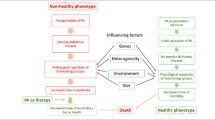
Abstract
Purpose
This study investigated the association between leisure-time physical activity and its different types, and the occurrence of falls that resulted in seeking health services, stratifying by age groups (60–64; 65–74; 75 or more).
Method
This is a cross sectional population-based study based on data from the National Health Survey (2013), with a final sample consisting of 8436 older adults. Logistic and multinomial regression models were used.
Results
There was an inverse association between sports practice and a fall episode across age groups; in the 60–64 age group (OR 4.1 × 10–7; 95% CI 4 × 10–8–4 × 10–6) and in the 65–74 age group (OR 1.8 × 10–7; 95% CI 3 × 10–8–10–6). In the older age group, significant associations were found between the practice of leisure-time physical activity and falling (OR 5.7 × 10–8; 95% CI 3 × 10–8–10–7), and in the three types of leisure-time physical activity and fall. (Aerobic OR 6.0 × 10–8; 95% CI 3 × 10–8–10–7/ Sports OR 3.4 × 10–7; 95% CI 5 × 10–8–2 × 10–6/ Resistance training OR 4.4 × 10–8; 95%CI 3 × 10–8–10–7).
Conclusion
Although less practiced by the studied population, sport was the type of leisure physical activity that promoted greater protection for falls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu H, Ouyang P (2017) Fall prevalence, time trend and its related risk factors among elderly people in China. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 73:294–299
Pimentel WRT, Pagotto V, Stopa SR, Hoffmann MCCL, Malta DC, de Menezes RL (2018) Falls requiring use of health services by the older adults: an analysis of the Brazilian National Health Survey, 2013. Cad Saude Publica 34(8):e00211417–e00211417
Prevention C. for D. C. and. (2005) Web-based injury statistics query and reporting system (WISQARS)[online]. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control
Burns ER, Stevens JA, Lee R (2016) The direct costs of fatal and non-fatal falls among older adults—United States. J Safety Res 58:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsr.2016.05.001
Krebs EE, Paudel M, Taylor BC, Bauer DC, Fink HA, Lane NE, Ensrud KE, Group, O. F. in M. (MrOS) S. R. (2016) Association of opioids with falls, fractures, and physical performance among older men with persistent musculoskeletal pain. J Gen Intern Med 31(5):463–469
JafariNasabian P, Inglis JE, Reilly W, Kelly OJ, Ilich JZ (2017) Aging human body: changes in bone, muscle and body fat with consequent changes in nutrient intake. J Endocrinol 234(1):R37–R51. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-16-0603
Tower J (2015) Programmed cell death in aging. Ageing Res Rev 23(Pt A):90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2015.04.002
de Smith A, A., Silva, A. O., Rodrigues, R. A. P., Moreira, M. A. S. P., Nogueira, J. de A., & Tura, L. F. R. (2017) Assessment of risk of falls in elderly living at home. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. https://doi.org/10.1590/1518-8345.0671.2754
Cuevas-Trisan R (2017) Balance problems and fall risks in the elderly. Phys Med Rehab Clin 28(4):727–737
Han BH, Ferris R, Blaum C (2014) Exploring ethnic and racial differences in falls among older adults. J Community Health 39(6):1241–1247
Holton A et al (2019) Potentially serious alcohol–medication interactions and falls in community-dwelling older adults: a prospective cohort study. Age Ageing 48(6):824–831
Bherer L (2015) Cognitive plasticity in older adults: effects of cognitive training and physical exercise. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1337(1):1–6
McPhee JS, French DP, Jackson D, Nazroo J, Pendleton N, Degens H (2016) Physical activity in older age: perspectives for healthy ageing and frailty. Biogerontology 17(3):567–580
Hallal PC, Andersen LB, Bull FC, Guthold R, Haskell W, Ekelund U, Group, L. P. A. S. W (2012) Global physical activity levels: surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. The Lancet 380(9838):247–257
Malta DC, de Andrade SSC, A., Stopa, S. R., Pereira, C. A., Szwarcwald, C. L., Silva Júnior, J. B. da, & Reis, A. A. C. dos. (2015) Brazilian lifestyles: National Health Survey results, 2013. Epidemiologia e Serviços de Saúde 24:217–226
Tornero-Quinones I, Saez-Padilla J, Espina Diaz A, Abad Robles MT, Sierra Robles A (2020) Functional ability, frailty and risk of falls in the elderly: relations with autonomy in daily living. IJERPH 17(3):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031006
Ganz DA, Latham NK (2020) Prevention of falls in community-dwelling older adults. N Engl J Med 382(8):734–743. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1903252
Gardner MM, Robertson MC, Campbell AJ (2000) Exercise in preventing falls and fall related injuries in older people: a review of randomised controlled trials. Br J Sports Med 34(1):7–17
Khan KM, Liu-Ambrose T, Donaldson MG, McKay HA (2001) Physical activity to prevent falls in older people: time to intervene in high risk groups using falls as an outcome. Br J Sports Med 35(3):144–145
Rubenstein LZ (2006) Falls in older people: epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for prevention. Age and Ageing 35(suppl_2): ii37–ii41
de Labra C, Guimaraes-Pinheiro C, Maseda A, Lorenzo T, Millan-Calenti JC (2015) Effects of physical exercise interventions in frail older adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Geriatr 15:154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-015-0155-4
de Souto Barreto P, Rolland Y, Vellas B, Maltais M (2019) Association of long-term exercise training with risk of falls, fractures, hospitalizations, and mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med 179(3):394–405. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.5406
Gillespie LD, Robertson MC, Gillespie WJ, Sherrington C, Gates S, Clemson LM, Lamb SE (2012) Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007146.pub3
Pedrinelli A, Garcez-Leme LE, Nobre R, do S. A. (2009) The effect of physical training on the locomotor apparatus in elderly people. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia 44(2):96–101
Bea JW, Thomson CA, Wallace RB, Wu C, Seguin RA, Going SB, LaCroix A, Eaton C, Ockene JK, LaMonte MJ, Jackson R, Jerry Mysiw W, Wactawski-Wende J (2017) Changes in physical activity, sedentary time, and risk of falling: the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Prev Med 95:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.11.025
Orwoll ES, Fino NF, Gill TM, Cauley JA, Strotmeyer ES, Ensrud KE, Kado DM, Barrett-Connor E, Bauer DC, Cawthon PM, Lapidus J (2019) The relationships between physical performance, activity levels, and falls in older men. J Gerontol Series A 74(9):1475–1483. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gly248
Souza LHR, da Silva Brandão JC, Fernandes AKC, Cardoso BLC (2017) Queda em idosos e fatores de risco associados. Ras 15(54):55–60
Sherrington C, Whitney JC, Lord SR, Herbert RD, Cumming RG, Close JCT (2008) Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 56(12):2234–2243
Szwarcwald CL, Malta DC, Pereira CA, Vieira MLFP, Conde WL, de Souza Júnior PRB, Damacena GN, Azevedo LO, Azevedo e Silva, G., & Theme Filha, M. M. (2014) National Health Survey in Brazil: design and methodology of application. Ciencia Saude Coletiva 19(2):333–342
Damacena GN, Szwarcwald CL, Malta DC, de Souza Júnior PRB, Vieira MLFP, Pereira CA, de Morais Neto OL, Júnior S (2015) O processo de desenvolvimento da Pesquisa Nacional de Saúde no Brasil, 2013. Epidemiol Serv Saúde 24:197–206
de Souza-Júnior PRB, de Freitas MPS, de Antonaci G, A., & Szwarcwald, C. L. (2015) Desenho da amostra da Pesquisa Nacional de Saúde 2013. Epidemiologia e Serviços de Saúde 24:207–216
Akyol Y, Ulus Y, Tander B, Tomak L, Zahiroğlu Y, Bilgici A, Kuru Ö (2018) Falls, fear of falling, and associated factors in ambulatory patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative study with healthy controls. Turk J Phys Med Rehab 64(3):213–221. https://doi.org/10.5606/tftrd.2018.1687
Lohman MC, Mezuk B, Dumenci L (2017) Depression and frailty: concurrent risks for adverse health outcomes. Aging Ment Health 21(4):399–408
Mansfield A, Inness EL, Mcilroy WE (2018) Stroke. Handb Clin Neurol 159:205–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63916-5.00013-6
Pereira GN, Morsch P, Lopes DGC, Trevisan MD, Ribeiro A, do Nascimento Navarro, J. H., Bos, D. da S. G., dos Santos Vianna, M. S., & Bos, A. J. G. (2013) Social and environmental factors associated with the occurrence of falls in the elderly/Fatores socioambientais associados a ocorrencia de quedas em idosos. Ciencia Saude Coletiva 18(12):3507–3515
Siqueira FV, Facchini LA, Piccini RX, Tomasi E, Thumé E, Silveira DS, Vieira V, Hallal PC (2007) Prevalence of falls and associated factors in the elderly. Rev Saude Publica 41(5):749–756
Ambrose AF, Cruz L, Paul G (2015) Falls and Fractures: a systematic approach to screening and prevention. Maturitas 82(1):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2015.06.035
de Sá GG, M., & Santos, A. M. R. dos. (2019) Functional independence of elderly patients who fell: a follow-up study. Rev Bras Enferm 72(6):1715–1722
Antes DL, Schneider IJC, d’Orsi E (2015) Mortality caused by accidental falls among the elderly: a time series analysis. Rev Bras Geriatr Gerontol 18(4):769–778
Lee J, Choi M, Kim CO (2017) Falls, a fear of falling and related factors in older adults with complex chronic disease. J Clin Nurs 26(23–24):4964–4972. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.13995
Santos RKM, Maciel ACC, Britto H, Lima JCC, de Souza TO (2015) Prevalence and factors associated with the risk of falls among the elderly registred in a primary healthcare unit of the city of Natal in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brasil. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 20(12):3753–3762
Deelen I, Ettema D, Kamphuis CBM (2018) Sports participation in sport clubs, gyms or public spaces: How users of different sports settings differ in their motivations, goals, and sports frequency. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0205198. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0205198
Lazzoli JK, de Oliveira MAB, Leitão MB, da Nóbrega ACL, Nahas RM, Rezende L, Drummond FA, Magni JRT, de Carvalho T, Borges SF (2001) Posicionamento oficial da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte sobre: esporte competitivo em indivíduos acima de 35 anos. Revista Brasileira de Medicina Do Esporte 7(3):83–92
Pedersen MT, Vorup J, Nistrup A, Wikman JM, Alstrøm JM, Melcher PS, Pfister GU, Bangsbo J (2017) Effect of team sports and resistance training on physical function, quality of life, and motivation in older adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports 27(8):852–864
Xu D, Hong Y, Li J, Chan K (2004) Effect of tai chi exercise on proprioception of ankle and knee joints in old people. Br J Sports Med 38(1):50–54
Hrysomallis C (2011) Balance ability and athletic performance. Sports Med 41(3):221–232
Li F, Harmer P, Fitzgerald K, Eckstrom E, Akers L, Chou L-S, Pidgeon D, Voit J, Winters-Stone K (2018) Effectiveness of a Therapeutic Tai Ji Quan Intervention vs a Multimodal Exercise Intervention to Prevent Falls Among Older Adults at High Risk of Falling: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 178(10):1301–1310. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.3915
Pliske G, Emmermacher P, Weinbeer V, Witte K (2016) Changes in dual-task performance after 5 months of karate and fitness training for older adults to enhance fall prevention. Aging Clin Exp Res 28(6):1179–1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0508-z
Sungkarat S, Boripuntakul S, Chattipakorn N, Watcharasaksilp K, Lord SR (2017) Effects of Tai Chi on Cognition and Fall Risk in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 65(4):721–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14594
Toronjo-Hornillo L, Castañeda-Vázquez C, Campos-Mesa MDC, González-Campos G, Corral-Pernía J, Chacón-Borrego F, DelCastillo-Andrés Ó (2018) Effects of the Application of a Program of Adapted Utilitarian Judo (JUA) on the Fear of Falling Syndrome (FOF) for the Health Sustainability of the Elderly Population. IJERPH 15(11):2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112526
Bruzi AT, Fialho J, Fonseca FS, Ugrinowitsch H (2013) Comparison of reaction time between basketball players, artistic gymnasts and non-athletes. Revista Brasileira de Ciencias Do Esporte 35(2):469–480
Okubo Y, Schoene D, Lord SR (2017) Step training improves reaction time, gait and balance and reduces falls in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med 51(7):586–593. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-095452
Daly RM (2017) Exercise and nutritional approaches to prevent frail bones, falls and fractures: an update. Climacteric 20(2):119–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/13697137.2017.1286890
van Ooijen MW, Roerdink M, Trekop M, Janssen TWJ, Beek PJ (2016) The efficacy of treadmill training with and without projected visual context for improving walking ability and reducing fall incidence and fear of falling in older adults with fall-related hip fracture: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr 16(1):215. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-016-0388-x
Dunsky A, Yahalom T, Arnon M, Lidor R (2017) The use of step aerobics and the stability ball to improve balance and quality of life in community-dwelling older adults—a randomized exploratory study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 71:66–74
Marques EA, Figueiredo P, Harris TB, Wanderley FA, Carvalho J (2017) Are resistance and aerobic exercise training equally effective at improving knee muscle strength and balance in older women? Arch Gerontol Geriatr 68:106–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures were approved by the National Research Ethics Commission (Process: 328.159, of June 26, 2013 / Approval Number: 10853812.7.0000.0008) and were in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
All participants were informed about the procedures and informed consent was obtained before data collection.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figueiredo, J.A., Lopes, C.S., Vale, W.S. et al. Association between types of leisure-time physical activity and falls in the older adults: a population-based study. Sport Sci Health 18, 689–697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-021-00835-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-021-00835-7