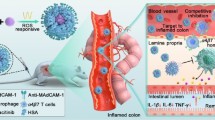
Abstract
Background
Tofacitinib (Tofa) has been approved for moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC). To improve its therapeutic efficacy and limit dose-dependent toxicity, we developed a macromolecular prodrug of Tofa (P-Tofa). If the prodrug design improves the potency and duration of Tofa therapy, it would widen its therapeutic window, potentially leading to improved safety and better clinical management of UC.
Methods
P-Tofa was synthesized by conjugating Tofa to N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymer via a cleavable carbamate linker. DSS-induced UC mouse model were treated with Tofa (daily oral gavage, from day 8), P-Tofa (single intravenous administration on day 8, dose equivalent to Tofa treatment) and saline. Healthy mice were used as a positive control. The therapeutic efficacy was evaluated using disease activity index (DAI), endoscopic score and end-point histology. The optical imaging, immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry were used to understand P-Tofa’s working mechanism.
Results
DAI results suggested that a single dose P-Tofa treatment was more efficacious than dose equivalent daily Tofa treatment. Endoscopic evaluation and histology analyses confirmed that while both P-Tofa and Tofa protected the colon, P-Tofa treated group was observed with better colon integrity with less tissue damage. Optical imaging, flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry results showed that P-Tofa passively targeted the inflamed colon and being retained via cellular sequestration.
Conclusions
Single intravenous administration of P-Tofa was more effective than dose equivalent daily oral Tofa gavage in ameliorating DSS-induced colitis. This observed superior therapeutic efficacy may be attributed to P-Tofa’s passive targeting to and retention by the inflamed colon.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Høivik ML, Moum B, Solberg IC, Henriksen M, Cvancarova M, Bernklev T, et al. Work disability in inflammatory bowel disease patients 10 years after disease onset: results from the IBSEN study. Gut. 2013;62(3):368–75.
Molodecky, N.A., et al., Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology, 2012. 142(1): p. 46–54. e42.
Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769–78.
Loftus EV Jr. Update on the incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;12(11):704–7.
Cohen R, et al. Systematic review: the costs of ulcerative colitis in Western countries. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31(7):693–707.
Danese S. New therapies for inflammatory bowel disease: from the bench to the bedside. Gut. 2012;61(6):918–32.
De Vries, L., et al., The Future of Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis, 2017: p. jjx003.
Friedman, S., Tofacitinib for Ulcerative Colitis—A Promising Step Forward. 2017, Mass Medical Soc.
Tanaka Y. Recent progress and perspective in JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis: from bench to bedside. The Journal of Biochemistry. 2015;158(3):173–9.
Wei X, Wu J, Zhao G, Galdamez J, Lele SM, Wang X, et al. Development of a Janus kinase inhibitor prodrug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(8):3456–67.
Liu X-M, Quan LD, Tian J, Alnouti Y, Fu K, Thiele GM, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a well-defined HPMA copolymer–dexamethasone conjugate for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm Res. 2008;25(12):2910–9.
Chassaing, B., et al., Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Current protocols in immunology, 2014: p. 15.25. 1–15.25. 14.
De Vries, L., et al. The Efficacy of Tofacitinib and a Selective Janus Kinase 1 Inhibitor in Dextran Sulphate Sodium Colitis Models. in JOURNAL OF CROHNS & COLITIS. 2016. OXFORD UNIV PRESS GREAT CLARENDON ST, OXFORD OX2 6DP, ENGLAND.
Cooper, H.S., et al., Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology, 1993. 69(2): p. 238–249.
Rumi G, et al. Dual role of endogenous nitric oxide in development of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in rats. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology: an Official Journal of the Polish Physiological Society. 2004;55(4):823–36.
Becker C, Fantini MC, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Kiesslich R, Lehr HA, et al. In vivo imaging of colitis and colon cancer development in mice using high resolution chromoendoscopy. Gut. 2005;54(7):950–4.
Moolenbeek C, Ruitenberg E. The ‘Swiss roll’: a simple technique for histological studies of the rodent intestine. Lab Anim. 1981;15(1):57–60.
Kim, C., et al., L-cysteine supplementation attenuates local inflammation and restores gut homeostasis in a porcine model of colitis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2009. 1790(10): p. 1161–1169.
Rieder F, Fiocchi C. Intestinal fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease—current knowledge and future perspectives. J Crohn's Colitis. 2008;2(4):279–90.
Pierezan F, Mansell J, Ambrus A, Hoffmann AR. Immunohistochemical expression of ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 in cutaneous histiocytic proliferative, neoplastic and inflammatory disorders of dogs and cats. J Comp Pathol. 2014;151(4):347–51.
Fuss IJ, Heller F, Boirivant M, Leon F, Yoshida M, Fichtner-Feigl S, et al. Nonclassical CD1d-restricted NK T cells that produce IL-13 characterize an atypical Th2 response in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(10):1490–7.
Heller F, Florian P, Bojarski C, Richter J, Christ M, Hillenbrand B, et al. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology. 2005;129(2):550–64.
Sandborn WJ, Ghosh S, Panes J, Vranic I, Su C, Rousell S, et al. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in active ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(7):616–24.
Sandborn WJ, Su C, Sands BE, D'Haens GR, Vermeire S, Schreiber S, et al. OCTAVE Induction 1, OCTAVE Induction 2, and OCTAVE Sustain Investigators., Tofacitinib as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(18):1723–36.
Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011;474(7351):298–306.
Yuan F, Quan LD, Cui L, Goldring SR, Wang D. Development of macromolecular prodrug for rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1205–19.
Wang D, Miller SC, Liu XM, Anderson B, Wang XS, Goldring SR. Novel dexamethasone-HPMA copolymer conjugate and its potential application in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis research & therapy. 2007;9(1):R2.
Wei X, Li F, Zhao G, Chhonker YS, Averill C, Galdamez J, et al. Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies of HPMA copolymer conjugates in an aseptic implant loosening mouse model. Mol Pharm. 2017;14(5):1418–28.
Yuan F, Nelson RK, Tabor DE, Zhang Y, Akhter MP, Gould KA, et al. Dexamethasone prodrug treatment prevents nephritis in lupus-prone (NZB× NZW) F1 mice without causing systemic side effects. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(12):4029–39.
Ren K, Yuan H, Zhang Y, Wei X, Wang D. Macromolecular glucocorticoid prodrug improves the treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice ulcerative colitis. Clin Immunol. 2015;160(1):71–81.
Bronte V, Pittet MJ. The spleen in local and systemic regulation of immunity. Immunity. 2013;39(5):806–18.
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Etzrodt M, Wildgruber M, Cortez-Retamozo V, Panizzi P, et al. Identification of splenic reservoir monocytes and their deployment to inflammatory sites. Science. 2009;325(5940):612–6.
Gäbele E, Dostert K, Hofmann C, Wiest R, Schölmerich J, Hellerbrand C, et al. DSS induced colitis increases portal LPS levels and enhances hepatic inflammation and fibrogenesis in experimental NASH. J Hepatol. 2011;55(6):1391–9.
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R. A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 1990;98(3):694–702.
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, Depew WT, Szewczuk MR, Wallace JL. Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology. 1989;96(2):795–803.
Boirivant M, Fuss IJ, Chu A, Strober W. Oxazolone colitis: a murine model of T helper cell type 2 colitis treatable with antibodies to interleukin 4. J Exp Med. 1998;188(10):1929–39.
Low, D., D.D. Nguyen, and E. Mizoguchi, Animal models of ulcerative colitis and their application in drug research. Drug design, development and therapy, 2013. 7: p. 1341.
Garrett WS, Lord GM, Punit S, Lugo-Villarino G, Mazmanian SK, Ito S, et al. Communicable ulcerative colitis induced by T-bet deficiency in the innate immune system. Cell. 2007;131(1):33–45.
Yang J, Zhang R, Radford DC, Kopeček J. FRET-trackable biodegradable HPMA copolymer-epirubicin conjugates for ovarian carcinoma therapy. J Control Release. 2015;218:36–44.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND DISCLOSURES
This study was supported in part by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (R01 AI119090) of the National Institute of Health of the United States of America, and China Scholarship Council (XW, GZ, FZ). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Wei, X., Wu, J. et al. A Macromolecular Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor Prodrug Effectively Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Pharm Res 36, 64 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2587-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2587-6