Abstract
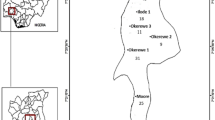
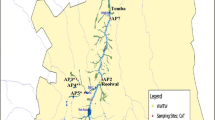
In Brazil, safe drinking water is not widely available, and consequently waterborne diseases are still associated with high morbidity and mortality rates. Among waterborne bacteria, diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) should be highlighted. This study targeted the evaluation of enteropathogenic (EPEC), enterotoxigenic (ETEC), and shiga toxin-producing (STEC)/enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in drinking water in Southeast Brazil and the georeferencing of generated data. A total of 1185 water samples were studied. Among them 7.8% and 4.1% gave positive results for total and fecal coliforms, respectively. By employing PCR, a total of 12 diarrheagenic E. coli (DEC) isolates (6 ETEC, 4 STEC, and 2 EPEC) from eight water samples (4, 2, and 2 positives for STEC, ETEC, and EPEC, respectively) were detected including samples collected in schools and a healthcare facility where particularly susceptible hosts are found. Data generated were submitted to georeferencing. A positive correlation (r2 = 0.9) between DEC detection and the rainy period was observed. The presence of DEC in drinking water samples in the studied municipalities highlights the relevance of controlling the sources of human and animal fecal pollution, as well as the management of municipal wastewater sources in order to reduce potential risks to human health. Searching for DEC and georeferencing DEC positive sites may subsidize the proposal of corrective and preventive actions by environmental surveillance agencies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranda, K. R., Fagundes-Neto, U., & Scaletsky, I. C. A. (2004). Evaluation of multiplex PCRs for diagnosis of infection with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli and Shigella spp. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 42(12), 5849–5853.
Chowdhury, F., Khan, I. A., Patel, S., Siddiq, A. U., Saha, N. C., Khan, A. I., Saha, A., Cravioto, A., Clemens, J., Qadri, F., & Ali, M. (2015). Diarrheal illness and healthcare seeking behavior among a population at high risk for diarrhea in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS One, 10(6), e0130105.
Fakhr, A. E., Gohar, M. K., & Atta, A. H. (2016). Impact of some ecological factors on fecal contamination of drinking water by diarrheagenic antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in Zagazig City, Egypt. International Journal of Microbiology, 2016, 1–9.
Fongaro, G., Viancelli, A., Magri, M. E., Elmahdy, E. M., Biesus, L. L., Kich, J. D., Kunz, A., & Barardi, C. R. M. (2014). Utility of specific biomarkers to assess safety of swine manure for biofertilizing purposes. Science of the Total Environment, 479-480, 277–283.
Fox, J. G., Dewhirst, F. E., Fraser, G. J., Paster, B. J., Shames, B., & Murphy, J. C. (1994). Intracellular campylobacter-like organism from ferrets and hamsters with proliferative bowel disease is a Desulfovibrio sp. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 32(5), 1229–1237.
Gomes, T. A. T., Elias, W. P., Scaletsky, I. C. A., Guth, B. E. C., Rodrigues, J. F., Piazza, R. M. F., Ferreira, L. C. S., & Martinez, M. B. (2016). Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 47(1), 3–30.
Gunzburg, S. T., Tornieporth, N. G., & Riley, L. W. (1995). Identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by PCR-based detection of the bundle-forming pilus gene. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 33(5), 1375–1377.
Guzmán, B. L., Nava, G., & Díaz, P. (2015). La calidad del agua para consumo humano y su associación con la morbimortalidad en Colombia, 2008-2012. Biomédica, 35, 177–190.
Hartland, E. L., & Leong, J. M. (2013). Enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic E. coli: ecology, pathogenesis, and evolution. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 3, 1–3.
Kaper, J. B., Nataro, J. P., & Mobley, H. L. T. (2004). Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev, 2(2), 123–140.
Lascowski, K. M., Guth, B. E., Martins, F. H., Rocha, S. P., Irino, K., & Pelayo, J. S. (2013). Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in drinking water supplies of North Paraná state, Brazil. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114(4), 1230–1239.
Masters, N., Wiegand, A., Ahmed, W., & Katouli, M. (2011). Escherichia coli virulence genes profile of surface waters as an indicator of water quality. Water Research, 45(19), 6321–6333.
Pessoa, G. V. A., & Silva, E. A. M. (1972). Meios de Rugai e lisina-motilidade combinados em um só tubo para identificação presuntiva de enterobactérias. Revista do Instituto Adolfo Lutz, 32, 97–100.
Reid, S. D., Betting, D. J., & Whittam, T. S. (1999). Molecular detection and identification of intimin alleles in pathogenic Escherichia coli by multiplex PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 37, 2719–2722.
Ribeiro, D. A., Niemann, F. S., Gatti, M. S. V., Lanna, M. C. S., Tsuji, T., & Yano, T. (2011). Putative new heat-stable cytotoxic and enterotoxic factors in culture supernatant of Escherichia coli isolated from drinking water. Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins Including Tropical Diseases, 17(1), 103–107.
Segalés, J., Olvera, A., Grau-Roma, L., Charreyre, C., Nauwynck, H., & Larsen-Let, A. L. (2008). PCV-2 genotype definition and nomenclature. Veterinary Record, 162(26), 867–868.
Semenov, A. V., Van Overbeek, L., Van Bruggen, A., & H. (2007). Percolation and survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in soil amended with contaminated dairy manure or slurry. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(10), 3206–3215.
Vidal, R., Vidal, M., Lagos, R., Levine, M., & Prado, V. (2004). Multiplex PCR for diagnosis of enteric infections associated with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 42(4), 1787–1789.
Walk, S. T., Alm, E. W., Clahoun, L. M., Mladonicky, J. M., & Whittam, T. M. (2007). Genetic diversity and population structure of Escherichia coli isolated from freshwater beaches. Environmental Microbiology, 9(9), 2274–2288.
Wang, L., Nakamura, H., Kage-Nakadai, E., Hara-Kudo, Y., & Nishikawa, Y. (2017). Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and multiple–locus variable-number tandem–repeat analysis profiles of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from different retail foods. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 249, 44–52.
Xavier-da-Silva, J., & Zaidan, R. T. (2011). Geoprocessamento & meio ambiente. Rio de Janeiro: Bertrand Brasil.
Funding
This study is financially supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, M., Ferreira, J.F.G., Salles, L.A.F. et al. Isolation, Molecular Characterization and Geoprocessing of Enteropathogenic, Enterotoxigenic, and Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Drinking Water Sources from Southeast Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 39 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4394-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4394-4