Abstract
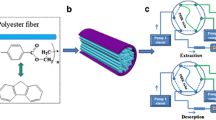
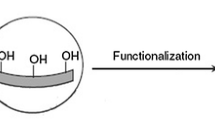
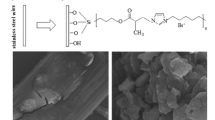
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) is an important organic contaminant substance in the environment. Their concentration monitoring is of great significance for predicting the potential environmental risk and protecting the organism safety. Here, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) coating was prepared on zylon heat-resistant fiber by in situ polymerization, which was packed to a stainless steel needle to develop a needle-type device (NTD) for the analysis of PAHs. Pyrene was used as the template molecule in this MIPs. To obtain excellent selectivity and adsorption efficiency, 4-vinylpyridine (4-VP) and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EDMA) were chosen as functional monomers and cross-linker, respectively, and the ratio of ingredients was optimized. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used for identifying micro-morphologic characteristics of the obtained MIPs-coating fiber. The PAHs from environmental water samples were extracted with the NTD by headspace extraction and detected by gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID). Under optimized conditions, the proposed method exhibited a good linearity dynamic range (LDR) of 0.5–1800 µg·L−1 with the correlation coefficients (R2) between 0.9953 and 0.9977. The limits of detection are in the ranges of 0.09–0.40 µg·L−1 and the limits of quantification are in the ranges of 0.37–1.40 µg·L−1. Furthermore, the device showed remarkable durability and storage capacity. It could be reused 60 times, and the loss ratio was less than 15% with relative standard deviations (RSDs) less than 6.4% after 3 days of storage. The developed method is easy, sensitive, and accurate, and it can be used for detection of trace PAHs in water sample.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- MIPs:
-
Molecularly imprinted polymers
- NTD:
-
Needle-type device
- PYR:
-
Pyrene
- 4-VP:
-
4-Vinylpyridine
- EDMA:
-
Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate
- MMA:
-
Methyl methacrylate
- TFMAA:
-
Trifluoromethacrylic acid
- NAP:
-
Naphthalene
- ACE:
-
Acenaphthene
- FLU:
-
Fluorene
- PHE:
-
Phenanthrene
- AIBN:
-
Azobisisobutyronitrile
- DVB:
-
Divinylbenzene
References
Arabi, M., Ghaedi, M., & Ostovan, A. (2017). Synthesis and application of in-situ molecularly imprinted silica monolithic in pipette-tip solid-phase microextraction for the separation and determination of gallic acid in orange juice samples. Journal of Chromatogrphy B, 1048, 102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.02.016
Bak, S. M., Nakata, H., Koh, D. H., Yoo, J., Iwata, H., & Kim, E. Y. (2019). In vitro and in silico AHR assays for assessing the risk of heavy oil-derived polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fish. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 181, 214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.008
BelBruno, J. J. (2019). Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chemical Reviews, 119, 94–119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00171
Camus, L., Brooks, S., Geraudie, P., Hjorth, M., Nahrgang, J., Olsen, G. H., & Smit, M. G. (2015). Comparison of produced water toxicity to Arctic and temperate species. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 248–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.007
Chopra, S., Ridley, L., Murphy, W. R., Sowa, J. R., Jr., Bentivegna, C. S., & Snow, N. H. (2019). Quantitative analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at part per billion levels in fish oil by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS). Journal of Chromatographic Science, 57, 87–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmy086
Dalvand, K., & Ghiasvand, A. (2019). Simultaneous analysis of PAHs and BTEX in soil by a needle trap device coupled with GC-FID and using response surface methodology involving Box-Behnken design. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1083, 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.07.063
Fernandez-Amado, M., Prieto-Blanco, M. C., Lopez-Mahia, P., Muniategui-Lorenzo, S., & Prada-Rodriguez, D. (2016). A novel and cost-effective method for the determination of fifteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in low volume rainwater samples. Talanta, 155, 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.04.032
Heidari, M., Bahrami, A., Ghiasvand, A. R., Shahna, F. G., & Soltanian, A. R. (2013). A needle trap device packed with a sol-gel derived, multi-walled carbon nanotubes/silica composite for sampling and analysis of volatile organohalogen compounds in air. Analytica Chimica Acta, 785, 67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.057
Heidari, N., Ghiasvand, A., & Abdolhosseini, S. (2017). Amino-silica/graphene oxide nanocomposite coated cotton as an efficient sorbent for needle trap device. Analytica Chimica Acta, 975, 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.031
Huang, Y., Zhou, Q., & Xie, G. (2011). Development of micro-solid phase extraction with titanate nanotube array modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide for sensitive determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 193, 82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.025
Jing, L., Chen, B., Zhang, B., & Li, P. (2015). Process simulation and dynamic control for marine oily wastewater treatment using UV irradiation. Water Research, 81, 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.03.023
Kedziora-Koch, K., & Wasiak, W. (2018). Needle-based extraction techniques with protected sorbent as powerful sample preparation tools to gas chromatographic analysis: Trends in application. Journal of Chromatography A, 1565, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.06.046
Kedziora, K., & Wasiak, W. (2017). Extraction media used in needle trap devices-Progress in development and application. Journal of Chromatography A, 1505, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.05.030
Koltsakidou, A., Zacharis, C. K., & Fytianos, K. (2015). A validated liquid chromatographic method for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in honey after homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction using hydrophilic acetonitrile and sodium chloride as mass separating agent. Journal of Chromatography A, 1377, 46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.12.039
Krupadam, R. J., Khan, M. S., & Wate, S. R. (2010). Removal of probable human carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymer. Water Research, 44, 681–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.09.044
Lai, J. P., Niessner, R., & Knopp, D. (2004). Benzo[a]pyrene imprinted polymers: Synthesis, characterization and SPE application in water and coffee samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 522, 137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.07.003
Lamichhane, S., Bal Krishna, K. C., & Sarukkalige, R. (2016). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal by sorption: A review. Chemosphere, 148, 336–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.01.036
Li, F., Gao, J., Li, X., Li, Y., He, X., Chen, L., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized carbon nanotubes for highly selective removal of aristolochic acid. J Chromatogr A, 1602, 168–177.
Liaud, C., Millet, M., & Le Calve, S. (2015). An analytical method coupling accelerated solvent extraction and HPLC-fluorescence for the quantification of particle-bound PAHs in indoor air sampled with a 3-stages cascade impactor. Talanta, 131, 386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.05.027
Liu, B., Chen, B., Zhang, B., Song, X., Zeng, G., & Lee, K. (2021). Photocatalytic ozonation of offshore produced water by TiO2 nanotube arrays coupled with UV-LED irradiation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402, 123456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123456
Liu, B., Chen, B., Zhang, B. Y., Jing, L., Zhang, H. & Lee, K. (2016). Photocatalytic degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in offshore produced water: Effects of water matrix, Journal of Environmental Engineering, 142. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)ee.1943-7870.0001135
Lou, D., Chen, H., Wang, X., Lian, L., Zhu, B., Yang, Q., Guo, T., Li, Q., Wang, R., & Guo, X. (2016). Preparation and application of a coated-fiber needle extraction device. Journal Separation Science, 39, 3769–3774. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600410
Lubeck, J. S., Malmquist, L. M. V., & Christensen, J. H. (2019). Supercritical fluid chromatography for the analysis of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic compounds in unconventional oils. Journal of Chromatography A, 1589, 162–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.12.056
Ma, W., An, Y., & Row, K. H. (2019). Preparation and evaluation of a green solvent-based molecularly imprinted monolithic column for the recognition of proteins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Analyst, 144, 6327–6333. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an01259a
Maleki, S., Hashemi, P., Rasolzadeh, F., Maleki, S., & Ghiasvand, A. R. (2018). A needle trap device packed with nanoporous silica sorbents for separation and gas chromatographic determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in contaminated soils. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 56, 771–778. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmy056
Ncube, S., Kunene, P., Tavengwa, N. T., Tutu, H., Richards, H., Cukrowska, E., & Chimuka, L. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation of the 16 US-EPA priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in solution. Journal of Environmental Management, 199, 192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.041
Peng, X., Sun, X., Yu, M., Fu, W., Chen, H., & Chen, J. (2019). Chronic exposure to environmental concentrations of phenanthrene impairs zebrafish reproduction. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 182, 109376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109376
Pfannkoch, E. A., Stuff, J. R., Whitecavage, J. A., Blevins, J. M., Seely, K. A., & Moran, J. H. (2015). A high throughput method for measuring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in seafood using QuEChERS extraction and SBSE. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 359629. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/359629
Poormohammadi, A., Bahrami, A., Farhadian, M., GhorbaniShahna, F., & Ghiasvand, A. (2017). Development of Carbotrap B-packed needle trap device for determination of volatile organic compounds in air. Journal of Chromatography A, 1527, 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.10.062
Krupadam, Reddithota J., Bhagyashree, B., Wate, Satish R., Bodhe, Ghanshyam L., Borje, S., & Anjaneyulu, Yerramilli. (2009). Fluorescence spectrophotometer analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental samples based on solid phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer. Environmental Science andTechnology, 43, 2871–2877. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802514c
Saito, Y., Imaizumi, M., Ban, K., Tahara, A., Wada, H., & Jinno, K. (2004). Development of miniaturized sample preparation with fibrous extraction media. Journal of Chromatography A, 1025, 27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2003.08.098
Santos, P. M., Del Nogal Sanchez, M., Perez Pavon, J. L., Cordero, B. M., & Fernandez, R. V. (2019). Liquid-liquid extraction-programmed temperature vaporizer-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in saliva samples. Application to the occupational exposure of firefighters. Talanta, 192, 69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.09.030
Song, X., Li, J., Xu, S., Ying, R., Ma, J., Liao, C., Liu, D., Yu, J., & Chen, L. (2012). Determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in seawater using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta, 99, 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.04.065
Speltini, A., Scalabrini, A., Maraschi, F., Sturini, M., & Profumo, A. (2017). Newest applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of contaminants from environmental and food matrices: A review. Anal Chim Acta, 974, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.042
Taghvaee, Z., Piravivanak, Z., Rezaei, K., & Faraji, M. (2015). Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in olive and refined pomace olive oils with modified low temperature and ultrasound-assisted liquid–liquid extraction method followed by the HPLC/FLD. Food Analytical Methods, 9, 1220–1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0297-1
Ueta, I., Razak, N. A., Mizuguchi, A., Kawakubo, S., Saito, Y., & Jinno, K. (2013). Needle-type extraction device for the purge and trap analysis of 23 volatile organic compounds in tap water. Journal of Chromatography A, 1317, 211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.07.011
Warren, J. M., & Pawliszyn, J. (2011). Development and evaluation of needle trap device geometry and packing methods for automated and manual analysis. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218, 8982–8988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.10.017
Yan, H., & Row, H. (2006). Characteristic and synthetic approach of molecularly imprinted polymer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 7, 155–178. https://doi.org/10.3390/i7050155
Yu, Y., Wang, X., Wang, B., Tao, S., Liu, W., Wang, X., Cao, J., Li, B., Lu, X., & Wong, M. H. (2011). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon residues in human milk, placenta, and umbilical cord blood in Beijing, China. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 10235–10242. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202827g
Yuan, Y., Lin, X., Li, T., Pang, T., Dong, Y., Zhuo, R., Wang, Q., Cao, Y., & Gan, N. (2019). A solid phase microextraction arrow with zirconium metal-organic framework/molybdenum disulfide coating coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometer for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fish samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 1592, 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.01.066
Zhang, X., Chen, J., Lian, L., Wang, X., Guo, X., Chen, H., Zhu, B., Hou, S., & Lou, D. (2019). Preparation and application of needle extraction device packed with sol–gel-derived perhydroxy cucurbit[6]uril coating fiber. Chromatographia, 82, 953–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-019-03720-1
Zheng J., Liu, B., Ping, J., Chen, B., Wu, H. & Zhang, B. (2015). Vortex- and shaker-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction (VSA-LLME) coupled with gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for analysis of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in offshore produced water. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2575-3
Zhou, D. B., Sheng, X., Han, F., Hu, Y. Y., Ding, L., Lv, Y. L., Song, W. & Zheng, P. (2018). Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on [60]fullerene functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for the determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 1578, 53-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.10.010
Funding
This investigation was supported by the Project of Science and Technology Development of Jilin Province (no. 20190303116SF and no. 202002008JC), the Research and Development Project for Industrial Technology of Jilin Province (no. 2020C028-1), the Talents Project for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Jilin province (no. 2020030), the Project of Science and Technology of the Education Department of Jilin Province (no. JJKH20210242KJ), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (grant number 20180101292JC). The financial support from the Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals of Jilin Province is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, B., Zhang, X., Wang, X. et al. A Needle Extraction Device Packed with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Functionalized Fiber for the Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon in Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 21 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05471-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05471-y