Abstract
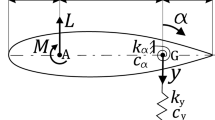
A compressed air generator hang under vehicle is simplified as a suspension mass connected to a vertical spring and two horizontal springs. It is configured generally as a geometrical negative stiffness to reduce dynamic stiffness. The periodic motion, chaotic motion and bifurcation of the compressed air generator model are investigated using the incremental harmonic balance method in combination with arc length continuation technique. The stability and bifurcation route are also distinguished with Floquet theory. The system exhibits a period doubling bifurcation route to chaos in different regions of excitation frequency. The stiffness ratio of the vertical spring and the horizontal spring has a significant influence on the dynamic response. When the vertical stiffness is close to the stiffness at horizontal direction, resonance occurs with the emergence of the chaotic motion. The dynamic response of the vibration system can be improved by reducing the stiffness in the horizontal direction to increase the stiffness ratio.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari, K.A., Khan, N.U.: Nonlinear vibrations of a slider-crank mechanism. Appl. Math. Model 10, 114–118 (1986)
Eissa, M., Sayed, M.: Vibration reduction of a three DOF non-linear spring pendulum. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13, 465–488 (2008)
Rivin, E.I.: Passive vibration isolation. American Society of Mechanical Engineers Press, New York (2003)
Robertson, W., Cazzolato, B., Zander, A.: Theoretical analysis of a non-contact spring with inclined permanent magnets for load-independent resonance frequency. J. Sound Vib. 331, 1331–1341 (2012)
Wu, S.-T., Siao, P.-S.: Auto-tuning of a two-degree-of-freedom rotational pendulum absorber. J. Sound Vib. 331, 3020–3034 (2012)
Acar, M.A., Yilmaz, C.: Design of an adaptive-passive dynamic vibration absorber composed of a string-mass system equipped with negative stiffness tension adjusting mechanism. J. Sound Vib. 332, 231–245 (2013)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P., Lopes Jr, V.: Force and displacement transmissibility of a nonlinear isolator with high-static-low-dynamic-stiffness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 55, 22–29 (2012)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P., Shin, K.: On the design of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator using linear mechanical springs and magnets. J. Sound Vib. 315, 712–720 (2008)
Robertson, W.S., Kidner, M.R.F., Cazzolato, B.S., Zander, A.C.: Theoretical design parameters for a quasi-zero stiffness magnetic spring for vibration isolation. J. Sound Vib. 326, 88–103 (2009)
Gatti, G., Brennan, M.J., Kovacic, I.: On the interaction of the responses at the resonance frequencies of a nonlinear two degrees-of-freedom system. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 239, 591–599 (2010)
Horton, B., Lenci, S., Pavlovskaia, E., Romeo, F., Rega, G., Wiercigroch, M.: Stability boundaries of period-1 rotation for a pendulum under combined vertical and horizontal excitation. J. Appl. Nonlinear Dyn. 2, 103–126 (2013)
Liu, X., Huang, X., Hua, H.: On the characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness isolator using Euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector. J. Sound Vib. 332, 3359–3376 (2013)
Huang, X., Liu, X., Sun, J., Zhang, Z., Hua, H.: Vibration isolation characteristics of a nonlinear isolator using Euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector: A theoretical and experimental study. J. Sound Vib. 333, 1132–1148 (2014)
Wu, W., Chen, X., Shan, Y.: Analysis and experiment of a vibration isolator using a novel magnetic spring with negative stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 333, 2958–2970 (2014)
Le, T.D., Ahn, K.K.: A vibration isolation system in low frequency excitation region using negative stiffness structure for vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 330, 6311–6335 (2011)
Le, T.D., Ahn, K.K.: Experimental investigation of a vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structure. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 70, 99–112 (2013)
Zhou, N., Liu, K.: A tunable high-static-low-dynamic stiffness vibration isolator. J. Sound Vib. 329, 1254–1273 (2010)
Tang, B., Brennan, M.J.: On the shock performance of a nonlinear vibration isolator with high-static-low-dynamic-stiffness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 81, 207–214 (2014)
Meyer, F., Hartl, M., Schneider, S.: Dual-stage, plunger-type piston compressor with minimal vibration. EP Patent 1,242,741, 2005
Lee, H., Song, G., Park, J., Hong, E., Jung, W., Park, K.: Development of the linear compressor for a household refrigerator. Fifteenth International Compressor Engineering Conference, Purdue University, West Lafayette (2000)
Gonçalves, P.J.P., Silveira, M., Balthazar, J.M., Pontes Jr, B.R., Balthazar, J.M.: The dynamic behavior of a cantilever beam coupled to a non-ideal unbalanced motor through numerical and experimental analysis. J. Sound Vib. 333, 5115–5129 (2014)
Yang, J., Xiong, Y.P., Xing, J.T.: Dynamics and power flow behaviour of a nonlinear vibration isolation system with a negative stiffness mechanism. J. Sound Vib. 332, 167–183 (2013)
Cheung, Y.K., Chen, S.H., Lau, S.L.: Application of the incremental harmonic balance method to cubic non-linearity systems. J. Sound Vib. 140, 273–286 (1990)
Crisfield, M.A.: A fast incremental/iterative solution procedure that handles snap-through. Comput. Struct. 13, 55–62 (1981)
Ritto-Corrêa, M., Camotim, D.: On the arc-length and other quadratic control methods: established, less known and new implementation procedures. Comput. Struct. 86, 1353–1368 (2008)
Fafard, M., Massicotte, B.: Geometrical interpretation of the arc-length method. Comput. Struct. 46, 603–615 (1993)
Farshidianfar, A., Saghafi, A.: Global bifurcation and chaos analysis in nonlinear vibration of spur gear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 75, 783–806 (2014)
Chen, S., Tang, J., Wu, L.: Dynamics analysis of a crowned gear transmission system with impact damping: based on experimental transmission error. Mech. Mach. Theory 74, 354–369 (2014)
Grolet, A., Thouverez, F.: Computing multiple periodic solutions of nonlinear vibration problems using the harmonic balance method and Groebner bases. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 52–53, 529–547 (2015)
Dou, S., Jensen, J.S.: Optimization of nonlinear structural resonance using the incremental harmonic balance method. J. Sound Vib. 334, 239–254 (2015)
Stoykov, S., Margenov, S.: Numerical computation of periodic responses of nonlinear large-scale systems by shooting method. Comput. Math. Appl. 67, 2257–2267 (2014)
Peletan, L., Baguet, S., Torkhani, M., Jacquet-Richardet, G.: A comparison of stability computational methods for periodic solution of nonlinear problems with application to rotordynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 72, 671–682 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) through Grants Nos. 51305462 and 51275530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuanping, L., Siyu, C. Periodic solution and bifurcation of a suspension vibration system by incremental harmonic balance and continuation method. Nonlinear Dyn 83, 941–950 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2378-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2378-5