Abstract
Objectives
To perform a detailed analysis of palatal process pneumatization (PPP) on cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Methods
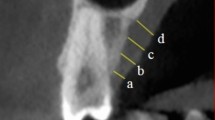
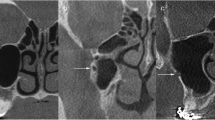
This study consisted of 376 maxillary sinuses of 188 patients aged 22–88 years who had maxillary CBCT scans. The radioanatomy of the PPP was evaluated at distances 4, 8, 16, and 24 mm posterior to incisive foramen. The types of PPP were classified as follows: type I: maxillary sinus palatal process non-gasified; type II: palatal process gasification into the nasal floor, but not more than half of the width of the nasal floor; and type III: palatal process gasification into the nasal floor more than half of the width of nasal floor. Sinus opening angle (SOA), palatonasal recess angle (PNRA), palatal junction angle (PJA), and palatal depth measurement (PDM) were the evaluated parameters.
Results
Among the identified 1315 PPPs, type I PPP (880, 66.92%) was the most frequently observed, followed by type II (426, 32.4%), and the least observed was type III PPP (9, 0.68%). There was no significant difference between SOA and PJA according to the types of PPP (p > 0.05). The difference between PNRA and PDM of type I and type II PPP showed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). Type I PPP was the most encountered with the highest PDM, and PNRA was narrower in type III than in type II PPP.
Conclusion
Physicians must be aware of these variations to prevent possible complications during surgery because 33.08% of the maxillary sinuses showed extensive pneumatization through the palatal process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoon A, Guilleminault C, Zaghi S, Liu SY. Distraction Osteogenesis Maxillary Expansion (DOME) for adult obstructive sleep apnea patients with narrow maxilla and nasal floor. Sleep Med. 2020;65:172–6.
Sánchez-Pérez A, Boracchia AC, López-Jornet P, Boix-García P. Characterization of the Maxillary Sinus Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. A Retro Radiograph Study Implant Dent. 2016;25(6):762–9.
Lana JP, Carneiro PM, Machado Vde C, de Souza PE, Manzi FR, Horta MC. Anatomic variations and lesions of the maxillary sinus detected in cone beam computed tomography for dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(12):1398–403.
Cavalcanti MC, Guirado TE, Sapata VM, Costa C, Pannuti CM, Jung RE, César Neto JB. Maxillary sinus floor pneumatization and alveolar ridge resorption after tooth loss: a cross-sectional study. Braz Oral Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2018.vol32.0064.
Wagner F, Dvorak G, Nemec S, Pietschmann P, Traxler H, Schicho K, Seemann R. Morphometric analysis of sinus depth in the posterior maxilla and proposal of a novel classification. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–7.
Marin S, Kirnbauer B, Rugani P, Payer M, Jakse N. Potential risk factors for maxillary sinus membrane perforation and treatment outcome analysis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(1):66–72.
Nunes LS, Bornstein MM, Sendi P, Buser D. Anatomical characteristics and dimensions of edentulous sites in the posterior maxillae of patients referred for implant therapy. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013;33(3):337–45.
Velloso GR, Vidigal GM Jr, de Freitas MM, Garcia de Brito OF, Manso MC, Groisman M. Tridimensional analysis of maxillary sinus anatomy related to sinus lift procedure. Implant Dent. 2006;15(2):192–6.
Chan HL, Monje A, Suarez F, Benavides E, Wang HL. Palatonasal recess on medial wall of the maxillary sinus and clinical implications for sinus augmentation via lateral window approach. J Periodontol. 2013;84(8):1087–93.
Niu L, Wang J, Yu H, Qiu L. New classification of maxillary sinus contours and its relation to sinus floor elevation surgery. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(4):493–500.
King KS, Lam EW, Faulkner MG, Heo G, Major PW. Vertical bone volume in the paramedian palate of adolescents: a computed tomography study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;132(6):783–8.
Yilmaz HG, Ayali A. Evaluation of the neurovascular bundle position at the palate with cone-beam computed tomography: an observational study. Head Face Med. 2015;11(1):1–5.
Liu JF, Dai JS, Zhou M, He PP, Liu QT, Wang NY. The CT observation and clinical significance of pneumatization of the anterior maxillary sinus Lin Chuang er bi yan hou tou Jing wai ke za zhi. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;30(16):1447–54.
Monje A, Urban IA, Miron RJ, Caballe-Serrano J, Buser D, Wang HL. Morphologic patterns of the atrophic posterior maxilla and clinical implications for bone regenerative therapy. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2017;37(5):e279–89.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Garcia-Denche JT, Abbushi A, Hernández G, Fernández-Tresguerres I, Lopez-Cabarcos E, Tamimi F. Nasal floor elevation for implant treatment in the atrophic premaxilla: a within-patient comparative study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17:e520–30.
Bauer RE, Ochs MW. Maxillary orthognathic surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2014;26(4):523–37.
Lozano-Carrascal N, Salomó-Coll O, Gehrke SA, Calvo-Guirado JL, Hernández-Alfaro F, Gargallo-Albiol J. Radiological evaluation of maxillary sinus anatomy: aA cross-sectional study of 300 patients. Ann Anat. 2017;214:1–8.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DNG: conceptualization, resources, writing—original draft, TEK resources, writing—original draft, BA and EZA: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors deny any conflicts of interest related to this study.
Ethical approval
The study design was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Recep Tayyip Erdogan University Faculty of Medicine (2021/62).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Günaçar, D.N., Köse, T.E., Arsan, B. et al. Radioanatomic study of maxillary sinus palatal process pneumatization. Oral Radiol 38, 398–404 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-021-00569-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-021-00569-9