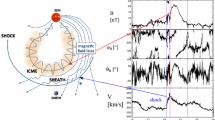
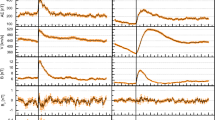
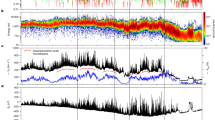
Abstract
Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections (ICMEs), their possible shocks and sheaths, and co-rotating interaction regions (CIRs) are the primary large-scale heliospheric structures driving geospace disturbances at the Earth. CIRs are followed by a faster stream where Alfvénic fluctuations may drive prolonged high-latitude activity. In this paper we highlight that these structures have all different origins, solar wind conditions and as a consequence, different geomagnetic responses. We discuss general solar wind properties of sheaths, ICMEs (in particular those showing the flux rope signatures), CIRs and fast streams and how they affect their solar wind coupling efficiency and the resulting magnetospheric activity. We show that there are two different solar wind driving modes: (1) Sheath-like with turbulent magnetic fields, and large Alfvén Mach (\(M_{A}\)) numbers and dynamic pressure, and (2) flux rope-like with smoothly varying magnetic field direction, and lower \(M_{A}\) numbers and dynamic pressure. We also summarize the key properties of interplanetary shocks for space weather and how they depend on solar cycle and the driver.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.-H. Ahn, S.-I. Akasofu, Y. Kamide, The Joule heat production rate and the particle energy injection rate as a function of the geomagnetic indices AE and AL. J. Geophys. Res. 88, 6275–6287 (1983). doi:10.1029/JA088iA08p06275
S.-I. Akasofu, Interplanetary energy flux associated with magnetospheric substorms. Planet. Space Sci. 27, 425–431 (1979). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(79)90119-3
S.-I. Akasofu, Energy coupling between the solar wind and the magnetosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 28, 121–190 (1981). doi:10.1007/BF00218810
C.W. Allen, Relation between magnetic storms and solar activity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 104, 13 (1944). doi:10.1093/mnras/104.1.13
M.V. Alves, E. Echer, W.D. Gonzalez, Geoeffectiveness of corotating interaction regions as measured by Dst index. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, A07S05 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011379
A. Badruddin, Z. Falak, Study of the geoeffectiveness of coronal mass ejections, corotating interaction regions and their associated structures observed during Solar Cycle 23. Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 253 (2016). doi:10.1007/s10509-016-2839-4
D.N. Baker, A.J. Klimas, D.A. Roberts, Examination of time-variable input effects in a nonlinear analogue magnetosphere model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 1631–1634 (1991). doi:10.1029/91GL01048
D.N. Baker, X. Li, A. Pulkkinen, C.M. Ngwira, M.L. Mays, A.B. Galvin, K.D.C. Simunac, A major solar eruptive event in July 2012: defining extreme space weather scenarios. Space Weather 11, 585–591 (2013). doi:10.1002/swe.20097
S.D. Bale, M.A. Balikhin, T.S. Horbury, V.V. Krasnoselskikh, H. Kucharek, E. Möbius, S.N. Walker, A. Balogh, D. Burgess, B. Lembège, E.A. Lucek, M. Scholer, S.J. Schwartz, M.F. Thomsen, Quasi-perpendicular shock structure and processes. Space Sci. Rev. 118, 161–203 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11214-005-3827-0
A. Balogh, P. Riley, Overview of Heliospheric Shocks, in Cosmic Winds and the Heliosphere (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1997)
A. Balogh, E.J. Smith, B.T. Tsurutani, D.J. Southwood, R.J. Forsyth, T.S. Horbury, The heliospheric magnetic field over the South polar region of the Sun. Science 268, 1007–1010 (1995). doi:10.1126/science.268.5213.1007
A. Balogh, V. Bothmer, N.U. Crooker, R.J. Forsyth, G. Gloeckler, A. Hewish, M. Hilchenbach, R. Kallenbach, B. Klecker, J.A. Linker, E. Lucek, G. Mann, E. Marsch, A. Posner, I.G. Richardson, J.M. Schmidt, M. Scholer, Y.-M. Wang, R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber, M.R. Aellig, P. Bochsler, S. Hefti, Z. Mikić, The solar origin of corotating interaction regions and their formation in the inner heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 89, 141–178 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1005245306874
J. Bartels, Terrestrial-magnetic activity and its relations to solar phenomena. Terr. Magn. Atmos. Electr. (J. Geophys. Res.) 37, 1 (1932). doi:10.1029/TE037i001p00001
J.W. Belcher, L. Davis Jr., Large-amplitude Alfvén waves in the interplanetary medium, 2. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3534 (1971). doi:10.1029/JA076i016p03534
X. Blanco-Cano, P. Kajdič, N. Omidi, C.T. Russell, Foreshock cavitons for different interplanetary magnetic field geometries: simulations and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 116, 09101 (2011). doi:10.1029/2010JA016413
X. Blanco-Cano, P. Kajdič, E. Aguilar-Rodríguez, C.T. Russell, L.K. Jian, J.G. Luhmann, Interplanetary shocks and foreshocks observed by STEREO during 2007–2010. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 992–1008 (2016). doi:10.1002/2015JA021645
J.E. Borovsky, The rudiments of a theory of solar wind/magnetosphere coupling derived from first principles. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113, 08228 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007JA012646
J.E. Borovsky, J. Birn, The solar wind electric field does not control the dayside reconnection rate. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 751–760 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JA019193
J.E. Borovsky, M.H. Denton, Differences between CME-driven storms and CIR-driven storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, A07S08 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011447
J.E. Borovsky, M.H. Denton, The differences between storms driven by helmet streamer CIRs and storms driven by pseudostreamer CIRs. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 5506–5521 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgra.50524
J.E. Borovsky, H.O. Funsten, Role of solar wind turbulence in the coupling of the solar wind to the Earth’s magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1246 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002JA009601
J.E. Borovsky, K. Yakymenko, Substorm occurrence rates, substorm recurrence times, and solar wind structure. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 122, 2973–2998 (2017). doi:10.1002/2016JA023625
J.E. Borovsky, R.J. Nemzek, R.D. Belian, The occurrence rate of magnetospheric-substorm onsets—random and periodic substorms. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 3807–3813 (1993). doi:10.1029/92JA02556
J.E. Borovsky, M.F. Thomsen, D.J. McComas, The superdense plasma sheet: plasmaspheric origin, solar wind origin, or ionospheric origin? J. Geophys. Res. 102, 22089–22106 (1997). doi:10.1029/96JA02469
V. Bothmer, R. Schwenn, The structure and origin of magnetic clouds in the solar wind. Ann. Geophys. 16, 1–24 (1998). doi:10.1007/s00585-997-0001-x
O.J. Brambles, W. Lotko, B. Zhang, J. Ouellette, J. Lyon, M. Wiltberger, The effects of ionospheric outflow on ICME and SIR driven sawtooth events. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 6026–6041 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgra.50522
D. Burgess, E.A. Lucek, M. Scholer, S.D. Bale, M.A. Balikhin, A. Balogh, T.S. Horbury, V.V. Krasnoselskikh, H. Kucharek, B. Lembège, E. Möbius, S.J. Schwartz, M.F. Thomsen, S.N. Walker, Quasi-parallel shock structure and processes. Space Sci. Rev. 118, 205–222 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11214-005-3832-3
L.F.E. Burlaga, in Magnetic Clouds, ed. by R. Schwenn, E. Marsch (1991), p. 152
L. Burlaga, E. Sittler, F. Mariani, R. Schwenn, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock—Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673–6684 (1981). doi:10.1029/JA086iA08p06673
L.F. Burlaga, L. Klein, N.R. Sheeley Jr., D.J. Michels, R.A. Howard, M.J. Koomen, R. Schwenn, H. Rosenbauer, A magnetic cloud and a coronal mass ejection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 9, 1317–1320 (1982). doi:10.1029/GL009i012p01317
L.F. Burlaga, K.W. Behannon, L.W. Klein, Compound streams, magnetic clouds, and major geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 5725–5734 (1987). doi:10.1029/JA092iA06p05725
L.F. Burlaga, R.M. Skoug, C.W. Smith, D.F. Webb, T.H. Zurbuchen, A. Reinard, Fast ejecta during the ascending phase of solar cycle 23: ACE observations, 1998–1999. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 20957–20978 (2001). doi:10.1029/2000JA000214
L.F. Burlaga, S.P. Plunkett, O.C. St. Cyr, Successive CMEs and complex ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 107, 1266 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA000255
R.K. Burton, R.L. McPherron, C.T. Russell, An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst. J. Geophys. Res. 80, 4204–4214 (1975). doi:10.1029/JA080i031p04204
H.V. Cane, I.G. Richardson, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections in the near-Earth solar wind during 1996-2002. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1156 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002JA009817
H.V. Cane, I.G. Richardson, G. Wibberenz, Helios 1 and 2 observations of particle decreases, ejecta, and magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 102, 7075–7086 (1997). doi:10.1029/97JA00149
R.C. Carrington, Description of a singular appearance seen in the Sun on September 1, 1859. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 20, 13–15 (1859). doi:10.1093/mnras/20.1.13
M.D. Cash, D.A. Biesecker, V. Pizzo, C.A. Koning, G. Millward, C.N. Arge, C.J. Henney, D. Odstrcil, Ensemble modeling of the 23 July 2012 coronal mass ejection. Space Weather 13, 611–625 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015SW001232
J.K. Chao, R.P. Lepping, A correlative study of ssc’s, interplanetary shocks, and solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 1799 (1974). doi:10.1029/JA079i013p01799
S. Chapman, V.C.A. Ferraro, The electrical state of solar streams of corpuscles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 89, 470 (1929). doi:10.1093/mnras/89.5.470
E.W. Cliver, L. Svalgaard, The 1859 solar-terrestrial disturbance and the current limits of extreme space weather activity. Sol. Phys. 224, 407–422 (2004). doi:10.1007/s11207-005-4980-z
G.T. Cocconi, K. Greisen, S. Hayakawa, P. Morrison, The cosmic ray flare effect. Nuovo Cimento 8, 161–168 (1958)
W.D. Cramer, N.E. Turner, M.-C. Fok, N.Y. Buzulukova, Effects of different geomagnetic storm drivers on the ring current: CRCM results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 1062–1073 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgra.50138
S.R. Cranmer, Coronal holes and the high-speed solar wind. Space Sci. Rev. 101, 229–294 (2002)
N.U. Crooker, Solar and heliospheric geoeffective disturbances. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 62, 1071–1085 (2000). doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(00)00098-5
N.U. Crooker, C.-L. Huang, S.M. Lamassa, D.E. Larson, S.W. Kahler, H.E. Spence, Heliospheric plasma sheets. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109, 03107 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JA010170
N.U. Crooker, S.K. Antiochos, X. Zhao, M. Neugebauer, Global network of slow solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 117, 04104 (2012). doi:10.1029/2011JA017236
J.J. Curto, T. Araki, L.F. Alberca, Evolution of the concept of sudden storm commencements and their operative identification. Earth Planets Space 59, i–xii (2007)
I.A. Daglis, J.U. Kozyra, Outstanding issues of ring current dynamics. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 64, 253–264 (2002). doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(01)00087-6
I.A. Daglis, R.M. Thorne, W. Baumjohann, S. Orsini, The terrestrial ring current: origin, formation, and decay. Rev. Geophys. 37, 407–438 (1999). doi:10.1029/1999RG900009
M.H. Denton, J.E. Borovsky, R.M. Skoug, M.F. Thomsen, B. Lavraud, M.G. Henderson, R.L. McPherron, J.C. Zhang, M.W. Liemohn, Geomagnetic storms driven by ICME- and CIR-dominated solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, A07S07 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011436
A.P. Dimmock, K. Nykyri, H. Karimabadi, A. Osmane, T.I. Pulkkinen, A statistical study into the spatial distribution and dawn-dusk asymmetry of dayside magnetosheath ion temperatures as a function of upstream solar wind conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 2767–2782 (2015). doi:10.1002/2014JA020734
J.W. Dungey, Interplanetary magnetic field and the auroral zones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 47–48 (1961). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.6.47
E. Echer, W.D. Gonzalez, Geoeffectiveness of interplanetary shocks, magnetic clouds, sector boundary crossings and their combined occurrence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, 09808 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003GL019199
E. Echer, W.D. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, Interplanetary conditions leading to superintense geomagnetic storms (\(\mbox{Dst} \leq - 250~\mbox{nT}\)) during Solar Cycle 23. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L06S03 (2008a). doi:10.1029/2007GL0317
E. Echer, W.D. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, A.L.C. Gonzalez, Interplanetary conditions causing intense geomagnetic storms (\(\mbox{Dst} \leq -100~\mbox{nT}\)) during Solar Cycle 23 (1996–2006). J. Geophys. Res. 113, A05221 (2008b). doi:10.1029/2007JA012744
W. Ellis, On the relation between the diurnal range of magnetic declination and horizontal force and the period of solar spot frequency. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. I 63, 64–78 (1898)
C. Farrugia, D. Berdichevsky, Evolutionary signatures in complex ejecta and their driven shocks. Ann. Geophys. 22, 3679–3698 (2004). doi:10.5194/angeo-22-3679-2004
C.J. Farrugia, M.P. Freeman, L.F. Burlaga, R.P. Lepping, K. Takahashi, The Earth’s magnetosphere under continued forcing—substorm activity during the passage of an interplanetary magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 7657–7671 (1993). doi:10.1029/92JA02351
C.J. Farrugia, V.K. Jordanova, M.F. Thomsen, G. Lu, S.W.H. Cowley, K.W. Ogilvie, A two-ejecta event associated with a two-step geomagnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, 11104 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006JA011893
F.R. Fenrich, J.G. Luhmann, Geomagnetic response to magnetic clouds of different polarity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2999–3002 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL51180
S.E. Forbush, On the effects in cosmic-ray intensity observed during the recent magnetic storm. Phys. Rev. 51, 1108–1109 (1937). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.51.1108.3
J. Geiss, G. Gloeckler, R. von Steiger, Origin of the solar wind from composition data. Space Sci. Rev. 72, 49–60 (1995). doi:10.1007/BF00768753
T. Gold, Discussion on shock waves and rarefied gas dynamics, in Gas Dynamics of Cosmic Clouds. IAU Symposium, vol. 2 (1955), pp. 97–105
T. Gold, Magnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 1, 100–114 (1962). doi:10.1007/BF00174637
H. Goldstein, On the field configuration in magnetic clouds, in NASA Conference Publication. NASA Conference Publication, vol. 228 (1983)
W.D. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, Criteria of interplanetary parameters causing intense magnetic storms (Dst of less than −100 nT). Planet. Space Sci. 35, 1101–1109 (1987). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(87)90015-8
W.D. Gonzalez, A.L.C. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, Dual-peak solar cycle distribution of intense geomagnetic storms. Planet. Space Sci. 38, 181–187 (1990). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(90)90082-2
W.D. Gonzalez, J.A. Joselyn, Y. Kamide, H.W. Kroehl, G. Rostoker, B.T. Tsurutani, V.M. Vasyliunas, What is a geomagnetic storm? J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5771–5792 (1994). doi:10.1029/93JA02867
W.D. Gonzalez, A.L.C. de Gonzalez, A. Dal Lago, B.T. Tsurutani, J.K. Arballo, G.K. Lakhina, B. Buti, C.M. Ho, S.-T. Wu, Magnetic cloud field intensities and solar wind velocities. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 963–966 (1998)
W.D. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, A.L. Clúa de Gonzalez, Interplanetary origin of geomagnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 88, 529–562 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1005160129098
W.D. Gonzalez, E. Echer, B.T. Tsurutani, A.L. Clúa de Gonzalez, A. Dal Lago, Interplanetary origin of intense, superintense and extreme geomagnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 158, 69–89 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11214-010-9715-2
J.A. González-Esparza, A. Balogh, R.J. Forsyth, M. Neugebauer, E.J. Smith, J.L. Phillips, Interplanetary shock waves and large-scale structures: Ulysses’ observations in and out of the ecliptic plane. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 17057–17072 (1996). doi:10.1029/96JA00685
N. Gopalswamy, S. Nunes, S. Yashiro, R.A. Howard, Variability of solar eruptions during cycle 23. Adv. Space Res. 34, 391–396 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2003.10.054
N. Gopalswamy, P. Makela, S. Akiyama, S. Yashiro, N. Thakur, CMEs during the two activity peaks in cycle 24 and their space weather consequences. Sun Geosph. 10, 111–118 (2015)
J.T. Gosling, The solar flare myth. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18937–18950 (1993). doi:10.1029/93JA01896
J.T. Gosling, D.J. McComas, Field line draping about fast coronal mass ejecta—a source of strong out-of-the-ecliptic interplanetary magnetic fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 14, 355–358 (1987). doi:10.1029/GL014i004p00355
J.T. Gosling, V.J. Pizzo, Formation and evolution of corotating interaction regions and their three dimensional structure. Space Sci. Rev. 89, 21–52 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1005291711900
J.T. Gosling, V. Pizzo, S.J. Bame, Anomalously low proton temperatures in the solar wind following interplanetary shock waves—evidence for magnetic bottles? J. Geophys. Res. 78, 2001 (1973). doi:10.1029/JA078i013p02001
J.T. Gosling, E. Hildner, R.M. MacQueen, R.H. Munro, A.I. Poland, C.L. Ross, Direct observations of a flare related coronal and solar wind disturbance. Sol. Phys. 40, 439–448 (1975). doi:10.1007/BF00162390
J.T. Gosling, J.R. Asbridge, S.J. Bame, W.C. Feldman, Solar wind stream interfaces. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 1401–1412 (1978). doi:10.1029/JA083iA04p01401
J.T. Gosling, D.J. McComas, J.L. Phillips, S.J. Bame, Geomagnetic activity associated with Earth passage of interplanetary shock disturbances and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 7831–7839 (1991). doi:10.1029/91JA00316
W.M.H. Greaves, H.W. Newton, On the recurrence of magnetic storms. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 89, 641–646 (1929). doi:10.1093/mnras/89.7.641
J. Guo, X. Feng, J. Zhang, P. Zuo, C. Xiang, Statistical properties and geoefficiency of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheaths during intense geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115, 09107 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JA015140
J. Guo, X. Feng, B.A. Emery, J. Zhang, C. Xiang, F. Shen, W. Song, Energy transfer during intense geomagnetic storms driven by interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 116, 05106 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011JA016490
M.R. Hairston, K.A. Drake, R. Skoug, Saturation of the ionospheric polar cap potential during the October-November 2003 superstorms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110, 0926 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004JA010864
R. Hajra, E. Echer, B.T. Tsurutani, W.D. Gonzalez, Solar wind-magnetosphere energy coupling efficiency and partitioning: HILDCAAs and preceding CIR storms during solar cycle 23. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 2675–2690 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JA019646
R.A. Harrison, J.A. Davies, C. Möstl, Y. Liu, M. Temmer, M.M. Bisi, J.P. Eastwood, C.A. de Koning, N. Nitta, T. Rollett, C.J. Farrugia, R.J. Forsyth, B.V. Jackson, E.A. Jensen, E.K.J. Kilpua, D. Odstrcil, D.F. Webb, An analysis of the origin and propagation of the multiple coronal mass ejections of 2010 August 1. Astrophys. J. 750, 45 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/750/1/45
H. Hasegawa, M. Fujimoto, T.-D. Phan, H. Rème, A. Balogh, M.W. Dunlop, C. Hashimoto, R. TanDokoro, Transport of solar wind into Earth’s magnetosphere through rolled-up Kelvin-Helmholtz vortices. Nature 430, 755–758 (2004). doi:10.1038/nature02799
T. Henke, J. Woch, R. Schwenn, U. Mall, G. Gloeckler, R. von Steiger, R.J. Forsyth, A. Balogh, Ionization state and magnetic topology of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10597–10614 (2001). doi:10.1029/2000JA900176
H. Hietala, T.V. Laitinen, K. Andréeová, R. Vainio, A. Vaivads, M. Palmroth, T.I. Pulkkinen, H.E.J. Koskinen, E.A. Lucek, H. Rème, Supermagnetosonic jets behind a collisionless quasiparallel shock. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(24), 245001 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.245001
J. Hirshberg, A. Alksne, D.S. Colburn, S.J. Bame, A.J. Hundhausen, Observation of a solar flare induced interplanetary shock and helium-enriched driver gas. J. Geophys. Res. 75, 1 (1970). doi:10.1029/JA075i001p00001
L. Holappa, K. Mursula, T. Asikainen, A new method to estimate annual solar wind parameters and contributions of different solar wind structures to geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 9407–9418 (2014). doi:10.1002/2014JA020599
C.-S. Huang, G. Le, G.D. Reeves, Periodic magnetospheric substorms during fluctuating interplanetary magnetic field B z . Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, 14801 (2004). doi:10.1029/2004GL020180
K. Huttunen, H. Koskinen, Importance of post-shock streams and sheath region as drivers of intense magnetospheric storms and high-latitude activity. Ann. Geophys. 22, 1729–1738 (2004). doi:10.5194/angeo-22-1729-2004
K.E.J. Huttunen, H.E.J. Koskinen, R. Schwenn, Variability of magnetospheric storms driven by different solar wind perturbations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 107, 1121 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA900171
K.E.J. Huttunen, R. Schwenn, V. Bothmer, H.E.J. Koskinen, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds in the rising, maximum and early declining phases of solar cycle 23. Ann. Geophys. 23, 625–641 (2005). doi:10.5194/angeo-23-625-2005
L. Jian, C.T. Russell, J.G. Luhmann, R.M. Skoug, Properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at one AU during 1995–2004. Sol. Phys. 239, 393–436 (2006a)
L. Jian, C.T. Russell, J.G. Luhmann, R.M. Skoug, Properties of stream interactions at one AU during 1995–2004. Sol. Phys. 239, 337–392 (2006b)
G.H. Jones, A. Balogh, Context and heliographic dependence of heliospheric planar magnetic structures. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 12713–12724 (2000). doi:10.1029/2000JA900003
G.H. Jones, A. Rees, A. Balogh, R.J. Forsyth, The draping of heliospheric magnetic fields upstream of coronal mass ejecta. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 1463 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001GL014110
V.K. Jordanova, H. Matsui, P.A. Puhl-Quinn, M.F. Thomsen, K. Mursula, L. Holappa, Ring current development during high speed streams. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 71, 1093–1102 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.09.043
J.A. Joselyn, B.T. Tsurutani, Geomagnetic sudden impulses and storm sudden commencements—a note on terminology. EOS Trans. 71, 1808 (1990). doi:10.1029/90EO00350
S. Jurac, J.C. Kasper, J.D. Richardson, A.J. Lazarus, Geomagnetic disturbances and their relationship to interplanetary shock parameters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 1463 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001GL014034
Y. Kamide, W. Baumjohann, I.A. Daglis, W.D. Gonzalez, M. Grande, J.A. Joselyn, R.L. McPherron, J.L. Phillips, E.G.D. Reeves, G. Rostoker, A.S. Sharma, H.J. Singer, B.T. Tsurutani, V.M. Vasyliunas, Current understanding of magnetic storms: storm-substorm relationships. J. Geophys. Res. 103 17705–17728 (1998a)
Y. Kamide, J.-H. Shue, X. Li, G. Lu, M.J. Brittnacher, G.K. Parks, G.D. Reeves, Internally and externally triggered substorms: a case study of the January 10, 1997 events, in Substorms-4, 1998b
Y. Kamide, N. Yokoyama, W. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, I.A. Daglis, A. Brekke, S. Masuda, Two-step development of geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 6917–6922 (1998c)
R. Kataoka, S. Watari, N. Shimada, H. Shimazu, K. Marubashi, Downstream structures of interplanetary fast shocks associated with coronal mass ejections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, 12103 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005GL022777
R. Kataoka, D. Shiota, E. Kilpua, K. Keika, Pileup accident hypothesis of magnetic storm on 17 March 2015. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 5155–5161 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015GL064816
E.K.J. Kilpua, J.G. Luhmann, J. Gosling, Y. Li, H. Elliott, C.T. Russell, L. Jian, A.B. Galvin, D. Larson, P. Schroeder, K. Simunac, G. Petrie, Small solar wind transients and their connection to the large-scale coronal structure. Sol. Phys. 256, 327–344 (2009). doi:10.1007/s11207-009-9366-1
E.K.J. Kilpua, L.K. Jian, Y. Li, J.G. Luhmann, C.T. Russell, Multipoint ICME encounters: pre-STEREO and STEREO observations. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 73, 1228–1241 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2010.10.012
E.K.J. Kilpua, Y. Li, J.G. Luhmann, L.K. Jian, C.T. Russell, On the relationship between magnetic cloud field polarity and geoeffectiveness. Ann. Geophys. 30, 1037–1050 (2012). doi:10.5194/angeo-30-1037-2012
E.K.J. Kilpua, H. Hietala, H.E.J. Koskinen, D. Fontaine, L. Turc, Magnetic field and dynamic pressure ULF fluctuations in coronal-mass-ejection-driven sheath regions. Ann. Geophys. 31, 1559–1567 (2013a)
E.K.J. Kilpua, A. Isavnin, A. Vourlidas, H.E.J. Koskinen, L. Rodriguez, On the relationship between interplanetary coronal mass ejections and magnetic clouds. Ann. Geophys. 31, 1251–1265 (2013b)
E.K.J. Kilpua, E. Lumme, K. Andreeova, A. Isavnin, H.E.J. Koskinen, Properties and drivers of fast interplanetary shocks near the orbit of the Earth (1995–2013). J. Geophys. Res. 120, 4112–4125 (2015a)
E.K.J. Kilpua, N. Olspert, A. Grigorievskiy, M.J. Käpylä, E.I. Tanskanen, H. Miyahara, R. Kataoka, J. Pelt, Y.D. Liu, Statistical study of strong and extreme geomagnetic disturbances and solar cycle characteristics. Astrophys. J. 806, 272 (2015b)
E.K.J. Kilpua, H. Hietala, D.L. Turner, H.E.J. Koskinen, T.I. Pulkkinen, J.V. Rodriguez, G.D. Reeves, S.G. Claudepierre, H.E. Spence, Unraveling the drivers of the storm time radiation belt response. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 3076–3084 (2015c)
E.K.J. Kilpua, H.E.J. Koskinen, T.I. Pulkkinen, Coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions in interplanetary space. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. (2017)
L.W. Klein, L.F. Burlaga, Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 613–624 (1982). doi:10.1029/JA087iA02p00613
A.J. Klimas, D.N. Baker, D.A. Roberts, D.H. Fairfield, J. Buechner, A nonlinear dynamical analogue model of geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 12 (1992). doi:10.1029/92JA00794
D.J. Knipp, W.K. Tobiska, B.A. Emery, Direct and indirect thermospheric heating sources for solar cycles 21–23. Sol. Phys. 224, 495–505 (2004). doi:10.1007/s11207-005-6393-4
H.E.J. Koskinen, Physics of Space Storms: From the Solar Surface to the Earth (Springer, Berlin, 2011)
H.E.J. Koskinen, E.I. Tanskanen, Magnetospheric energy budget and the epsilon parameter. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 107, 1415 (2002). doi:10.1029/2002JA009283
J.U. Kozyra, M.W. Liemohn, C.R. Clauer, A.J. Ridley, M.F. Thomsen, J.E. Borovsky, J.L. Roeder, V.K. Jordanova, W.D. Gonzalez, Multistep Dst development and ring current composition changes during the 4–6 June 1991 magnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 107, 1224 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA000023
A.S. Krieger, A.F. Timothy, E.C. Roelof, A coronal hole and its identification as the source of a high velocity solar wind stream. Sol. Phys. 29, 505–525 (1973). doi:10.1007/BF00150828
B. Lavraud, J.E. Borovsky, Altered solar wind-magnetosphere interaction at low Mach numbers: coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113, 0008 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JA013192
B. Lavraud, M.F. Thomsen, J.E. Borovsky, M.H. Denton, T.I. Pulkkinen, Magnetosphere preconditioning under northward IMF: evidence from the study of coronal mass ejection and corotating interaction region geoeffectiveness. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, 09208 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011566
B. Lavraud, A. Ruffenach, A.P. Rouillard, P. Kajdic, W.B. Manchester, N. Lugaz, Geo-effectiveness and radial dependence of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 26–35 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JA019154
G.-M. Le, Z.-Y. Cai, H.-N. Wang, Z.-Q. Yin, P. Li, Solar cycle distribution of major geomagnetic storms. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 13, 739–748 (2013). doi:10.1088/1674-4527/13/6/013
R.P. Lepping, L.F. Burlaga, J.A. Jones, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11957–11965 (1990). doi:10.1029/JA095iA08p11957
R.P. Lepping, L.F. Burlaga, A. Szabo, K.W. Ogilvie, W.H. Mish, D. Vassiliadis, A.J. Lazarus, J.T. Steinberg, C.J. Farrugia, L. Janoo, F. Mariani, The wind magnetic cloud and events of October 18-20, 1995: interplanetary properties and as triggers for geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 14049–14064 (1997). doi:10.1029/97JA00272
Y. Li, J.G. Luhmann, B.J. Lynch, E.K.J. Kilpua, Cyclic reversal of magnetic cloud poloidal field. Sol. Phys. 270, 331–346 (2011)
M.W. Liemohn, J.U. Kozyra, M.F. Thomsen, J.L. Roeder, G. Lu, J.E. Borovsky, T.E. Cayton, Dominant role of the asymmetric ring current in producing the stormtime Dst. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10883–10904 (2001). doi:10.1029/2000JA000326
M.W. Liemohn, M. Jazowski, J.U. Kozyra, N. Ganushkina, M.F. Thomsen, J.E. Borovsky, CIR versus CME drivers of the ring current during intense magnetic storms. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 466, 3305–3328 (2010). doi:10.1098/rspa.2010.0075
F.A. Lindeman, Note on the theory of magnetic storms. Philos. Mag. 38, 669–684 (1911)
Y. Liu, J.D. Richardson, J.W. Belcher, A statistical study of the properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections from 0.3 to 5.4 AU. Planet. Space Sci. 53, 3–17 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.pss.2004.09.023
Y. Liu, J.D. Richardson, J.W. Belcher, J.C. Kasper, R.M. Skoug, Plasma depletion and mirror waves ahead of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, 09108 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006JA011723
Y. Liu, J.G. Luhmann, R. Müller-Mellin, P.C. Schroeder, L. Wang, R.P. Lin, S.D. Bale, Y. Li, M.H. Acuña, J.-A. Sauvaud, A comprehensive view of the 2006 December 13 CME: from the Sun to interplanetary space. Astrophys. J. 689, 563–571 (2008a). doi:10.1086/592031
Y. Liu, W.B. Manchester, J.D. Richardson, J.G. Luhmann, R.P. Lin, S.D. Bale, Deflection flows ahead of ICMEs as an indicator of curvature and geoeffectiveness. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A00B03 (2008b)
Y.D. Liu, J.G. Luhmann, C. Möstl, J.C. Martinez-Oliveros, S.D. Bale, R.P. Lin, R.A. Harrison, M. Temmer, D.F. Webb, D. Odstrcil, Interactions between coronal mass ejections viewed in coordinated imaging and in situ observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 746, 15 (2012). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/746/2/L15
Y.D. Liu, J.G. Luhmann, N. Lugaz, C. Möstl, J.A. Davies, S.D. Bale, R.P. Lin, On Sun-to-Earth propagation of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 769, 45 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/769/1/45
Y.D. Liu, J.G. Luhmann, P. Kajdič, E.K.J. Kilpua, N. Lugaz, N.V. Nitta, C. Möstl, B. Lavraud, S.D. Bale, C.J. Farrugia, A.B. Galvin, Observations of an extreme storm in interplanetary space caused by successive coronal mass ejections. Nat. Commun. 5, 3481 (2014a)
Y.D. Liu, Z. Yang, R. Wang, J.G. Luhmann, J.D. Richardson, N. Lugaz, Sun-to-Earth characteristics of two coronal mass ejections interacting near 1 AU: formation of a complex ejecta and generation of a two-step geomagnetic storm. Astrophys. J. Lett. 793, L41 2014b)
Y.D. Liu, H. Hu, R. Wang, Z. Yang, B. Zhu, Y.A. Liu, J.G. Luhmann, J.D. Richardson, Plasma and magnetic field characteristics of solar coronal mass ejections in relation to geomagnetic storm intensity and variability. Astrophys. J. Lett. 809, 34 (2015). doi:10.1088/2041-8205/809/2/L34
Y.D. Liu, H. Hu, C. Wang, J.G. Luhmann, J.D. Richardson, Z. Yang, R. Wang, On sun-to-Earth propagation of coronal mass ejections: II. Slow events and comparison with others. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 222, 23 (2016). doi:10.3847/0067-0049/222/2/23
M. Lockwood, M.J. Owens, L.A. Barnard, S. Bentley, C.J. Scott, C.E. Watt, On the origins and timescales of geoeffective IMF. Space Weather 14 406–432 (2015). doi:10.1002/2016SW001375
R.E. Lopez, M. Wiltberger, S. Hernandez, J.G. Lyon, Solar wind density control of energy transfer to the magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, 08804 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003GL018780
R.E. Lopez, R. Bruntz, E.J. Mitchell, M. Wiltberger, J.G. Lyon, V.G. Merkin, Role of magnetosheath force balance in regulating the dayside reconnection potential. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115, 12216 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JA014597
E.A. Lucek, A. Balogh, The identification and characterization of Alfvénic fluctuations in ULYSSES data at midlatitudes. Astrophys. J. 507, 984–990 (1998). doi:10.1086/306372
E.A. Lucek, T.S. Horbury, I. Dandouras, H. RèMe, Cluster observations of the Earth’s quasi-parallel bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113, 0702 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007JA012756
N. Lugaz, C.J. Farrugia, A new class of complex ejecta resulting from the interaction of two CMEs and its expected geoeffectiveness. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 769–776 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013GL058789
N. Lugaz, C.J. Farrugia, C.W. Smith, K. Paulson, Shocks inside CMEs: a survey of properties from 1997 to 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 2409–2427 (2015). doi:10.1002/2014JA020848
N. Lugaz, C.J. Farrugia, C.-L. Huang, R.M. Winslow, H.E. Spence, N.A. Schwadron, Earth’s magnetosphere and outer radiation belt under sub-Alfvénic solar wind. Nat. Commun. 7, 13001 (2016)
L.R. Lyons, G.T. Blanchard, J.C. Samson, R.P. Lepping, T. Yamamoto, T. Moretto, Coordinated observations demonstrating external substorm triggering. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 27039–27052 (1997). doi:10.1029/97JA02639
W. Manchester, E.K.J. Kilpua, Y.D. Liu, N. Lugaz, P. Riley, T. Török, B. Vršnak, The physical processes of CME/ICME evolution. Space Sci. Rev. (2017, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-017-0394-0. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017SSRv..tmp...90M. Provided by the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System
E.W. Maunder, Magnetic disturbance and associated sun-spots. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 65, 2 (1904). doi:10.1093/mnras/65.1.2
P.N. Mayaud, Derivation, Meaning, and Use of Geomagnetic Indices. Geophysical Monograph, vol. 22 (American Geophysical Union, Washington, 1980)
D.J. McComas, J.T. Gosling, S.J. Bame, E.J. Smith, H.V. Cane, A test of magnetic field draping induced BZ perturbations ahead of fast coronal mass ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 1465–1471 (1989). doi:10.1029/JA094iA02p01465
R.L. McPherron, T. Terasawa, A. Nishida, Solar wind triggering of substorm expansion onset. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 38, 1089–1108 (1986)
M.B. Moldwin, S. Ford, R. Lepping, J. Slavin, A. Szabo, Small-scale magnetic flux ropes in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 57–60 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999GL010724
S.K. Morley, M.P. Freeman, On the association between northward turnings of the interplanetary magnetic field and substorm onsets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, 08104 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006GL028891
P. Morrison, Solar origin of cosmic-ray time variations. Phys. Rev. 101, 1397–1404 (1956). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.101.1397
C. Möstl, C.J. Farrugia, E.K.J. Kilpua, L.K. Jian, Y. Liu, J.P. Eastwood, R.A. Harrison, D.F. Webb, M. Temmer, D. Odstrcil, J.A. Davies, T. Rollett, J.G. Luhmann, N. Nitta, T. Mulligan, E.A. Jensen, R. Forsyth, B. Lavraud, C.A. de Koning, A.M. Veronig, A.B. Galvin, T.L. Zhang, B.J. Anderson, Multi-point shock and flux rope analysis of multiple interplanetary coronal mass ejections around 2010 August 1 in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 758, 10 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/758/1/10
T. Mulligan, C.T. Russell, J.G. Luhmann, Solar cycle evolution of the structure of magnetic clouds in the inner heliosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2959–2962 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL01302
M. Myllys, N. Partamies, L. Juusola, Latitude dependence of long-term geomagnetic activity and its solar wind drivers. Ann. Geophys. 33, 573–581 (2015). doi:10.5194/angeo-33-573-2015
M. Myllys, E.K.J. Kilpua, B. Lavraud, T.I. Pulkkinen, Solar wind-magnetosphere coupling efficiency during ejecta and sheath-driven geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 4378–4396 (2016). doi:10.1002/2016JA022407
M. Myllys, E.K.J. Kipua, B. Lavraud, Interplay of solar wind parameters and physical mechanisms producing the saturation of the cross polar cap potential. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44, 3019–3027 (2017). doi:10.1002/2017GL072676
P.T. Newell, K. Liou, Solar wind driving and substorm triggering. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 116, 03229 (2011). doi:10.1029/2010JA016139
P.T. Newell, T. Sotirelis, K. Liou, C.-I. Meng, F.J. Rich, A nearly universal solar wind-magnetosphere coupling function inferred from 10 magnetospheric state variables. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112, 01206 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JA012015
H.W. Newton, A.S. Milsom, The distribution of great and small geomagnetic storms in the sunspot cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 59, 203–214 (1954). doi:10.1029/JZ059i002p00203
N.S. Nikolaeva, Y.I. Yermolaev, I.G. Lodkina, Dependence of geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms on the solar wind parameters for different types of streams. Geomagn. Aeron. 51, 49–65 (2011). doi:10.1134/S0016793211010099
J.T. Nolte, A.S. Krieger, A.F. Timothy, R.E. Gold, E.C. Roelof, G. Vaiana, A.J. Lazarus, J.D. Sullivan, P.S. McIntosh, Coronal holes as sources of solar wind. Sol. Phys. 46, 303–322 (1976). doi:10.1007/BF00149859
T.P. O’Brien, R.L. McPherron, An empirical phase space analysis of ring current dynamics: solar wind control of injection and decay. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 7707–7720 (2000). doi:10.1029/1998JA000437
D.M. Oliveira, J. Raeder, Impact angle control of interplanetary shock geoeffectiveness. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 8188–8201 (2014). doi:10.1002/2014JA020275
D.M. Oliveira, J. Raeder, Impact angle control of interplanetary shock geoeffectiveness: a statistical study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 4313–4323 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015JA021147
N. Omidi, H. Zhang, D. Sibeck, D. Turner, Spontaneous hot flow anomalies at quasi-parallel shocks: 2. Hybrid simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 173–180 (2013). doi:10.1029/2012JA018099
A. Osmane, A.P. Dimmock, R. Naderpour, T.I. Pulkkinen, K. Nykyri, The impact of solar wind ULF B z fluctuations on geomagnetic activity for viscous timescales during strongly northward and southward IMF. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 9307–9322 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015JA021505
M.J. Owens, P.J. Cargill, C. Pagel, G.L. Siscoe, N.U. Crooker, Characteristic magnetic field and speed properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110, 01105 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004JA010814
E. Palmerio, E.K.J. Kilpua, N.P. Savani, Planar magnetic structures in coronal mass ejection-driven sheath regions. Ann. Geophys. 34, 313–322 (2016). doi:10.5194/angeo-34-313-2016
M. Palmroth, T.I. Pulkkinen, P. Janhunen, D.J. McComas, C.W. Smith, H.E.J. Koskinen, Role of solar wind dynamic pressure in driving ionospheric Joule heating. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109, 11302 (2004). doi:10.1029/2004JA010529
M. Palmroth, H.E.J. Koskinen, T.I. Pulkkinen, P.K. Toivanen, P. Janhunen, S.E. Milan, M. Lester, Magnetospheric feedback in solar wind energy transfer. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115, 0010 (2010). doi:10.1029/2010JA015746
W. Park, J. Lee, Y. Yi, N. Ssessanga, S. Oh, Storm sudden commencements without interplanetary shocks. J. Astron. Space Sci. 32, 181–187 (2015). doi:10.5140/JASS.2015.32.3.181
J.H. Piddington, Interplanetary magnetic field and its control of cosmic-ray variations. Phys. Rev. 112, 589–596 (1958). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.112.589
T. Pulkkinen, Space weather: terrestrial perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 4, 1 (2007). doi:10.12942/lrsp-2007-1
T.I. Pulkkinen, A.P. Dimmock, A. Osmane, K. Nykyri, Solar wind energy input to the magnetosheath and at the magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 4723–4730 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015GL064226
J. Raeder, G. Lu, Polar cap potential saturation during large geomagnetic storms. Adv. Space Res. 36, 1804–1808 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2004.05.010
P.H. Reiff, R.W. Spiro, T.W. Hill, Dependence of polar cap potential drop on interplanetary parameters. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 7639–7648 (1981). doi:10.1029/JA086iA09p07639
I.G. Richardson, H.V. Cane, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23 (1996–2009): catalog and summary of properties. Sol. Phys. 264, 189–237 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11207-010-9568-6
I.G. Richardson, H.V. Cane, Solar wind drivers of geomagnetic storms during more than four solar cycles. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2(27), 01 (2012). doi:10.1051/swsc/2012001
I.G. Richardson, D.F. Webb, J. Zhang, D.B. Berdichevsky, D.A. Biesecker, J.C. Kasper, R. Kataoka, J.T. Steinberg, B.J. Thompson, C.-C. Wu, A.N. Zhukov, Major geomagnetic storms (\(\mbox{Dst} \leq -100~\mbox{nT}\)) generated by corotating interaction regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, 0709 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011476
P. Riley, R.M. Caplan, J. Giacalone, D. Lario, Y. Liu, Properties of the fast forward shock driven by the July 23 2012 extreme coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J. 819, 57 (2016). doi:10.3847/0004-637X/819/1/57
A.P. Rouillard, N.R. Sheeley Jr., T.J. Cooper, J.A. Davies, B. Lavraud, E.K.J. Kilpua, R.M. Skoug, J.T. Steinberg, A. Szabo, A. Opitz, J.-A. Sauvaud, The solar origin of small interplanetary transients. Astrophys. J. 734, 7 (2011). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/734/1/7
A. Ruffenach, B. Lavraud, C.J. Farrugia, P. Démoulin, S. Dasso, M.J. Owens, J.-A. Sauvaud, A.P. Rouillard, A. Lynnyk, C. Foullon, N.P. Savani, J.G. Luhmann, A.B. Galvin, Statistical study of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 43–60 (2015). doi:10.1002/2014JA020628
C.T. Russell, R.L. McPherron, Semiannual variation of geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 92 (1973). doi:10.1029/JA078i001p00092
C.T. Russell, L.K. Jian, X. Blanco-Cano, J.G. Luhmann, STEREO observations of upstream and downstream waves at low Mach number shocks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, 03106 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008GL036991
C.T. Russell, R.A. Mewaldt, J.G. Luhmann, G.M. Mason, T.T. von Rosenvinge, C.M.S. Cohen, R.A. Leske, R. Gomez-Herrero, A. Klassen, A.B. Galvin, K.D.C. Simunac, The very unusual interplanetary coronal mass ejection of 2012 July 23: a blast wave mediated by solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 770, 38 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/770/1/38
T. Saemundsson, Statistics of geomagnetic storms and solar activity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 123, 299 (1962). doi:10.1093/mnras/123.4.299
M.D. Salas, The curious events leading to the theory of shock waves. Shock Waves 16, 477–487 (2007). doi:10.1007/s00193-007-0084-z
A.A. Samsonov, D.G. Sibeck, J. Imber, MHD simulation for the interaction of an interplanetary shock with the Earth’s magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112, 12220 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JA012627
A.A. Samsonov, V.A. Sergeev, M.M. Kuznetsova, D.G. Sibeck, Asymmetric magnetospheric compressions and expansions in response to impact of inclined interplanetary shock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 4716–4722 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015GL064294
R. Schwenn, Direct correlations between coronal transients and interplanetary disturbances. Space Sci. Rev. 34, 85–99 (1983). doi:10.1007/BF00221199
R. Schwenn, A. dal Lago, E. Huttunen, W.D. Gonzalez, The association of coronal mass ejections with their effects near the Earth. Ann. Geophys. 23, 1033–1059 (2005). doi:10.5194/angeo-23-1033-2005
V.A. Sergeev, R.J. Pellinen, T.I. Pulkkinen, Steady magnetospheric convection: a review of recent results. Space Sci. Rev. 75, 551–604 (1996). doi:10.1007/BF00833344
N.R. Sheeley Jr., A.P. Rouillard, Tracking streamer blobs into the heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 715, 300–309 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/715/1/300
N.R. Sheeley Jr., R.A. Howard, D.J. Michels, M.J. Koomen, R. Schwenn, K.H. Muehlhaeuser, H. Rosenbauer, Coronal mass ejections and interplanetary shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 163–175 (1985). doi:10.1029/JA090iA01p00163
N.R. Sheeley, Y.-M. Wang, S.H. Hawley, G.E. Brueckner, K.P. Dere, R.A. Howard, M.J. Koomen, C.M. Korendyke, D.J. Michels, S.E. Paswaters, D.G. Socker, O.C. St. Cyr, D. Wang, P.L. Lamy, A. Llebaria, R. Schwenn, G.M. Simnett, S. Plunkett, D.A. Biesecker, Measurements of flow speeds in the corona between 2 and 30 \(R_{\odot}\). Astrophys. J. 484, 472–478 (1997)
J.-H. Shue, P. Song, C.T. Russell, J.T. Steinberg, J.K. Chao, G. Zastenker, O.L. Vaisberg, S. Kokubun, H.J. Singer, T.R. Detman, H. Kawano, Magnetopause location under extreme solar wind conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 17691–17700 (1998). doi:10.1029/98JA01103
G. Siscoe, D. Odstrcil, Ways in which ICME sheaths differ from magnetosheaths. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113, 0007 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JA013142
G. Siscoe, P.J. MacNeice, D. Odstrcil, East-West asymmetry in coronal mass ejection geoeffectiveness. Space Weather 5, 04002 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006SW000286
E.J. Smith, J.A. Slavin, R.D. Zwickl, S.J. Bame, Shocks and storm sudden commencements, in Solar Wind Magnetosphere Coupling, ed. by Y. Kamide, J.A. Slavin. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol. 126 (1986), pp. 345–365
K. Snekvik, E.I. Tanskanen, E.K.J. Kilpua, An automated identification method for Alfvénic streams and their geoeffectiveness. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 5986–5998 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgra.50588
C.P. Sonett, D.S. Colburn, L. Davis, E.J. Smith, P.J. Coleman, Evidence for a collision-free magnetohydrodynamic shock in interplanetary space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 13, 153–156 (1964). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.13.153
P. Subramanian, K.P. Dere, Source regions of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 561, 372–395 (2001). doi:10.1086/323213
E.I. Tanskanen, J.A. Slavin, A.J. Tanskanen, A. Viljanen, T.I. Pulkkinen, H.E.J. Koskinen, A. Pulkkinen, J. Eastwood, Magnetospheric substorms are strongly modulated by interplanetary high-speed streams. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, 16104 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005GL023318
M. Temmer, N.V. Nitta, Interplanetary propagation behavior of the fast coronal mass ejection on 23 July 2012. Sol. Phys. 290, 919–932 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11207-014-0642-3
T. Terasawa, M. Fujimoto, T. Mukai, I. Shinohara, Y. Saito, T. Yamamoto, S. Machida, S. Kokubun, A.J. Lazarus, J.T. Steinberg, R.P. Lepping, Solar wind control of density and temperature in the near-Earth plasma sheet: WIND/GEOTAIL collaboration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 935–938 (1997). doi:10.1029/96GL04018
K. Toman, Identification of M-regions on the Sun. Nature 181, 641–642 (1958). doi:10.1038/181641a0
S. Tomczyk, S.W. McIntosh, Time-distance seismology of the solar corona with CoMP. Astrophys. J. 697, 1384–1391 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/697/2/1384
R. Tousey, The solar corona, in Space Research Conference, ed. by M.J. Rycroft, S.K. Runcorn. Space Research Conference, vol. 2 (1973), pp. 713–730
R.A. Treumann, Fundamentals of collisionless shocks for astrophysical application, 1. Non-relativistic shocks. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 17, 409–535 (2009). doi:10.1007/s00159-009-0024-2
B.T. Tsurutani, W.D. Gonzalez, The cause of high-intensity long-duration continuous AE activity (HILDCAAS)—interplanetary Alfven wave trains. Planet. Space Sci. 35, 405–412 (1987). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(87)90097-3
B.T. Tsurutani, E.J. Smith, W.D. Gonzalez, F. Tang, S.I. Akasofu, Origin of interplanetary southward magnetic fields responsible for major magnetic storms near solar maximum (1978–1979). J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8519–8531 (1988). doi:10.1029/JA093iA08p08519
B.T. Tsurutani, Y.T. Lee, W.D. Gonzalez, F. Tang, Great magnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 73–76 (1992). doi:10.1029/91GL02783
B.T. Tsurutani, W.D. Gonzalez, A.L.C. Gonzalez, F. Tang, J.K. Arballo, M. Okada, Interplanetary origin of geomagnetic activity in the declining phase of the solar cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 21717–21734 (1995). doi:10.1029/95JA01476
B.T. Tsurutani, X.-Y. Zhou, W.D. Gonzalez, A lack of substorm expansion phases during magnetic storms induced by magnetic clouds, in Disturbances in Geospace: The Storm-Substorm Relationship, ed. by A. Surjalal Sharma, Y. Kamide, G.S. Lakhina. Washington DC American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 142 (2003), p. 23. doi:10.1029/142GM03
B.T. Tsurutani, W.D. Gonzalez, X.-Y. Zhou, R.P. Lepping, V. Bothmer, Properties of slow magnetic clouds. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 66, 147–151 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2003.09.007
B.T. Tsurutani, W.D. Gonzalez, A.L.C. Gonzalez, F.L. Guarnieri, N. Gopalswamy, M. Grande, Y. Kamide, Y. Kasahara, G. Lu, I. Mann, R. McPherron, F. Soraas, V. Vasyliunas, Corotating solar wind streams and recurrent geomagnetic activity: a review. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111, 0701 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011273
B.T. Tsurutani, R. Hajra, E. Echer, J.W. Gjerloev, Extremely intense (\(\mbox{SML} \leq- 2500~\mbox{nT}\)) substorms: isolated events that are externally triggered? Ann. Geophys. 33, 519–524 (2015). doi:10.5194/angeo-33-519-2015
L. Turc, D. Fontaine, P. Savoini, R. Modolo, 3D hybrid simulations of the interaction of a magnetic cloud with a bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 6133–6151 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015JA021318
L. Turc, C.P. Escoubet, D. Fontaine, E.K.J. Kilpua, S. Enestam, Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth’s bow shock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 4781–4789 (2016). doi:10.1002/2016GL068818
N.E. Turner, E.J. Mitchell, D.J. Knipp, B.A. Emery, Energetics of magnetic storms driven by corotating interaction regions: a study of geoeffectiveness, in Recurrent Magnetic Storms: Corotating Solar Wind, ed. by R. McPherron, W. Gonzalez, G. Lu, H.A. José, S. Natchimuthukonar Gopalswamy. Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 167 (2006, American Geophysical Union, Washington), p. 113. doi:10.1029/167GM11
N.E. Turner, W.D. Cramer, S.K. Earles, B.A. Emery, Geoefficiency and energy partitioning in CIR-driven and CME-driven storms. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 71, 1023–1031 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2009.02.005
M. Vandas, S. Fischer, M. Dryer, Z. Smith, T. Detman, A. Geranios, MHD simulation of an interaction of a shock wave with a magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 22295–22300 (1997). doi:10.1029/97JA01675
V.M. Vasyliunas, Theoretical models of magnetic field line merging. I. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 13, 303–336 (1975). doi:10.1029/RG013i001p00303
R. von Steiger, Space physics—grand challenges for the 21st century. Front. Phys. 1, 6 (2013). doi:10.3389/fphy.2013.00006
R. von Steiger, T.H. Zurbuchen, A. Kilchenmann, Latitude distribution of interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar maximum, in Solar Wind 11/SOHO 16, Connecting Sun and Heliosphere, ed. by B. Fleck, T.H. Zurbuchen, H. Lacoste. ESA Special Publication, vol. 592 (2005), p. 317
M.-T. Walach, S.E. Milan, Are steady magnetospheric convection events prolonged substorms? J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 1751–1758 (2015). doi:10.1002/2014JA020631
B.M. Walsh, D.G. Sibeck, Y. Wang, D.H. Fairfield, Dawn-dusk asymmetries in the Earth’s magnetosheath. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 117, 12211 (2012). doi:10.1029/2012JA018240
Y.M. Wang, P.Z. Ye, S. Wang, G.P. Zhou, J.X. Wang, A statistical study on the geoeffectiveness of Earth-directed coronal mass ejections from March 1997 to December 2000. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 107, 1340 (2002). doi:10.1029/2002JA009244
Y.M. Wang, P.Z. Ye, S. Wang, Multiple magnetic clouds: several examples during March–April 2001. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1370 (2003). doi:10.1029/2003JA009850
Y.-M. Wang, N.R. Sheeley Jr., N.B. Rich, Coronal pseudostreamers. Astrophys. J. 658, 1340–1348 (2007). doi:10.1086/511416
C. Wang, J.B. Liu, H. Li, Z.H. Huang, J.D. Richardson, J.R. Kan, Geospace magnetic field responses to interplanetary shocks. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114, 05211 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JA013794
Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, J. Liu, C. Shen, F. Shen, Z. Yang, T. Zic, B. Vrsnak, D.F. Webb, R. Liu, S. Wang, J. Zhang, Q. Hu, B. Zhuang, On the propagation of a geoeffective coronal mass ejection during 15–17 March 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 7423–7434 (2016). doi:10.1002/2016JA022924
D.F. Webb, T.A. Howard, Coronal mass ejections: observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 9, 3 (2012). doi:10.1007/lrsp-2012-3. http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2012-3
D.F. Webb, E.W. Cliver, N.U. Crooker, O.C.S. Cry, B.J. Thompson, Relationship of halo coronal mass ejections, magnetic clouds, and magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 7491–7508 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999JA000275
D.F. Webb, C. Möstl, B.V. Jackson, M.M. Bisi, T.A. Howard, T. Mulligan, E.A. Jensen, L.K. Jian, J.A. Davies, C.A. de Koning, Y. Liu, M. Temmer, J.M. Clover, C.J. Farrugia, R.A. Harrison, N. Nitta, D. Odstrcil, S.J. Tappin, H.-S. Yu, Heliospheric imaging of 3D density structures during the multiple coronal mass ejections of late July to early August 2010. Sol. Phys. 285, 317–348 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11207-013-0260-5
R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber, R. von Steiger, R. Paerli, Solar wind stream interfaces in corotating interaction regions: SWICS/Ulysses results. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 17407–17418 (1997). doi:10.1029/97JA00951
R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber, N.U. Crooker, A. Balogh, V. Bothmer, R.J. Forsyth, P. Gazis, J.T. Gosling, T. Horbury, A. Kilchenmann, I.G. Richardson, J.D. Richardson, P. Riley, L. Rodriguez, R.V. Steiger, P. Wurz, T.H. Zurbuchen, Understanding interplanetary coronal mass ejection signatures. Space Sci. Rev. 123, 177–216 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11214-006-9017-x. Report of Working Group B
Y.Q. Xie, P.B. Zuo, X.S. Feng, Y. Zhang, Properties of solar wind dynamic pressure pulses at 1 AU during the deep minimum between solar cycles 23 and 24. Sol. Phys. 290, 1835–1849 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11207-015-0700-5
Y.I. Yermolaev, N.S. Nikolaeva, I.G. Lodkina, M.Y. Yermolaev, Specific interplanetary conditions for CIR-, sheath-, and ICME-induced geomagnetic storms obtained by double superposed epoch analysis. Ann. Geophys. 28, 2177–2186 (2010). doi:10.5194/angeo-28-2177-2010
W. Yu, C.J. Farrugia, N. Lugaz, A.B. Galvin, E.K.J. Kilpua, H. Kucharek, C. Möstl, M. Leitner, R.B. Torbert, K.D.C. Simunac, J.G. Luhmann, A. Szabo, L.B. Wilson, K.W. Ogilvie, J.-A. Sauvaud, A statistical analysis of properties of small transients in the solar wind 2007-2009: STEREO and wind observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 689–708 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JA019115
R. Zelwer, P.C.B. Fernando, S.H. Ward, Interplanetary magnetic field data and corresponding geomagnetic effects for the storm of October 7, 1962. J. Geophys. Res. 72, 3471–3482 (1967). doi:10.1029/JZ072i013p03471
J. Zhang, I.G. Richardson, D.F. Webb, N. Gopalswamy, E. Huttunen, J.C. Kasper, N.V. Nitta, W. Poomvises, B.J. Thompson, C.-C. Wu, S. Yashiro, A.N. Zhukov, Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (\(\mbox{Dst} \leq -100~\mbox{nT}\)) during 1996–2005. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112, 10102 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JA012321
Y. Zhang, W. Sun, X.S. Feng, C.S. Deehr, C.D. Fry, M. Dryer, Statistical analysis of corotating interaction regions and their geoeffectiveness during solar cycle 23. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113, 08106 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008JA013095
H. Zhang, D.G. Sibeck, Q.-G. Zong, N. Omidi, D. Turner, L.B.N. Clausen, Spontaneous hot flow anomalies at quasi-parallel shocks: 1. observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 3357–3363 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgra.50376
J.J. Zhang, C. Wang, T.R. Sun, C.M. Liu, K.R. Wang, GIC due to storm sudden commencement in low-latitude high-voltage power network in China: observation and simulation. Space Weather 13, 643–655 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015SW001263
L. Zhao, T.H. Zurbuchen, L.A. Fisk, Global distribution of the solar wind during solar cycle 23: ACE observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, 14104 (2009). doi:10.1029/2009GL039181
P. Zuo, X. Feng, Y. Xie, Y. Wang, X. Xu, A statistical survey of dynamic pressure pulses in the solar wind based on WIND observations. Astrophys. J. 808, 83 (2015). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/808/1/83
T.H. Zurbuchen, I.G. Richardson, In-situ solar wind and magnetic field signatures of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev. 123, 31–43 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11214-006-9010-4
Acknowledgements
Y. D. Liu was supported by the Recruitment Program of Global Experts of China, NSFC under grant 41374173 and the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories of China. EK acknowledges Academy of Finland project 1267087, UH three-year grant project 490162 and HELCATS project 400931. This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (SolMAG 724391).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Scientific Foundation of Space Weather
Edited by Rudolf von Steiger, Daniel Baker, André Balogh, Tamás Gombosi, Hannu Koskinen and Astrid Veronig
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilpua, E.K.J., Balogh, A., von Steiger, R. et al. Geoeffective Properties of Solar Transients and Stream Interaction Regions. Space Sci Rev 212, 1271–1314 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0411-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0411-3