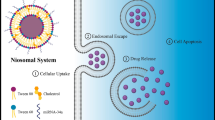
Abstract
Purpose
In this study, miR-542-3p appended SRF/ATRA-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle was successfully prepared and demonstrated for its therapeutic efficacy against gastric cancers.
Methods
The particles were nanosized and typically spherical in shape. In vitro release study showed that release of ATRA was significantly slower compared to that of SRF from the NPs.
Results
MTT assay showed that miR-542-3p have a strong inhibitory effect on the proliferation of MGC-803 cancer cells in a typical dose dependent manner. Nanocarrier encapsulation of SRF + ATRA induced a significantly higher cytotoxic effect compared to either individual drug or cocktail combinations indicating that the cellular uptake of different formulations was rate limiting factor in the therapeutic efficacy. Importantly, miR-542-3p-based miSRNP exhibited an extremely significant toxic effect compared to any other treated group. Importantly, miSRNP induced a significantly higher early (~55%) and late (~15%) apoptotic effect in gastric cancer cells. In vivo anticancer analysis results clearly suggest that nanoparticle encapsulation of combination of SRF and miRNA (with miRNA) will have greater antitumor efficacy in tumor mice.
Conclusion
Overall, unique combination of miRNA coupled with SRF + ATRA in a lipid nanocarrier could be a promising therapeutic approach in gastric cancer treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEG-1:
-
Astrocyte-elevated gene-1
- ATRA:
-
All-trans retinoic acid
- EPR:
-
Enhanced permeation and retention
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- SRF:
-
Sorafenib
- SLN:
-
Solid lipid nanoparticles
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics for Hispanics/Latinos. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Oh SC. Update of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected gastric cancer. J Gastric Cancer. 2012;12:3–6.
Schwarz RE, Smith DD. Clinical impact of lymphadenectomy extent in resectable gastric cancer of advanced stage. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:317–28.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Schwarz RE, Zagala-Nevarez K. Recurrence patterns after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: prognostic factors and implications for postoperative adjuvant therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:394–400.
Cappetta A, Lonardi S, Pastorelli D, Bergamo F, Lombardi G, Zagonel V. Advanced gastric cancer (GC) and cancer of the gastro-oesophageal junction (GEJ): focus on targeted therapies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012;81:38–48.
Kim do H, Kim MD, Choi CW, Chung CW, Ha SH, Kim CH, et al. Antitumor activity of sorafenib-incorporated nanoparticles of dextran/poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) block copolymer. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012;7:91.
Yang YC, Cai J, Yin J, Zhang J, Wang KL, Zhang ZT. Heparin-functionalized Pluronic nanoparticles to enhance the antitumor efficacy of sorafenib in gastric cancers. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;136:782–90.
Poojari R, Kini S, Srivastava R, Panda D. Intracellular interactions of electrostatically mediated layer-by-layer assembled polyelectrolytes based sorafenib nanoparticles in oral cancer cells. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2016;143:131–8.
Thapa RK, Choi JY, Poudel BK, Hiep TT, Pathak S, Gupta B, et al. Multilayer-coated liquid crystalline nanoparticles for effective Sorafenib delivery to hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:20360–8.
Gao DY, TsT L, Sung YC, Liu YC, Chiang WH, Chang CC, et al. CXCR4-targeted lipid-coated PLGA nanoparticles deliver sorafenib and overcome acquired drug resistance in liver cancer. Biomaterials. 2015;67:194–203.
Maden M. Retinoic acid in the development, regeneration and maintenance of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:755–65.
Shimizu K, Tamagawa K, Takahashi N, Takayama K, Maitani Y. Stability and antitumor effects of all-trans retinoic acid-loaded liposomes contained sterylglucoside mixture. Int J Pharm. 2003;258:45.
Tang XH, Gudas LJ. Retinoids, retinoic acid receptors, and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:345.
Carneiro G, Silva EL, Pacheco LA, de Souza-Fagundes EM, Corrêa NCR, de Goes AM, et al. Formation of ion pairing as an alternative to improve encapsulation and anticancer activity of all-trans retinoic acid loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:6011.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Mendell JT, Olson EN. MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 2012;148:1172–87.
Zimmerman AL, Wu S. MicroRNAs, cancer and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2011;300:10–9.
Wong HL, Bendayan R, Rauth AM, Wu XY. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles containing ionically complexed chemotherapeutic drugs and chemosensitizers. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:1993–2008.
Wong HL, Bendayan R, Rauth AM, Li Y, Wu XY. Chemotherapy with anticancer drugs encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:491–504.
Mody N, Tekade RK, Mehra NK, Chopdey P, Jain NK. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014;15:388.
Subedi RK, Kang KW, Choi HK. Preparation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2009;37:508.
Ramasamy T, Khandasami US, Ruttala H, Shanmugam S. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles enriched hydrogels for topical delivery of anti-fungal agent. Macromol Res. 2012;20:682–92.
Kataoka K, Harada A, Nagasaki Y. Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: design, characterization and biological significance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47:113–31.
Mishra S, Webster P, Davis ME. PEGylation significantly affects cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of non-viral gene delivery particles. Eur J Cell Biol. 2004;83:97–111.
Ramasamy T, Tran TH, Choi JY, Cho HJ, Kim JH, Yong CS, et al. Layer-by-layer coated lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles designed for use in anticancer drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;102:653–61.
Jain A, Thakur D, Ghoshal G, Katare OP, Shivhare US. Characterization of microcapsulated -carotene formed by complex coacervation using casein and gum tragacanth. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;87:101–13.
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:228–34.
Ramasamy T, Ruttala HB, Kanu BG, Poudel BK, Choi HG, Yong CS, et al. Smart chemistry-based nanosized drug delivery systems for systemic applications: a comprehensive review. J Control Release. 2017; doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.04.043.
Gupta B, Ramasamy T, Poudel BK, et al. Development of bioactive PEGylated nanostructured platforms for sequential delivery of doxorubicin and imatinib to overcome drug resistance in metastatic tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(11):9280–90.
Ramasamy T, Ruttala HB, Chitrapriya N, et al. Engineering of cell microenvironment-responsive polypeptide nanovehicle co-encapsulating a synergistic combination of small molecules for effective chemotherapy in solid tumors. Acta Biomater. 2017;48:131–43.
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
The work is funded from the research grant of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Zhang, Y., Meng, YP. et al. miR-542-3p Appended Sorafenib/All-trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA)-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles to Enhance the Anticancer Efficacy in Gastric Cancers. Pharm Res 34, 2710–2719 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-017-2202-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-017-2202-7