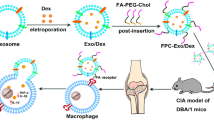
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this research was to design dexamethasone palmitate (DP) loaded sialic acid modified liposomes, with the eventual goal of using peripheral blood neutrophils (PBNs) that carried drug-loaded liposomes to improve the therapeutic capacity for rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
A sialic acid – cholesterol conjugate (SA-CH) was synthesized and anchored on the surface of liposomal dexamethasone palmitate (DP-SAL). The physicochemical characteristics and in vitro cytotoxicity of liposomes were evaluated. Flow cytometry and confocal laser scanning microscopy were utilized to investigate the accumulation of liposomes in PBNs. The adjuvant-induced arthritis was adopted to investigate the targeting ability and anti-inflammatory effect of DP loaded liposomes.
Results
Both DP-CL and DP-SAL existed an average size less than 200 nm with remarkably high encapsulation efficiencies more than 90%. In vitro and in vivo experiments manifested SA-modified liposomes provided a reinforced accumulation of DP in PBNs. As well, DP-SAL displayed a greater degree of accumulation in the joints and a stronger anti-inflammatory effect in terms of RA suppression.
Conclusions
SA-modified liposomal DP was a promising candidate for RA-targeting treatment through the neutrophil-mediated drug delivery system.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCK8:
-
Cell Counting Kit-8
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
- DiR:
-
1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindotricarbocyanine iodide
- DP:
-
Dexamethasone palmitate
- EDC:
-
N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
- FCM:
-
Flow cytometry
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- HSPC:
-
Hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine
- NHS:
-
N-hydroxy-succinimide
- PBNs:
-
Peripheral blood neutrophils
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- SA-CH:
-
A sialic acid-cholesterol conjugate
- TNF:
-
Tumor-necrosis factor
References
Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61.
Bax M, Heemst JV, Huizinga TWJ, Toes REM. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Immunogenetics. 2011;63:459–66.
Kourilovitch M, Galarza-Maldonado C, Ortiz-Prado E. Diagnosis and classification of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:26–30.
Scottand DL, Kingsley GH. Rheumatoid arthritis. Die Med Welt. 1975;26:2250–5.
Smolenand JS, Steiner G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:473–88.
Yang MD, Feng XR, Ding JX, Chang F, Chen XS. Nanotherapeutics relieve rheumatoid arthritis. J Control Release. 2017;252:108–24.
IBand M. S. G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–42.
B.T. Wipkeand P.M. Allen. Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 167:(2001).
Wright HL, Moots RJ, Bucknall RC, Edwards SW. Neutrophil function in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Rheumatology. 2010;49:1618–31.
Powelland DR, Huttenlocher A. Neutrophils in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:41–52.
Kruger P, Saffarzadeh M, Weber ANR, Rieber N, Radsak M, von Bernuth H, et al. Neutrophils: between host Defence, immune modulation, and tissue injury. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11.
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, Jaillon S. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:519–31.
Chu DF, Gao J, Wang ZJ. Neutrophil-mediated delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles across blood vessel barrier for treatment of inflammation and infection. ACS Nano. 2015;9:11800–11.
Engblom C, Pfirschke C, Zilionis R, Martins JD, Bos SA, Courties G, et al. Osteoblasts remotely supply lung tumors with cancer-promoting SiglecF(high) neutrophils. Science. 2017;358:eaal5081.
Su YX, Xie ZW, Kim GB, Dong C, Yang J. Design strategies and applications of circulating cell-mediated drug delivery systems. Acs Biomateri Sci Eng. 2015;1:201–17.
Fu JJ, Wang D, Mei D, Zhang HR, Wang ZY, He B, et al. Macrophage mediated biomimetic delivery system for the treatment of lung metastasis of breast cancer. J Control Release. 2015;204:11–9.
Raffler NA, Rivera-Nieves J, Ley K. L -selectin in inflammation, infection and immunity. Drug Discovery Today Therapeutic Strategies. 2005;2:213–20.
Smolen JE, Petersen TK, Koch C, O'Keefe SJ, Hanlon WA, Seo S, et al. L-selectin signaling of neutrophil adhesion and degranulation involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:–15876, 15884.
Coussensand LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Zhang T, She Z, Huang Z, Li J, Luo X, Deng Y. Application of sialic acid/polysialic acid in the drug delivery systems. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2014;9:75–81.
Smoakand KA, Cidlowski JA. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid receptor signaling during inflammation. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004;125:697–706.
Allenand TM, Cullis PR. Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65:36–48.
Ozbakir B, Crielaard BJ, Metselaar JM, Storm G, Lammers T. Liposomal corticosteroids for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer. J Control Release. 2014;190:624–36.
Wang Q, Jiang J, Chen W, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Sun X. Targeted delivery of low-dose dexamethasone using PCL-PEG micelles for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Control Release. 2016;230:64–72.
Zhang X, Goncalves R, Mosser DM. The Isolation and Characterization of Murine Macrophages. In: The isolation and characterization of murine macrophages: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2008.
Zhou S, Zhang T, Peng B, Luo X, Liu X, Hu L, et al. Targeted delivery of epirubicin to tumor-associated macrophages by sialic acid-cholesterol conjugate modified liposomes with improved antitumor activity. Int J Pharm. 2017;523:203–16.
Sun J, Song Y, Lu M, Lin X, Liu Y, Zhou S, et al. Evaluation of the antitumor effect of dexamethasone palmitate and doxorubicin co-loaded liposomes modified with a sialic acid-octadecylamine conjugate. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016;93:177–83.
Anderson R, Franch A, Castell M, Perez-Cano FJ, Bräuer R, Pohlers D, et al. Liposomal encapsulation enhances and prolongs the anti-inflammatory effects of water-soluble dexamethasone phosphate in experimental adjuvant arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R147.
Drummond DC, Meyer O, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, Papahadjopoulos D. Optimizing liposomes for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to solid tumors. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:691.
Ireneand C, Giuseppe B. Endocytosis at the nanoscale. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:2718–39.
Von Andrian UH, Hansell P, Chambers JD, Berger EM, Torres FI, Butcher EC, et al. L-selectin function is required for beta 2-integrin-mediated neutrophil adhesion at physiological shear rates in vivo. Am J Phys. 1992;263:1034–44.
Schleiffenbaum B, Spertini O, Tedder TF. Soluble L-selectin is present in human plasma at high levels and retains functional activity. J Cell Biol. 1992;119:229–38.
Kallinteri P, Antimisiaris SG, Karnabatidis D, Kalogeropoulou C, Tsota I, Siablis D. Dexamethasone incorporating liposomes: an in vitro study of their applicability as a slow releasing delivery system of dexamethasone from covered metallic stents. Biomaterials. 2002;23:4819–26.
Choi SH, Byeon HJ, Choi JS, Thao L, Kim I, Lee ES, et al. Inhalable self-assembled albumin nanoparticles for treating drug-resistant lung cancer. J Control Release. 2015;197:199–207.
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: theory to practice. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:283–318.
Yuan F, Quan LD, Cui L, Goldring SR, Wang D. Development of macromolecular prodrug for rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1205–19.
Kolaczkowskaand E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:159–75.
Pham CTN. Nanotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnology. 2011;3:607–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Luo, X., Zhou, S. et al. Neutrophil-Mediated Delivery of Dexamethasone Palmitate-Loaded Liposomes Decorated with a Sialic Acid Conjugate for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Pharm Res 36, 97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2609-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2609-4