Abstract
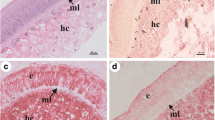
Diplopods feed organic matter in decomposition; however, some environmental factors can promote changes in tissues of these animals. Sewage sludge has been applied for recuperation of physical structure of degraded soil. This work analyzed the influence of the sludge from a city of São Paulo in the midgut of the diplopod Rhinocricus padbergi. After the exposition to sludge, the midgut was prepared for histological and ultra-structural analyses. After 1 week of exposition, there were various glycoprotein globules in the fat body, which appeared, ultrastructurally, little electron dense. In the animals exposed for 2 weeks, there was an intensive renovation of the epithelium with the invasion of regenerative cells, which was observed in the histological and ultra-structural analyses. These data showed that the sludge present various substances that were very hazardous for these animals; more studies were necessary before the application of this in agriculture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti, G., Seniczak, A., & Seniczak, S. (2003). The digestive system and fat body of an early-derivative oribatid mites, Archegozetes longisetous Aoki (Acari: Oribatida, Trhypochthoniidae). Acarologia, 43, 151–222.
Amaral Sobrinho, N. M. B., Velloso, A. C., & Oliveira, C. (1997) Solubilidade de metais pesados em solo tratado com resíduo siderúrgico. Rev. Bras. de Ciência do Solo, Campinas, v.21, n.1, p.9–16.
Arab, A., Zacarin, G. G., Fontanetti, C. S., Camargo-mathias, M. I., Dos Santos, M. G., & Cabrera, A. C. (2003). Composition of the defensive secretion of the Neotropical millipede Rhinocricus padbergi Verhoeff 1938 (Diplopoda: Spirobolida: Rhinocricidae). Entomotropica, 18(2), 79–82.
Camargo-mathias, M. I. & Fontanetti, C. S. (2000). Ultrastructural features of the fat body and oenocytes of Rhinocricus padbergi Verhoeff (Diplopoda, Spirobolida). Biocell, Mendoza, 24(1), 1–12.
Camargo-mathias, M. I., Fontanetti, C. S., & Micó-Balaguer, E. (1998). Histochemical studies of Rhinocricus padbergi Verhoeff ovaries (Diplopoda, Spirobolida, Rhinocricidae). Cytobios, 94, 169–184.
Camargo-mathias, M. I., Fantazzini, E. R., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2004). Ultrastructural features of the midgut of Rhinocricus padbergi (Diplopoda: Spirobolida). Braz J morphol Sci, 21(2), 65–71.
Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental-Cetesb. (1999). Aplicação de biossólidos de sistemas de tratamento biológico em áreas agrícolas: critérios para projeto e operação. Norma P4230. São Paulo.
Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental-Cetesb. (2004). Relatório de qualidade das águas interiores do estado de São Paulo 2003/CETESB–São Paulo: Cetesb, 273p.
Edinger, A. L. & Thompson, C. B. (2004). Death by design: Apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 16, 663–669.
Elliot, H. A., Liberraty, M. R., & Huang, C. P. (1986). Effect of iron oxide removal on heavy metal sorption by acid subsoils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, Dorcdrecht, 37(3/4), 379–389.
Fantazzini, E. R., Fontanetti, C. S., & Camargo-mathias, M. I. (1998). Anatomy of the digestive tube, histology and histochemistry of the foregut and salivary glands of Rhinocricus padbergi (Diplopoda, Rhinocricidae). Arthropoda Selecta, 7, 256–264.
Fantazzini, E. R., Fontanetti, C. S., & Camargo-mathias, M. I. (2002). Midgut of the millipede “Rhinocricus padbergi” Verhoeff, 1938 (Diplopoda: Spirobolida): Histology and histochemistry. Arthropoda Selecta, 11, 135–142.
Fontanetti, C. S. & Camargo-mathias, M. I. (2004). External morphology of the antennae of Rhinocricus padbergi Verhoeff, 1938 (Diplopoda: Spirobolida). Braz J Morphol Sci, 21(2), 73–79.
Hopkin, S. P. (1989). Ecophysiology of metals in terrestrial invertebrates. New York: Elsevier.
Hopkin, S. P. (1990). Critical concentrations, pathways of detoxification and cellular ecotoxicology of metals in terrestrial arthropods. Functional Ecology, 4, 321–327.
Hopkin, S. P. & Read, H. J. (1992). The biology of millipedes. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 233p.
Hopkin, S. P., Watson, K., Martin, M. H., & Mould, M. L. (1985). The assimilation of heavy metals by Lithobius variegatus and Glomeris marginata (Chil: Dipl.). Bijdr Duerk, 55, 88–94.
Hopkin, S. P., Homes, C. A. C., & Bray, A. (1989). X-ray microanalytical mapping of the intracellular distribution of pollutant metals. Z Micr Anal, 14, 23–27.
Hubert, M. (1979). Localization and identification of mineral elements and nitrogenous waste in Diplopoda. In M. Camatini (Ed.), Myriapod biology (pp. 127–134). London: Academic Press.
Junqueira, L. C. & Junqueira, L. M. M. S. (1983). Técnicas Básicas de Citologia e Histologia (p. 123p). São Paulo: Livraria Editora Santos.
Kocssis, M. A., & De Maria, I. C. (2004). O efeito do lodo de esgoto na recuperação da estrutura física de solos degradados.
Köhler, H. R., & Alberti, G. (1992) The effect of heavy metal stress on the intestine of diplopods. In E. Meyer, K. Thaler & W. Schedl, (Eds.), Advances in Myriapodology. Ber. nat.-med. Ver. Innsbruck, Suppl., v.10, p. 257-267.
Köhler, H. R. & Triebskorn, R. (1998). Assessment of the cytotoxic impact of heavy metals on soil invertebrates using a protocol integrating qualitative and quantitative components. Biomarkers, 3, 109–127.
Köhler, H. R., Hüttenrauch, K., Berkus, M., Gräff, S., & Alberti, G. (1996). Cellular hepatopancreatic reactions in Porcellio scaber (Isopoda) as biomarker for the evaluation of heavy metal toxicity in soils. Appl Soil Ecol, 3, 1–15.
Ludwig, M., Kratzmann, M., & Alberti, G. (1992). Observations on the proventricular glands (‘organes racemiformes’) on the oribatid mites Chamobates borealis (Acari, Oribatida): An organ of interest for studies on adaptation of animals to acid soils. Experimental & Applied Acarology, 15, 49–57.
Pawert, M., Triebskorn, R., Gräff, S., Berkus, M., Schulz, J., & Köhler, H. R. (1996). Cellular alterations in collembolan midgut cells as a marker of heavy metals exposure: Ultrastructure and intracellular metal distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 181, 187–200.
Pearse, A. G. E. (1985). Histochemistry: Theoretical and apllied, volume 2 (4th ed., p. 998p). London: J&A. Churchill.
Petersen, H. & Luxton, M. (1982). A comparative analysis of soil fauna populations and their role in decomposition processes. Oikos, 39(3), 291–357.
Pigino, G., Migliorini, M., Paccagnini, E., Bernini, F., & Leonzio, C. (2005). Fine structure of the midgut and Malpighian papillae in Campodea (Monocampa) quilisi Silvestri, 1932 (Hexapoda, Diplura) with special reference to the metal composition and physiological significance of midgut intracellular electron-dense granules. Tissue and Cell, 37, 223–232.
Pigino, G., Migliorini, M., Paccagnini, E., & Bernini, F. (2006). Localisation of heavy metals in the midgutepithelial cells of Xenillus tegeocranus (Hermann, 1804) (Acari: Oribatida). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64, 257–263.
Pires, M. G. & Nascimento, P. M. (2003). FEC pesquisa uso de lodo de esgoto como fertilizante. http://www.unicamp.br/saladeimprensa.
Schubart, O. (1942) Os miriápodos e suas relações com a agricultura. Pap. Avul. Dep. Zool., v.2, n.16, p.205–234.
Simkiss, K. & Mason, A. Z. (1984). Cellular responses of molluscan tissues to environmental metals. Marine Environmental Research, 14, 103–118.
Steinhaus, E. A. (1949). Principles of insect pathology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Triebskorn, R. & Künast, C. (1990). Ultrastructural change in the digestive system of Deroceras reticulatum (Mollusca: Gastropoda) induced by lethal and sublethal concentrations of the carbamate molluscicide cloethocarb. Malacologia, 32(1), 89–106.
Triebskorn, R., Köhler, H. R., Zanh, T., Vogt, G., Ludwig, M., Rumpf, S., et al. (1991). Invertebrate cells as targets for hazardous substances ziet. Fur angewandte Zool, 78, 277–287.
Triebskorn, R., Henderson, I. F., & Martin, A. P. (1999). Detection of iron in tissues from slugs (Deroceras reticulatum Müller) after ingestion of iron chelates by means of energy-filtering transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM). Pesticide Science, 55, 55–61.
Tsutyia, M. T. (2001) Características de biossólidos gerados em estações de tratamento de esgotos. In: M. T. Tsutiya, J. B. Comparini, A. P. Sobrinho, I. Hespanhol, P. C. T. Carvalho, & A. J. Melfi (Ed). Biossólidos na agricultura (pp. 89–131). São Paulo: Sabesp, cap.4.
Vandenbulcke, F., Grelle, C., Fabre, M. C., & Descamps, M. (1998). Implication of the midgut of the centipede Lithobius forficatus in the heavy metal detoxification process. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 41, 258–268.
Vieira, R. F. & Silva, C. M. M. S. (2004). Utilização do lodo de esgoto como fonte de fósforo na cultura de soja. EMBRAPA. Circular Técnica-6, Jaguariúna-SP, junho.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Godoy, J.A.P., Fontanetti, C.S. Diplopods as Bioindicators of Soils: Analysis of Midgut of Individuals Maintained in Substract Containing Sewage Sludge. Water Air Soil Pollut 210, 389–398 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0261-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0261-z