Abstract
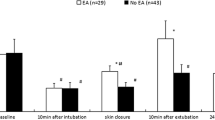
We measured perioperative plasma concentrations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a major mediator of synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system, in males, 30–65 years old, undergoing lumbar or cervical discotomy. Patients were randomly allocated to a general anesthetic with propofol induction and maintenance or with thiopental induction and isoflurane maintenance. BDNF plasma concentrations were measured before induction (baseline), 15 min after induction but before start of surgery, at skin closure, in the post-anesthetic care unit, and 24 h postoperatively. Data from 26 patients (13 in each group) were analyzed. At each time point, BDNF plasma concentrations showed large variability. At baseline, concentrations were 631 ± 337 (mean ± SD) pg ml−1 in the propofol group and were 549 ± 512 pg ml−1 in the thiopental–isoflurane group (P = 0.31). At 15 min, concentrations significantly decreased in the propofol group (247 ± 219 pg ml−1, P = 0.0012 compared with baseline) but remained unchanged in the thiopental–isoflurane group (597 ± 471 pg ml−1, P = 0.798 compared with baseline). At skin closure and in the post-anesthetic care unit, concentrations were not different from baseline in both groups. At 24 h, concentrations significantly decreased below baseline in both groups (propofol: 232 ± 129 pg ml−1, P = 0.0015; thiopental–isoflurane: 253 ± 250 pg ml−1, P = 0.016). In the propofol group, there was a weak but statistically significant positive correlation (R 2 = 0.38, P = 0.026) between the duration of surgery and BDNF plasma concentrations at skin closure. These data suggest that in males undergoing elective minor surgery, BDNF plasma concentrations show a specific pattern that is influenced by the anesthetic technique and, possibly, by the duration of surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snider WD (1996) Functions of the neurotrophins during nervous system development: what the knockouts are teaching us. Cell 5:627–638
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:677–736
Lu B (2003) BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn Mem 2:86–98
Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS (2006) Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 2:167–173
Beck T, Lindholm D, Castren E et al (1994) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemic cell damage in rat hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:689–692
Yamashita K, Wiessner C, Lindholm D et al (1997) Post-occlusion treatment with BDNF reduces infarct size in a model of permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rat. Metab Brain Dis 4:271–280
Lommatzsch M, Zingler D, Schuhbaeck K et al (2005) The impact of age, weight and gender on BDNF levels in human platelets and plasma. Neurobiol Aging 1:115–123
Radka SF, Holst PA, Fritsche M et al (1996) Presence of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain and human and rat but not mouse serum detected by a sensitive and specific immunoassay. Brain Res 1:122–301
Fujimura H, Altar CA, Chen R et al (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is stored in human platelets and released by agonist stimulation. Thromb Haemost 4:728–734
Yamamoto H, Gurney ME (1990) Human platelets contain brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci 11:3469–3478
Lommatzsch M, Braun A, Mannsfeldt A et al (1999) Abundant production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor by adult visceral epithelia. Implications for paracrine and target-derived Neurotrophic functions. Am J Pathol 4:1183–1193
Nakahashi T, Fujimura H, Altar CA et al (2000) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett 2:113–117
Pan W, Banks WA, Fasold MB et al (1998) Transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood-brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 12:1553–1561
Karege F, Schwald M, Cisse M (2002) Postnatal developmental profile of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat brain and platelets. Neurosci Lett 3:261–264
Huang AM, Jen CJ, Chen HF et al (2006) Compulsive exercise acutely upregulates rat hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neural Transm 7:803–811
Neeper SA, Gomez-Pinilla F, Choi J et al (1996) Physical activity increases mRNA for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in rat brain. Brain Res 1–2:49–56
Ferris LT, Williams JS, Shen CL (2007) The effect of acute exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and cognitive function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 4:728–734
Karege F, Perret G, Bondolfi G et al (2002) Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in major depressed patients. Psychiatry Res 2:143–148
Lee BH, Kim H, Park SH et al (2007) Decreased plasma BDNF level in depressive patients. J Affect Disord 1–3:239–244
Shimizu E, Hashimoto K, Watanabe H et al (2003) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in schizophrenia are indistinguishable from controls. Neurosci Lett 2:111–114
Castren E, Voikar V, Rantamaki T (2007) Role of neurotrophic factors in depression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 1:18–21
Balkowiec A, Katz DM (2002) Cellular mechanisms regulating activity-dependent release of native brain-derived neurotrophic factor from hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 23:10399–10407
Goggi J, Pullar IA, Carney SL et al (2003) The control of [125I]BDNF release from striatal rat brain slices. Brain Res 1–2:201–209
Lu LX, Yon JH, Carter LB et al (2006) General anesthesia activates BDNF-dependent neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Apoptosis 9:1603–1615
Schnider TW, Minto CF, Shafer SL et al (1999) The influence of age on propofol pharmacodynamics. Anesthesiology 6:1502–1516
Rosenfeld RD, Zeni L, Haniu M et al (1995) Purification and identification of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from human serum. Protein Expr Purif 4:465–471
Rage F, Givalois L, Marmigere F et al (2002) Immobilization stress rapidly modulates BDNF mRNA expression in the hypothalamus of adult male rats. Neuroscience 2:309–318
Marmigere F, Givalois L, Rage F et al (2003) Rapid induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during immobilization stress challenge in adult rats. Hippocampus 5:646–655
Duric V, McCarson KE (2006) Persistent pain produces stress-like alterations in hippocampal neurogenesis and gene expression. J Pain 8:544–555
Lysakowski C, Dumont L, Tramer MR et al (2003) A needle-free jet-injection system with lidocaine for peripheral intravenous cannula insertion: a randomized controlled trial with cost-effectiveness analysis. Anesth Analg 1:215–219
Yamakura T, Bertaccini E, Trudell JR et al (2001) Anesthetics and ion channels: molecular models and sites of action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:23–51
Culley DJ, Yukhananov RY, Xie Z et al (2006) Altered hippocampal gene expression 2 days after general anesthesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 1–3:71–78
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Prof. Jozsef Z. Kiss (Department of Neuroscience, Faculty of Medicine, Geneva University, Geneva, Switzerland), Prof. Edömer Tassonyi (Division of Anesthesiology, University Hospitals of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland), Dr. Yvan Gasche (Division of Intensive Care, University Hospitals of Geneva, Switzerland) and Dr. Eduardo Gascon (Department of Neuroscience, Faculty of Medicine, Geneva University, Geneva, Switzerland) for helpful discussions. We are grateful to Natasha Turck (Department of Structural Biology and Bioinformatics, Faculty of Medicine, Geneva University, Geneva, Switzerland) and Sylvie Chliate (Department of Neuroscience, Faculty of Medicine, Geneva University, Geneva, Switzerland) for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant no. 310000-113555) to Dr. Vutskits, by grants from the Division of Anesthesiology, University Hospitals of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland (to Dr. Vutskits and Prof. Tramèr) and by grants from the Faculty of Medicine, Geneva University, Geneva, Switzerland (to Dr. Vutskits and Prof. Tramèr).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vutskits, L., Lysakowski, C., Czarnetzki, C. et al. Plasma Concentrations of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor in Patients Undergoing Minor Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurochem Res 33, 1325–1331 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9586-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9586-4