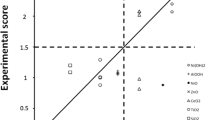
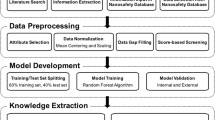
Abstract
Systematization of knowledge on nanomaterials has become a necessity with the fast growth of applications of these species. Building up predictive models that describe properties (both beneficial and hazardous) of nanomaterials is vital for computational sciences. Classic quantitative structure– property/activity relationships (QSPR/QSAR) are not suitable for investigating nanomaterials because of the complexity of their molecular architecture. However, some characteristics such as size, concentration, and exposure time can influence endpoints (beneficial or hazardous) related to nanoparticles and they can therefore be involved in building a model. Application of the optimal descriptors calculated with the so-called correlation weights of various concentrations and different exposure times are suggested in order to build up a predictive model for cell membrane damage caused by a series of nano metal-oxides. The numerical data on correlation weights are calculated by the Monte Carlo method. The obtained results are in good agreement with the experimental data.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achary PGR (2014a) QSPR modelling of dielectric constants of π-conjugated organic compounds by means of the CORAL software. SAR and QSAR Environ Res 25:507–526
Achary PGR (2014b) Simplified molecular input line entry system-based optimal descriptors: QSAR modelling for voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.2. SAR and QSAR Environ Res 25:73–90
Afantitis A, Melagraki G, Koutentis PA, Sarimveis H, Kollias G (2011) Ligand-based virtual screening procedure for the prediction and the identification of novel β-amyloid aggregation inhibitors using Kohonen maps and counterpropagation artificial neural networks. Eur J Med Chem 46:497–508
Comelli NC, Ortiz EV, Kolacz M, Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Duchowicz PR, Castro EA (2014) Conformation-independent QSAR on c-Src tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 134:47–52
Deng F, Xie M, Zhang X, Li P, Tian Y, Zhai H, Li Y (2014a) Combined molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and quantitative structure-activity relationship study of pyrimido[1,2-c][1,3]benzothiazin-6- imine derivatives as potent anti-HIV drugs. J Mol Struct 1067:1–13
Deng F-F, Xie M-H, Li P-Z, Tian Y-L, Zhang X-Y, Zhai H-L (2014b) Study on the antagonists for the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR55 by quantitative structure-activity relationship. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 131:51–60
Furtula B, Gutman I (2011) Relation between second and third geometric-arithmetic indices of trees. J Chemometr 25:87–91
García J, Duchowicz PR, Rozas MF, Caram JA, Mirífico MV, Fernández FM, Castro EA (2011) A comparative QSAR on 1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one 1,1-dioxide compounds as selective inhibitors of human serine proteinases. J Mol Graph Model 31:10–19
Garro Martinez JC, Duchowicz PR, Estrada MR, Zamarbide GN, Castro EA (2011) QSAR study and molecular design of open-chain enaminones as anticonvulsant agents. Int J Mol Sci 12:9354–9368
Gutman I, Hansen P, Mélot H (2005) Variable neighborhood search for extremal graphs. 10. Comparison of irregularity indices for chemical trees. J Chem Inf Model 45:222–230
Hollas B, Gutman I, Trinajstić N (2005) On reducing correlations between topological indices. Croat Chem Acta 78:489–492
Ibezim E, Duchowicz PR, Ortiz EV, Castro EA (2012) QSAR on aryl-piperazine derivatives with activity on malaria. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 110:81–88
Leszczynski J (2010) Bionanoscience: nano meets bio at the interface. Nat Nanotech 5:633–634
Liu R, Rallo R, George S, Ji Z, Nair S, Nel AE, Cohen Y (2011) Classification NanoSAR development for cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Small 7:1118–1126
Mullen LMA, Duchowicz PR, Castro EA (2011) QSAR treatment on a new class of triphenylmethyl-containing compounds as potent anticancer agents. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 107:269–275
OECD, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (2007) Guidance document on the validation of (quantitative) structure-activity relationships [(Q)SAR] models, OECD, Paris. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/55/35/38130292.pdf
Ojha PK, Roy K (2011) Comparative QSARs for antimalarial endochins: importance of descriptor-thinning and noise reduction prior to feature selection. Chemometr Intell Lab 109:146–161
Patel T, Low-Kam C, Ji ZH, Zhang H, Xia T, Nel AE, Zinc JI, Telesca D (2012) Relating nanoparticle properties to biological outcomes in exposure escalation experiments COBRA preprint series 2012, Working Paper 101. http://biostats.bepress.com/cobra/art101
Puzyn T, Rasulev B, Gajewicz A, Hu X, Dasari TP, Michalkova A, Hwang HM, Toropov A, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2011) Using nano-QSAR to predict the cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nat Nanotech 6:175–178
Rasulev B, Gajewicz A, Puzyn T, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2012) Nano-QSAR: advances and challenges. RSC Nanosci Nanotech 2012:220–256
Roy K, Mitra I, Ojha PK, Kar S, Das RN, Kabir H (2012a) Introduction of rm 2 (rank) metric incorporating rank-order predictions as an additional tool for validation of QSAR/QSPR models. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 118:200–210
Roy K, Mitra I, Kar S, Ojha PK, Das RN, Kabir H (2012b) Comparative studies on some metrics for external validation of QSPR models. J Chem Inf Model 52:396–408
Toropov AA, Leszczynski J (2006) A new approach to the characterization of nanomaterials: predicting Young’s modulus by correlation weighting of nanomaterials codes (2006) Chem. Phys Lett 433:125–129
Toropov AA, Toropova AP (2003) QSPR modeling of alkanes properties based on graph of atomic orbitals. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 637:1–10
Toropov AA, Toropova AP (2014) Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic data into endpoint prediction: mutagenicity of fullerene as a mathematical function of conditions. Chemosphere 104:262–264
Toropov AA, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2007) Predicting thermal conductivity of nanomaterials by correlation weighting technological attributes codes. Mater Lett 61:4777–4780
Toropov AA, Toropova AP, Benfenati E, Gini G, Puzyn T, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2012) Novel application of the CORAL software to model cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles to bacteria Escherichia coli. Chemosphere 89:1098–1102
Toropov AA, Toropova AP, Puzyn T, Benfenati E, Gini G, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2013) QSAR as a random event: modeling of nanoparticles uptake in PaCa2 cancer cells. Chemosphere 92:31–37
Toropova AP, Toropov AA (2013) Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic information into the prediction of membrane damage by means of various TiO2 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 93:2650–2655
Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Benfenati E, Gini G (2011a) QSAR modelling toxicity toward rats of inorganic substances by means of CORAL. Cent Eur J Chem 9:75–85
Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Benfenati E, Gini G, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2011b) CORAL: quantitative structure-activity relationship models for estimating toxicity of organic compounds in rats. J Comput Chem 32:2727–2733
Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Benfenati E, Gini G (2011c) Co-evolutions of correlations for QSAR of toxicity of organometallic and inorganic substances: an unexpected good prediction based on a model that seems untrustworthy. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 105:215–219
Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Benfenati E, Gini G, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2011d) CORAL: QSPR models for solubility of [C60] and [C70] fullerene derivatives. Mol Divers 15:249–256
Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Benfenati E, Gini G, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2012) CORAL: models of toxicity of binary mixtures. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 119:39–43
Toropova AP, Toropov AA, Benfenati E, Puzyn T, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2014) Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic information into the prediction of membrane damage: the case of a group of ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles. Ecotox Environ Safe 108:203–209
Veselinović AM, Milosavljević JB, Toropov AA, Nikolić GM (2013a) SMILES-based QSAR model for arylpiperazines as high-affinity 5-HT1A receptor ligands using CORAL. Eur J Pharm Sci 48:532–541
Veselinović AM, Milosavljević JB, Toropov AA, Nikolić GM (2013b) SMILES-based QSAR models for the calcium channel-antagonistic effect of 1,4-dihydropyridines. Arch Pharm 346:134–139
Weininger D (1988) SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 28:31–36
Weininger D (1990) Smiles. 3. Depict. Graphical depiction of chemical structures. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 30:237–243
Weininger D, Weininger A, Weininger JL (1989) SMILES. 2. Algorithm for generation of unique SMILES notation. JChemInfComputSci 29:97–101
Worachartcheewan A, Nantasenamat C, Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya C, Prachayasittikul V (2014) QSAR study of H1N1 neuraminidase inhibitors from influenza A virus. Lett Drug Des Discov 11:420–427
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the EC FP7 project NanoPUZZLES (Project Reference: 309837) and EU FP7 project PreNanoTox (contract 309666). D.L. and J.L. acknowledge support from the National Science Foundation (NSF/CREST HRD-0833178). The authors also express their gratitude to Dr. L. Cappellini, Dr. G. Bianchi and Dr. R. Bagnati for valuable consultations on the computer science.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Michael Matthies
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 914 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toropova, A.P., Toropov, A.A., Benfenati, E. et al. Optimal nano-descriptors as translators of eclectic data into prediction of the cell membrane damage by means of nano metal-oxides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 745–757 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3566-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3566-4