Abstract
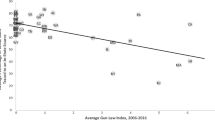
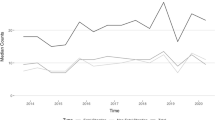
The purpose of the present study is to determine if permit-to-purchase laws are significantly related to firearm murder rates. There has been very little research done on the effect of this particular gun control measure on crime. The present study differs from prior research in two ways. First, a large longitudinal data set is used, and data for all 50 states for the period 1980 to 2011 are examined. Second, a fixed effects model, controlling for both state and year effects is used. Results suggest that permit-to-purchase laws have no statistically-significant effect on state-level firearm murder rates. These results are contrary to the results found in prior studies on this topic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartley, W., & Cohen, M. (1998). The effect of concealed weapons Laws: an extreme bound analysis. Economic Inquiry, 36, 258–265.
Census Bureau (1980–2013). Various reports. www.census.gov.
Crifasi, C., Meyers, J., Vernick, J., & Webster, D. (2015). Effects of changes in permit-to-purchase handgun Laws in Connecticut and Missouri on suicide rates. Preventive Medicine, 79, 43–49.
Dezhbakhsh, H., & Rubin, P. (1998). Lives saved or lives lost? The effects of concealed handgun Laws on crime. The American Economic Review, 88(2), 468–474.
Gius, M. (2014). An examination of the effects of concealed weapons Laws and Assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates. Applied Economics Letters, 21(4), 265–267.
Kleck, G., & Patterson, E. B. (1993). The impact of gun control and gun ownership levels on violence rates. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 9(3), 249–287.
Lott, J., & Mustard, D. (1997). Crime, deterrence, and right-to-carry concealed handguns. The Journal of Legal Studies, 26(1), 1–68.
Ludwig, J., & Cook, P. (Eds.) (2003). Evaluating gun policy: effects on crime and violence. Washington: The Brookings Institution.
Moody, C. (2001). Testing for the effects of concealed weapons Laws: specification errors and robustness. Journal of Law and Economics, 44(S2), 799–813.
Moody, C., & Marvell, T. (2009). The debate on shall issue Laws, continued. Econ Journal Watch, 6(2), 203–217.
Olson, D., & Maltz, M. (2001). Right-to-carry concealed weapon Laws and Homicide in large U.S. counties: the effect on weapon types, victim characteristics, and victim-offender relationships. Journal of Law and Economics, 44(S2), 747–770.
Rubin, P., & Dezhbakhsh, H. (2003). The effect of concealed handgun Laws on crime: beyond the dummy variables. International Review of Law and Economics, 23, 199–216.
Rudolph, K., Stuart, E., Vernick, J., & Webster, D. (2015). Association between Connecticut’s permit-to-purchase handgun law and homicides. American Journal of Public Health, 105(8), e49–e54.
Supplementary Homicide Reports (1980–2012). www.icpsr.umich.edu/icpsrweb/landing.jsp. Bureau of Justice Statistics, U.S. Department of Justice.
The Law Center to Prevent Gun Violence (2013). www.smartgunlaws.org.
Webster, D., Crifasi, C. K., & Vernick, J. (2014). Effects of the repeal of Missouri’s handgun purchaser licensing law on homicides. Journal of Urban Health, 91(2), 293–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gius, M. Effects of Permit-to-Purchase Laws on State-Level Firearm Murder Rates. Atl Econ J 45, 73–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11293-016-9529-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11293-016-9529-z