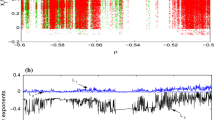
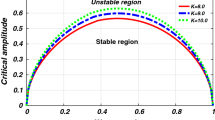
Abstract
In this paper, a small Hopfield neural network with three neurons is studied, in which one of the three neurons is considered to be exposed to electromagnetic radiation. The effect of electromagnetic radiation is modeled and considered as magnetic flux across membrane of the neuron, which contributes to the formation of membrane potential, and a feedback with a memristive type is used to describe coupling between magnetic flux and membrane potential. With the electromagnetic radiation being considered, the previous steady neural network can present abundant chaotic dynamics. It is found that hidden attractors can be observed in the neural network under different conditions. Moreover, periodic motion and chaotic motion appear intermittently with variations in some system parameters. Particularly, coexistence of periodic attractor, quasiperiodic attractor, and chaotic strange attractor, coexistence of bifurcation modes and transient chaos can be observed. In addition, an electric circuit of the neural network is implemented in Pspice, and the experimental results agree well with the numerical ones.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hopfield, J.J.: Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81, 3088 (1984)
Korn, H., Faure, P.: Is there chaos in the brain? II. Experimental evidence and related models. C. R. Biol. 326, 787–840 (2003)
Axmacher, N., Mormann, F., Fernandez, G., et al.: Memory formation by neuronal synchronization. Brain Res. Rev. 52, 170–182 (2006)
Wang, Z., Fan, H.: Memory retrieval in a neural network with chaotic neurons and dynamic synapses. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 3512, 654–660 (2005)
Babloyantz, A.: Brain chaos and computation. Int. J. Neural Syst. 7, 461–471 (1996)
Guevara, M.R., Glass, L., Mackey, M.C., et al.: Chaos in neurobiology. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. SMC–13, 790–798 (1983)
Yang, X.-S., Yuan, Q.: Chaos and transient chaos in simple Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 69, 232–241 (2005)
Dror, G., Tsodyks, M.: Chaos in neural networks with dynamic synapses. Neurocomputing 32–33, 365–370 (2000)
Huang, W.-Z., Huang, Y.: Chaos of a new class of Hopfield neural networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 206, 1–11 (2008)
Yang, X.S., Huang, Y.: Complex dynamics in simple Hopfield neural networks. Chaos 16, 033114 (2006)
Huang, Y., Yang, X.-S.: Hyperchaos and bifurcation in a new class of four-dimensional Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 69, 1787–1795 (2006)
Li, Q., Yang, X.-S., Yang, F.: Hyperchaos in Hopfield-type neural networks. Neurocomputing 67, 275–280 (2005)
Mestl, T., Lemay, C., Glass, L.: Chaos in high-dimensional neural and gene networks. Physica D 98, 33–52 (1996)
de Jess Rubio, J.: Stable Kalman filter and neural network for the chaotic systems identification. J. Frankl. Inst. (2017) (Europhys. Lett.) 83, 50008 (2008)
Rubio, J.D.J.: USNFIS: uniform stable neuro fuzzy inference system. Neurocomputing 262, 57–66 (2017)
Wang, Q., Chen, G., Perc, M.: Synchronous bursts on scale-free neuronal networks with attractive and repulsive coupling. PLoS ONE 6, e15851 (2011)
Wang, Q., Duan, Z., Perc, M., et al.: Synchronization transitions on small-world neuronal networks: Effects of information transmission delay and rewiring probability. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 83, 50008 (2008)
Bogaard, A., Parent, J., Zochowski, M., et al.: Interaction of cellular and network mechanisms in spatiotemporal pattern formation in neuronal networks. J. Neurosci. (The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience) 29, 1677–1687 (2009)
Lindner, B.: Effects of noise in excitable systems. Phys. Rep. 392, 321–424 (2004)
Gong, Y., Xie, Y., Lin, X., et al.: Non-Gaussian noise-optimized intracellular cytosolic calcium oscillations. Biosystems 103, 13–17 (2011)
Wang, Q., Perc, M., Duan, Z., et al.: Synchronization transitions on scale-free neuronal networks due to finite information transmission delays. Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 80, 026206 (2009)
Song, X., Wang, C., Ma, J., et al.: Transition of electric activity of neurons induced by chemical and electric autapses. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 1007–1014 (2015)
Wang, H., Wang, L., Chen, Y., et al.: Effect of autaptic activity on the response of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Chaos 24, 033122 (2014)
Wang, H., Ma, J., Chen, Y., et al.: Effect of an autapse on the firing pattern transition in a bursting neuron. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 3242–3254 (2014)
Dhamala, M., Jirsa, V.K., Ding, M.: Enhancement of neural synchrony by time delay. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 074104 (2004)
Li, J., Liu, S., Liu, W., et al.: Suppression of firing activities in neuron and neurons of network induced by electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 83, 801–810 (2015)
Robertson, J.A., Thberge, J., Weller, J., et al.: Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field exposure can alter neuroprocessing in humans. J. R. Soc. Interface 7, 467–473 (2010)
Wang, H., Chen, Y.: Spatiotemporal activities of neural network exposed to external electric fields. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 881–891 (2016)
Chua, L., Sbitnev, V., Kim, H.: HodgkinHuxley axon is made of memristors. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 22, 1230011 (2012)
Sah, M.P., Kim, H., Eroglu, A., et al.: Memristive model of the barnacle giant muscle fibers. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 26, 1630001 (2016)
Hegab, A.M., Salem, N.M., Radwan, A.G., et al.: Neuron model with simplified memristive ionic channels. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 25, 1530017 (2015)
Pham, V.T., Jafari, S., Vaidyanathan, S., et al.: A novel memristive neural network with hidden attractors and its circuitry implementation. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59, 358–363 (2015)
Li, Q., Tang, S., Zeng, H., et al.: On hyperchaos in a small memristive neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 78, 1087–1099 (2014)
Thomas, A.: Memristor-based neural networks. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 093001 (2013)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205, 375–381 (2016)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., et al.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 1479–1490 (2016)
Ma, J., Wu, F., Wang, C.: Synchronization behaviors of coupled neurons under electromagnetic radiation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31, 1650251 (2017)
Wu, F., Wang, C., Xu, Y., et al.: Model of electrical activity in cardiac tissue under electromagnetic induction. Sci. Rep. 6, 28 (2016)
Wang, Y., Ma, J., Xu, Y., et al.: The electrical activity of neurons subject to electromagnetic induction and Gaussian white noise. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 1750030 (2017)
Wu, F., Wang, C., Jin, W., et al.: Dynamical responses in a new neuron model subjected to electromagnetic induction and phase noise. Physica A 469, 81–88 (2017)
Leonov, G.A., Kuznetsov, N.V., Vagaitsev, V.I.: Hidden attractor in smooth Chua systems. Physica D 241, 1482–1486 (2012)
Dudkowski, D., Jafari, S., Kapitaniak, T., et al.: Hidden attractors in dynamical systems. Phys. Rep. 637, 1–50 (2016)
Leonov, G.A., Kuznetsov, N.V., Vagaitsev, V.I.: Localization of hidden Chuas attractors. Phys. Lett. A 375, 2230–2233 (2011)
Channell, P., Cymbalyuk, G., Shilnikov, A.: Origin of bursting through homoclinic spike adding in a neuron model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 134101 (2007)
Shilnikov, A.: Complete dynamical analysis of a neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 68, 305–328 (2012)
Shilnikov, A., Cymbalyuk, G.: Transition between tonic spiking and bursting in a neuron model via the blue-sky catastrophe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 048101 (2005)
Venkatesan, A., Lakshmanan, M.: Bifurcation and chaos in the double well Duffing–van der Pol oscillator: numerical and analytical studies. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 56, 6321–6330 (1997)
Abshagen, J., Lopez, J.M., Marques, F., et al.: Bursting dynamics due to a homoclinic cascade in Taylor? Couette flow. J. Fluid Mech. 613, 357–384 (2008)
Mccann, K., Yodzis, P.: Nonlinear dynamics and population disappearances. Am. Nat. 144, 873–879 (1994)
Li, C., Sprott, J.C.: Multistability in the Lorenz System: a broken butterfly. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24, 1450131 (2014)
Li, C., Sprott, J.C.: Coexisting hidden attractors in a 4-D simplified Lorenz system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24, 1450034 (2014)
Sharma, P.R., Shrimali, M.D., Prasad, A., et al.: Control of multistability in hidden attractors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 224, 1485–1491 (2015)
Grebogi, C., Ott, E., Yorke, J.A.: Critical exponent of chaotic transients in nonlinear dynamical systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 1284–1287 (1986)
Dhamala, M., Lai, Y.C., Kostelich, E.J.: Analyses of transient chaotic time series. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 64, 056207 (2001)
Bao, B.C., Liu, Z., Xu, J.P.: Steady periodic memristor oscillator with transient chaotic behaviours. Electron. Lett. 46, 228 (2010)
Duan, S., Liao, X.: An electronic implementation for Liao’s chaotic delayed neuron model with non-monotonous activation function. Phys. Lett. A 369, 37–43 (2007)
Conti, M., Turchetti, C.: Approximation identify neural networks for analog synthesis of nonlinear dynamical system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 41, 841–858 (1994)
Ozkurt, N., Savaci, F.A., Gunduzalp, M.: The circuit implementation of a wavelet function approximator. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 32, 171–175 (2002)
Hu, X., Liu, C., Liu, L., et al.: An electronic implementation for MorrisLecar neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 84, 2317–2332 (2016)
Kesari, K.K., Siddiqui, M.H., Meena, R., et al.: Cell phone radiation exposure on brain and associated biological systems. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 51, 187 (2013)
Johansen, C.: Electromagnetic fields and health effects-epidemiologic studies of cancer, diseases of the central nervous system and arrhythmia-related heart disease. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 30(Suppl 1), 1–30 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grant Nos. 51307130 and 51177117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Liu, C., Liu, L. et al. Chaotic dynamics in a neural network under electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn 91, 1541–1554 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3963-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3963-6