Abstract
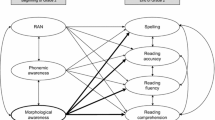
We investigated the effects of morphological awareness on five measures of reading in 103 children from Grades 1 to 3. Morphological awareness was assessed with a word analogy task that included a wide range of morphological transformations. Results indicated that the new measure had satisfactory reliability, and that morphological awareness was a significant predictor of word reading accuracy and speed, pseudoword reading accuracy, text reading speed, and reading comprehension, after controlling the effects of verbal and nonverbal ability and phonological awareness. Morphological awareness also explained variance in reading comprehension after further controlling word reading. We conclude that morphological awareness has important roles in word reading and reading comprehension, and we suggest that it should be included more frequently in assessments and instruction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. J. (1990). Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about print. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Anglin, J. M. (1993). Vocabulary development: A morphological analysis. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 58 (Serial No. 238).
Berko, J. (1958). The child’s learning of English morphology. Word, 14, 150–177.
Bowers, P. N., Kirby, J. R., & Deacon, S. H. (2010). The effects of morphological instruction on literacy skills: A systematic review of the literature. Review of Educational Research, 80, 144–179.
Brittain, M. (1970). Inflectional performance and early reading achievement. Reading Research Quarterly, 6, 34–48.
Carlisle, J. F. (1988). Knowledge of derivational morphology and spelling ability in fourth, sixth, and eighth graders. Applied Psycholinguistics, 9, 247–266.
Carlisle, J. F. (1995). Morphological awareness and early reading achievement. In L. B. Feldman (Ed.), Morphological aspects of language processing (pp. 189–209). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Carlisle, J. F. (2000). Awareness of the structure and meaning of morphologically complex words: Impact on reading. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 12, 169–190.
Carlisle, J. F. (2003). Morphology matters in learning to read: A commentary. Reading Psychology, 24, 291–332.
Carlisle, J. F., & Fleming, J. (2003). Lexical processing of morphologically complex words in the elementary years. Scientific Studies of Reading, 7, 239–254.
Carlisle, J. F., & Nomanbhoy, D. M. (1993). Phonological and morphological awareness in first graders. Applied Psycholinguistics, 14, 177–195.
Carlisle, J. F., & Stone, C. A. (2005). Exploring the role of morphemes in word reading. Reading Research Quarterly, 40, 428–449.
Carlisle, J. F., Stone, C. A., & Katz, L. A. (2001). The effect of phonological transparency on reading derived words. Annals of Dyslexia, 51, 249–274.
Chen, Z., Sanchez, R. P., & Campbell, T. (1997). From beyond to within their grasp: The rudiments of analogical problem solving in 10- and 13-month-olds. Developmental Psychology, 33, 790–801.
Clark, E. (1982). The young word maker: A case study of innovation in the child’s lexicon. In E. Wanner & L. Gleitman (Eds.), Language acquisition: The state of the art (pp. 390–425). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Deacon, S. H., & Kirby, J. R. (2004). Morphological awareness: Just “more phonological”? The roles of morphological and phonological awareness in reading development. Applied Psycholinguistics, 25, 223–238.
Deacon, S. H., Parrila, R., & Kirby, J. R. (2008). A review of the evidence on morphological processing in dyslexics and poor readers: A strength or weakness? In F. Manis, A. Fawcett, G. Reid, & L. Siegel (Eds.), Sage handbook of dyslexia (pp. 212–237). USA: Sage Publications.
Deacon, S. H., Wade-Woolley, L., & Kirby, J. R. (2009). Flexibility in young second-language learners: Examining the language specificity of orthographic processing. Journal of Research in Reading, 32, 215–229.
Dunn, L. M., & Dunn, L. M. (1997). Peabody picture vocabulary test (3rd ed.). Circle Pines, Minnesota: American Guidance Service.
Elbro, C., & Arnbak, E. (1996). The role of morpheme recognition and morphological awareness in dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 46, 209–240.
Empirisoft Corporation. (2002). DirectRT research software (v2002). New York: Empirisoft.
Goswami, U. (1995). Transitive relational mappings in 3- and 4-year-olds: The analogy of Goldilocks and the Three Bears. Child Development, 66, 877–892.
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, reading, and reading disability. Remedial and Special Education, 7, 6–10.
Kemp, N. (2006). Children’s spelling of base, inflected, and derived words: Links with morphological awareness. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 19, 737–765.
Kuo, L., & Anderson, R. C. (2006). Morphological awareness and learning to read: A cross-language perspective. Educational Psychologist, 41, 161–180.
Mahony, D., Singson, M., & Mann, V. (2000). Reading ability and sensitivity to morphological relations. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 12, 191–218.
Nagy, W., Berninger, V. W., & Abbott, R. D. (2006). Contributions of morphology beyond phonology to literacy outcomes of upper elementary and middle-school students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 134–147.
Nunes, T., & Bryant, P. (Eds.). (2006). Improving literacy by teaching morphemes. London: Routledge.
Nunes, T., Bryant, P., & Bindman, M. (1997a). Children’s understanding of the connection between grammar and spelling. In B. Blachman (Ed.), Foundations of reading acquisition and dyslexia: Implications for early intervention (pp. 219–240). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Nunes, T., Bryant, P., & Bindman, M. (1997b). Morphological spelling strategies: Developmental stages and processes. Developmental Psychology, 33, 637–649.
Parrila, R. K., Aunola, K., Leskinen, E., Nurmi, J.-E., & Kirby, J. R. (2005). Development of individual differences in reading: Results from longitudinal studies in English and Finnish. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97, 299–319.
Rabin, J., & Deacon, H. (2008). The representation of morphologically complex words in the developing lexicon. Journal of Child Language, 35, 1–13.
Raven, J. C. (1965). Coloured progressive matrices test. London: Lewis.
Raven, J., Raven, J. C., & Court, J. H. (1998). Manual for raven’s progressive matrices and vocabulary scales. Oxford, England: Psychologists Press.
Roman, A. A., Kirby, J. R., Parrila, R. K., Wade-Woolley, L., & Deacon, S. H. (2009). Toward a comprehensive view of the skills involved in word reading in Grades 4, 6, and 8. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 102, 96–113.
Roth, L., Lai, S., White, B., & Kirby, J. R. (2006). Orthographic and morphological processing as predictors of reading achievement. Poster presented at the annual meeting of the Society for the Scientific Study of Reading, Vancouver, BC.
Shankweiler, D., Crain, S., Katz, L., Fowler, A. E., Liberman, A. E., Brady, S. A., et al. (1995). Cognitive profiles of reading-disabled children: Comparison of language skills in phonology, morphology, and syntax. Psychological Science, 6, 149–156.
Singson, M., Mahony, D., & Mann, V. (2000). The relationship between reading ability and morphological skills: Evidence from derivational suffixes. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 12, 219–253.
Tabachnick, B. C., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (4th ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Torgesen, J. K., Wagner, R. W., & Rashotte, C. A. (1999). Test of word reading efficiency (TOWRE). Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Tyler, A., & Nagy, W. (1989). The acquisition of English derivational morphology. Journal of Memory and Language, 28, 649–667.
Wagner, R. K., Torgesen, J. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (1999). Comprehensive test of phonological processing. Austin, TX: PRO-ED Inc.
Wiederholt, J. K., & Bryant, B. R. (2001). GORT 4—gray oral reading tests. Austin, TX: PRO-ED, Inc.
Woodcock, R. (1998). Woodcock reading mastery tests–revised. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: word analogy items
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirby, J.R., Deacon, S.H., Bowers, P.N. et al. Children’s morphological awareness and reading ability. Read Writ 25, 389–410 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9276-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9276-5