Abstract
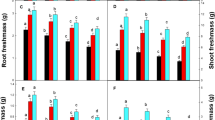
Soil metal contamination leads to a decrease in a yield of crops and is a threat to human health. In the present study, the properties (i.e., photosynthetic pigments, gas-exchange parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence, biomass, leaf area, leaf mass per area) of three green vegetables (i.e., Brassica chinensis, Chrysanthemum coronarium, Brassica alboglabra) grown under various Cu treatments [0, 200, 400, and 600 mg(Cu) kg–1] were measured and analysed. The results showed that soil Cu contamination resulted in the damage of photosynthetic pigments, negative effects on gas exchange, and hampered growth of all three vegetables. However, it did not significantly influence PSII functions of the three vegetables. It indicates that soil Cu contamination negatively affected photosynthesis particularly due to stomatal factors, but not due to the damage of photosynthetic apparatus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABS/RC:
-
absorption
- Car:
-
carotenoids
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- C i :
-
intercellular CO2 concentration
- DFabs :
-
driving forces
- DI0/RC:
-
dissipation at t = 0
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- ET0/RC:
-
electron transport at t = 0
- Fm :
-
maximum Chl fluorescence intensity
- F0 :
-
minimum Chl fluorescence intensity
- Fv/Fm :
-
maximum yield of PSII photochemistry
- gs:
-
stomatal conductance
- HCu:
-
high Cu contamination
- LA:
-
leaf area
- LCu:
-
low Cu contamination
- LMA:
-
leaf mass per area
- MCu:
-
middle Cu contamination
- OEC:
-
oxygen-evolving complex
- PIabs :
-
photosynthetic performance index
- P N :
-
net photosynthetic rate
- QA :
-
primary bound plastoquinone
- QB :
-
secondary bound plastoquinone
- RC:
-
reaction center
- TR0/RC:
-
energy flux for trapping at t = 0
- φE0 :
-
probability that an absorbed photon will move an electron into the electron transport chain
- φP0 :
-
maximum quantum yield of primary photochemistry
- ΨE0 :
-
efficiency with which a trapped exciton can move an electron into the electron transport chain
References
Appenroth K.J., Stöckel J., Srivastava A. et al.: Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spirodela polyrhiza as probed by OJIP Chl a fluorescence measurements.–Environ. Pollut. 115: 49–64, 2001.
Arnon I.D.: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris.–Plant Physiol. 24: 1–15, 1949.
Capsi V., Droppa M., Horváth G. et al.: The effect of copper on Chl organization during greening of barley leaves.–Photosynth. Res. 62: 165–174, 1999.
Chen C.T., Chen L.M., Lin C.C. et al.: Regulation of proline accumulation in detached rice leaves exposed to excess copper.–Plant Sci. 160: 283–290, 2001.
Chen H.Y., Teng Y.G., Lu S.J. et al.: Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China.–Sci. Total Environ. 512: 143–153, 2015.
da Costa M.V.J., Sharma P.K.: Effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on growth, morphology, photosynthesis, and antioxidant response in Oryza sativa.–Photosynthetica 54: 110–119, 2016.
Fu W.G., Wang F.K.: Effects of high soil lead concentration on photosynthetic gas exchange and Chl fluorescence in Brassica chinensis L.–Plant Soil Environ. 61: 316–321, 2015.
Guo R.F., Huang Z.K., Deng Y.P. et al.: Comparative transcriptome analyses reveal a special glucosinolate metabolism mechanism in Brassica alboglabra sprouts.–Front Plant Sci. 7: 1497, 2016.
Huang J.G.: [Trace elements nutrition and plant fertilizer.]–In: Huang J.G. (ed.): [Plant Nutrition.] Pp. 187–239. China Forestry Press, Beijing 2004. [In Chinese]
Kopsell D.A., Kopsell D.E., Lefsrud M.G.: Pre-harvest cultural growing conditions can influence carotenoid phytochemical concentrations in vegetable crops.–Acta Hortic. 841: 283–294, 2007.
Krupa Z., Skorzynska E., Maksymiec W. et al.: Effect of cadmium treatment on the photosynthetic apparatus and its photochemical activities in greening radish seedlings.–Photosynthetica 21: 156–164, 1988.
Lichtenthaler H.K., Wellburn A.R.: Determinations of total carotenoids and Chl a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents.–Biochem. Soc. T. 11: 591–592, 1983.
Lin M.Z., Lin N.W., Qiu X.F. et al.: [Wedelia trilobata's response to heavy metals and heavy metal absorption and enrichment in its body with sludge as a part of growth substrate.]–J. Anhui Agr. U. 39: 286–291, 2012a. [In Chinese]
Lin M.Z., Qiu X.F., Lin N.W. et al.: [Response of Alternanthera philoxeroides to heavy metals and its sorption effectiveness for heavy metals.]–Pratacult. Sci. 29: 681–686, 2012b. [In Chinese]
Lin M.Z., Wang Z.W., He L.C. et al.: Plant photosynthesisirradiance curve responses to pollution show non-competitive inhibited Michaelis kinetics.–PLoS ONE 10: e142712, 2015.
Lü C., Ren H., Zhang Y. et al.: Leaf area measurement based on image processing.–In: Lisa O. (ed.): 2010 International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation. Pp. 580–582. IEEE Changsha 2010.
Lykholat Y., Alekseeva A., Khromykh N. et al.: Assesssment and prediction of viability and metabolic activity of Tilia platyphyllos in arid steppe climate of Ukraine.–Agricult. Forestry 62: 57–66, 2016.
Meng L.L., Song J.F., Wen J. et al.: Effects of drought stress on fluorescence characteristics of photosystem II in leaves of Plectranthus scutellarioides.–Photosynthetica 54: 414–421, 2016.
Meng X.H., Zhang J.B., Li P. et al.: [Summary of livestock environmental pollution and environmental management policies.]–J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 30: 1–8, 2014. [In Chinese]
Mishra G., Zhang W., Deng F. et al.: A bifurcating pathway directs abscisic acid effects on stomatal closure and opening in Arabidopsis.–Science 312: 264–266, 2006.
Moussaoui F., Alaoui T.: Evaluation of antibacterial activity and synergistic effect between antibiotic and the essential oils of some medicinal plants.–Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 6: 32–37, 2016.
Planquart P., Bonin G., Prone A. et al.: Distribution, movement and plant availability of trace metals in soils amended with sewage sludge composts: application to low metal loadings.–Sci. Total Environ. 241: 161–179, 1999.
Rai R., Agrawal M., Agrawal S.B.: Impact of heavy metals on physiological processes of plants: with special reference to photosynthetic system.–In: Singh A, Prasad S.M., Singh R.P. (ed.): Plant Responses to Xenobiotics. Pp. 127–140. Springer, Singapore 2016.
Razinger J., Dermastia M., Drinovec L. et al.: Antioxidative responses of duckweed (Lemna minor L.) to short-term copper exposure.–Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 14: 194–201, 2007.
Razinger J., Drinovec L., Zrimec A.: Real-time visualization of oxidative stress in a floating macrophyte Lemna minor L. exposed to cadmium, copper, menadione, and AAPH.–Environ. Toxicol. 25: 573–580, 2010.
Razinger J., Drinovec L., Berden-Zrimec M.: Delayed fluorescence imaging of photosynthesis inhibitor and heavy metal induced stress in potato.–Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 7: 531–541, 2012.
Sánchez Vilas J., Campoy J.G., Retuerto R.: Sex and heavy metals: Study of sexual dimorphism in response to soil pollution.–Environ. Exp. Bot. 126: 68–75, 2016.
Shi H.P., Zhu Y.F., Wang Y.L. et al.: Effect of cadmium on cytogenetic toxicity in hairy roots of Wedelia trilobata L. and their alleviation by exogenous CaCl2.–Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 21: 1436–1443, 2014.
Song X., Li H.: Effects of building shade on photosynthesis and Chl fluorescence of Euonymus fortunei.–Acta Ecol. Sin. 36: 350–355, 2016.
Stolpe C., Krämer U., Müller C.: Heavy metal (hyper) accumulation in leaves of Arabidopsis halleri is accompanied by a reduced performance of herbivores and shifts in leaf glucosinolate and element concentrations.–Environ. Exp. Bot. 133: 78–86, 2017.
Strasser R.J., Srivastava A., Tsimilli-Michael M.: The fluorescence transient as a tool to characterize and screen photosynthetic samples.–In: Yunus M., Pathre U., Mohanty P. (ed.): Probing Photosynthesis: Mechanism, Regulation & Adaptation. Pp. 445–483. CRC Press, Boca Raton 2000.
Susplugas S., Srivastava A., Strasser R.J.: Changes in the photosynthetic activities during several stages of vegetative growth of Spirodela polyrhiza: effect of chromate.–J. Plant Physiol. 157: 503–512, 2000.
Tang X., Li X., Liu X. et al.: Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the uptake of lead and trace elements by Brassica chinensis grown in an acidic red soil.–Chemosphere 119: 177–183, 2015.
Vinit-Dunand F., Epron D., Alaoui-Sossé B. et al.: Effects of copper on growth and on photosynthesis of mature and expanding leaves in cucumber plants.–Plant Sci. 163: 53–58, 2002.
Wang S.G.: Copper.–In: Wang S.G. (ed.): [Trace Elements and Physical Health.] Pp. 97–118. Shanghai Popular Sci. Press, Shanghai 2004. [In Chinese]
Wilson A., Ajlani G., Verbavatz J.M. et al.: A soluble carotenoid protein involved in phycobilisome-related energy dissipation in Cyanobacteria.–Plant Cell 18: 992–1007, 2006.
Xia J.R., Tian Q.R.: Early stage toxicity of excess copper to photosystem II of Chlorella pyrenoidosa–OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence analysis.–J. Environ. Sci. 21: 1569–1574, 2009.
Xu J., Yang L., Wang Z. et al.: Toxicity of copper on rice growth and accumulation of copper in rice grain in copper contaminated soil.–Chemosphere 62: 602–607, 2006.
Zeng X.B., Li L.F., Mei X.R.: [Heavy metal content in soils of vegetable-growing lands in China and source analysis.]–Sci. Agricult. Sin. 40: 2507–2517, 2007. [In Chinese]
Zupančič N.: Influence of climate factors on soil heavy metal content in Slovenia.–J. Soil Sediments 17: 1073–1083, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: We thank three anonymous reviewers and the associate editor for their constructive comments that improved this manuscript. This study was partly supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (31370589) and the Open Project Program of Provincial Key Laboratory of Eco-Industrial Green Technology, Wuyi University. We would like to thank L.-R. Lin, A.-L. Liu, and L.-Y. Zhu, Fuqing Branch of Fujian Normal University, for their help in experiment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, MZ., Jin, MF. Soil Cu contamination destroys the photosynthetic systems and hampers the growth of green vegetables. Photosynthetica 56, 1336–1345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0831-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0831-7