) Biochemical modeling of the Nhue River (Hanoi, Vietnam): practical identifiability analysis and parameter estimation. Ecol Model 193:182–204
Bao K, Pang Y, Sun H (2011) A water environment capacity calculation method based on water quality standards at the control sections: a case study of the Yincun Port. Resour Sci 33:249–252 (in Chinese)
Bowen JD, Hieronymus JW (2003) A CE-QUAL-W2 model of Neuse Estuary for total maximum daily load development. J Water Resour Plann Manag-ASCE 129:283–294
Brown LC, Barnwell TO (1987) The enhanced stream water quality models QUAL2E and QUAL2E-UNCAS: Documentation and user manual. USEPA, Athens, GA. Environmental Research Laboratory, [U.S.EPA/600/3-87/007]
Butcher JC (2003) Numerical methods for ordinary differential equations. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Cai H, Sun Y (2007) Management of marine cage aquaculture. Environmental carrying capacity method based on dry feed conversion rate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14:463–469
Černý V (1985) Thermodynamical approach to the traveling salesman problem: an efficient simulation algorithm. J Optim Theory App 45:41–51
Chapra SC, Pelletier GJ, Tao H (2006) QUAL2K: a modeling framework for simulating river and stream water quality, version 2.04: documentation and users manual. Civil and Environmental Engineering Dept, Tufts University, Medford
Chapra SC, Pelletier GJ, Tao H (2008) QUAL2K: a modeling framework for simulating river and stream water quality, version 2.11: documentation and users manual, Civil and Environmental Engineering Dept, Tufts University, Medford
Chen D, Lu J, Jin S, Shen Y (2007) Estimation and allocation of water environmental capacity in nonpoint source polluted river. Environ Sci 28:1416–1424 (in Chinese)
Chen CW, Herr JW, Goldstein RA (2008) Model calculations of total maximum daily loads of mercury for drainage lakes. J Am Water Resour As 44:1295–1307
Chen DJ, Lu J, Wang HL, Shen YN, Gong DQ (2011) Combined inverse modeling approach and load duration curve method for variable nitrogen total maximum daily load development in an agricultural watershed. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1405–1413
Chen Q, Wang Q, Li Z, Li R (2014) Uncertainty analyses on the calculation of water environmental capacity by an innovative holistic method and its application to the Dongjiang River. J Environ Sci 26:1783–1790
Cho JH, Ha SR (2010) Parameter optimization of the QUAL2K model for a multiple-reach river using an influence coefficient algorithm. Sci Total Environ 408:1985–1991
Dilks DW, Freedman PL (2004) Improved consideration of the margin of safety in total maximum daily load development. J Environ Eng 6:690–694
Eatherall A, Boorman DB, Williams RJ, Kowe R (1998) Modeling in-stream water quality in LOIS. Sci Total Environ 210(211):499–517
Fan C, Ko CH, Wang WS (2009) An innovative modeling approach using QUAL2K and HEC-RAS integration to assess the impact of tidal effect on river water quality simulation. J Environ Manag 90:1824–1832
Fang X, Zhang J, Chen Y, Xu X (2008) QUAL2K model used in the water quality assessment of Qiantang river, China. Water Environ Res 80:2125–2133
Horn AL, Rueda FJ, Hormann G, Fohrer N (2004) Implementing river water quality modeling issues in mesoscale watershed models for water policy demands—An overview on current concepts, deficits, and future tasks. Phys Chem Earth 29:725–737
Jia X, Lu WX, Huang H, Zhang L (2012) Study on water environment capacity for Dongliao River based on WASP. Water Saving Irrig 6:56–63 (in Chinese)
Kim D, Wang Q, Soriala GA, Dionysioua DD, Timberlakeb D (2004) A model approach for evaluating effects of remedial actions on mercury speciation and transport in a lake system. Sci Total Environ 327:1–15
Lavkulich LM, Ulazzi E (2008) Environmental indicators for water resources management. Integr Water Manag 80:325–342
Li R, Qian J, Wang J (2003) Study on distribution of total amount of drainage water pollutant in a region. J Hydraul Eng 5:112–116 (in Chinese)
Li C, Farahbakhshazadb N, Jaynes DB (2006) Modeling nitrate leaching with a biogeochemical model modified based on observations in a row-crop field in Iowa. Ecol Model 196:116–130
Li W, Li C, Wang L, Zhou L (2007) Analog calculation of nitrogen and phosphorus capacities in Wuliangsuhai water environment under different mathematic models. J Agro-Environ Sci 2007(26):379–385 (in Chinese)
Li ZK, Zhang XJ, Yang ZY (2009) Ecological engineering experiment for Jinshan Lake in Zhenjiang base on techniques of immobilized nitrogen cycling bacteria. Environ Sci 30:1626–1631 (in Chinese)
Li YX, Qiu RZ, Yang ZF, Li CH, Yu JS (2010) Parameter determination to calculate water environmental capacity in Zhangweinan Canal Sub-basin in China. J Environ Sci 22:904–907
Li JA, Zhou HZ, Liu QH, Tan ZL, Li XD (2011) Progress in bioaugmention technology research for biological treatment of wastewaters. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 17:273–279 (in Chinese)
Liang T, Wang SN, Cao HY, Zhang CS, Li HT, Li HP, Song WC, Chong ZY (2008) Estimation of ammonia nitrogen load from nonpoint sources in the Xitiao River catchment, China. J Environ Sci 20:1195–1201
Liu SY, Ma F, Jiang QP (2007) Intensification capability of dominant consortium on landscaping water remediation by compound ecological filter. Huan Jing Ke Xue 28:1204–1208 (in Chinese)
Ma F, Guo JB, Zhao LJ, Chang CC, Cui D (2009) Application of bioaugmentation to improve the activated sludge system into the contact oxidation system treating petrochemical wastewater. Bioresour Technol 100:597–602
Mahamah DS (1998) Simplifying assumptions in water quality modeling. Ecol Model 109:295–300
Meng W, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Zheng B (2007) The study on technique of basin water quality target management pollutant total amount control technique in control unit. Res Environ Sci 20:3–8 (in Chinese)
Omlyody L, Henze M, Koncsos L, Rauch W, Reichert P, Shanahan P, Vanrolleghem P (1998) River quality modelling: III. Future of the art. Water Sci Technol 38:253–260
Pang Y, Lu GH (2010) Theory and research of water environmental capacity. Science, Beijing (in Chinese)
Park SS, Lee YS (2002) Water quality modeling study of the Nakdong river, Korea. Ecol Model 152:66–75
Pelletier GJ, Chapra SC, Tao H (2006) QUAL2Kw—A framework for modeling water quality in stream and rivers using a genetic algorithm for calibration. Environ Model Softw 21:419–425
Petrescu V, Sumbasacu GO, Sirbu N (2011) Monitoring and mathematical modeling-important tools for environmental problems. Environ Eng Manag J 10:1779–1787
Putnam H (1965) Trial and error predicates and the solution to a problem of Mostowski. J Symb Logic 30:49–57
Refsgaard JC, Knudsen J (1996) Operational validation and intercomparison of different types of hydrological models. Water Resour Res 32:2189–2202
Rode M, Suhr U, Wriedt G (2007) Multi-objective calibration of a river water quality model-information content of calibration data. Ecol Model 204:129–142
Schiewer U, Schernewski G (2004) Self-purification capacity and management of Baltic coastal ecosystems. J Coast Conserv 10:25–32
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration of the P.R. China) (2002) Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB3838-2002). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Shu SH, Ma H (2010) Comparison of two models for calculating waterenvironment capacity of Songhua River. Lect Notes Comput Sci 6330:683–690
Sin G, de Pauw DJW, Weijers S, Vanrolleghem PA (2008) An efficient approach to automate the manual trial and error calibration of activated sludge models. Biotechnol Bioeng 100:516–528
Song GJ, Wang J, Zhou JT, Lu H (2008) Treatment of bromoamine acid waste-water in bioaugmented sequencing batch membrane bioreactor. China Environ Sci 28:229–232 (in Chinese)
Tian M, Zhang YC (2006) Experimental study on permeable dam technique to control rural non-point pollution in Taihu basin. Acta Sci Circumst 26:1665–1670 (in Chinese)
USEPA (1985) Rates, constants and kinetics formulations in surface water quality. EPA 600/3-85-040, 2nd edn. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Athens, retrieved 20 October 2006 from: http://www.ecy.wa.gov/
Wang HJ, Wang HZ (2009) Mitigation of lake eutrophication: loosen nitrogen control and focus on phosphorus abatement. Prog Nat Sci 19:1445–1451
Wang QG, Gu G, Higano Y (2006) Toward integrated environmental management for challenges in water environmental protection of Lake Taihu basin in China. Environ Manag 37:579–588
Wang XY, Zhang YF, Ou Y, Yan Y (2009) Predicting effectiveness of best management practices for control of nonpoint source pollution-a case of Taishitun Town, Miyun County, Beijing. Acta Sci Circumst 29:2440–2450 (in Chinese)
Wang Z, Zou R, Zhu X, He B, Yuan G, Zhao L, Liu Y (2014) Predicting lake water quality responses to load reduction: a three-dimensional modeling approach for total maximum daily load. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:423–436
Xie P (2008) Historical development of cyanobacteria with bloom disaster in LakeTaihu. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xie RR, Pang Y, Bao K (2014) Spatiotemporal distribution of water environmental capacity-a case study on the western areas of Taihu Lake in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5465–5473
Zhang HX, Fillmore LA (2003) Is the TMDL on targer? Water Environ Technol 15:27–31
Zhang L, Sun W, Cheng W, Liu W, Wang C (2009) Overall treatment of water environment for inflow rivers of Lake Taihu. Environ Monit Manag Technol 21:1–5 (in Chinese)
Zhang R, Qian X, Li H, Yuan X, Ye R (2012) Selection of optimal river water quality improvement programs using QUAL2K: a case study of Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci Total Environ 431:278–285
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20140603), the State Water Pollution Control and Treatment Technique Program of China (Grant Nos. 2012ZX07101006-05 and 2013ZX07101014-05), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 20620140486).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Michael Matthies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Gao, H., Zhu, W. et al. Calculation of permissible load capacity and establishment of total amount control in the Wujin River Catchment—a tributary of Taihu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 11493–11503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4311-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4311-3