Abstract
Purpose
Magnetic resonance imagining (MRI) is helpful for diagnosis of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LMC) and localizing LMC symptoms. Goal of this study is how MRI findings of LMC are associated with clinical characteristics or prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods
We retrospectively collected data on 283 patients with LMC from NSCLC, adenocarcinoma based on cerebrospinal fluid cytology. All patients had brain MRI with gadolinium enhancement at LMC diagnosis, and spinal MRI was performed at the physician’s discretion. We evaluated the prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) of all patients and subgroup of patients with central nervous system cause of death.
Results
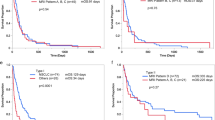
Two-hundred sixteen patients (76%) had definite or suggestive LMC findings and 67 had negative findings on brain MRI. Of the 37 patients who presented with cauda equina syndrome, 35 (95%) exhibited typical spinal MRI findings. Median OS of all patients was 3.65 months (95% confidence interval, 3.06–4.18). There was no significant difference in median OS between MRI-negative and MRI-positive groups (4.31 vs. 3.48 months, p = 0.711), whereas negative MRI finding showed longer median OS significantly in a subgroup of 77 patients with a central nervous system cause of death (p = 0.035). Considering clinical characteristics, progressive systemic disease, and altered mentality were significant prognostic factors associated with poor OS, whereas presenting symptom of headache with nausea/vomiting, intra-CSF chemotherapy, WBRT after LMC diagnosis, and concurrent RTKi treatment were significant for favorable OS in multivariable analysis.
Conclusions
Positive MRI findings suggests heavier disease burden than negative MRI findings in patients with LMC who died of a central nervous system cause. Spinal MRI findings in patients with LMC correlate with cauda equina symptoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa040938
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973–2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol 22:2865–2872
Fox BD, Cheung VJ, Patel AJ, Suki D, Rao G (2011) Epidemiology of metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am 22:1–6
Gwak HS, Joo J, Kim S, Yoo H, Shin SH, Han JY, Kim HT, Lee JS, Lee SH (2013) Analysis of treatment outcomes of intraventricular chemotherapy in 105 patients for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 8:599–605. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318287c943
Lee Y, Han JY, Kim HT, Yun T, Lee GK, Kim HY, Lee JS (2013) Impact of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy on the development of leptomeningeal metastasis in never smokers with advanced adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Neurooncol 115:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1199-y
Chamberlain MC (2010) Leptomeningeal metastasis. Curr Opin Oncol 22:627–635
Gwak HS, Lee SH, Park WS, Shin SH, Yoo H, Lee SH (2015) Recent advancements of treatment for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.1
Chamberlain MC, Glantz M, Groves MD, Wilson WH (2009) Diagnostic tools for neoplastic meningitis: detecting disease, identifying patient risk, and determining benefit of treatment. Semin Oncol 36:S35–S45. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2009.05.005
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Glantz LK, Cobb J, Mills P, Lekos A, Walters BC, Recht LD (1998) Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in patients with cancer: minimizing false-negative results. Cancer 82:733–739
Twijnstra A, Ongerboer de Visser BW, van Zanten AP (1987) Diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 89:79–85
Freilich RJ, Krol G, DeAngelis LM (1995) Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann Neurol 38:51–57
Straathof CS, de Bruin HG, Dippel DW, Vecht CJ (1999) The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurol 246:810–814
Paakko E, Patronas NJ, Schellinger D (1990) Meningeal Gd-DTPA enhancement in patients with malignancies. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:542–546
Zeiser R, Burger JA, Bley TA, Windfuhr-Blum M, Schulte-Monting J, Behringer DM (2004) Clinical follow-up indicates differential accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and immunocytology of the cerebral spinal fluid for the diagnosis of neoplastic meningitis—a single centre experience. Br J Haematol 124:762–768
Clarke J, Perez H, Jacks L, Panageas K, Deangelis L (2010) Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology 74:1449–1454
Collie D, Brush J, Lammie G, Grant R, Kunkler I, Leonard R, Gregor A, Sellar R (1999) Imaging features of leptomeningeal metastases. Clin Radiol 54:765–771
Grossman SA, Krabak MJ (1999) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat Rev 25:103–119. https://doi.org/10.1053/ctrv.1999.0119
Chamberlain MC (1995) Comparative spine imaging in leptomeningeal metastases. J Neuro-oncol 23:233–238
Chamberlain MC (1998) Radioisotope CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. J Neurooncol 38:135–140
Glantz MJ, Hall WA, Cole BF, Chozick BS, Shannon CM, Wahlberg L, Akerley W, Marin L, Choy H (1995) Diagnosis, management, and survival of patients with leptomeningeal cancer based on cerebrospinal fluid-flow status. Cancer 75:2919–2931
Gomori JM, Heching N, Siegal T (1998) Leptomeningeal metastases: evaluation by gadolinium enhanced spinal magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurooncol 36:55–60
Chamberlain M, Junck L, Brandsma D, Soffietti R, Ruda R, Raizer J, Boogerd W, Taillibert S, Groves MD, Le Rhun E, Walker J, van den Bent M, Wen PY, Jaeckle KA (2017) Leptomeningeal metastases: a RANO proposal for response criteria. Neuro Oncol 19:484–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now183
Grossman S, Finkelstein D, Ruckdeschel J, Trump D, Moynihan T, Ettinger D (1993) Randomized prospective comparison of intraventricular methotrexate and thiotepa in patients with previously untreated neoplastic meningitis. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 11:561–569
Boogerd W, Hart AA, van der Sande JJ, Engelsman E (1991) Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer. Prognostic factors and influence of treatment. Cancer 67:1685–1695
Sherman AM, Jaeckle K, Meyers CA (2002) Pretreatment cognitive performance predicts survival in patients with leptomeningeal disease. Cancer 95:1311–1316
Glantz MJ, Jaeckle KA, Chamberlain MC, Phuphanich S, Recht L, Swinnen LJ, Maria B, LaFollette S, Schumann GB, Cole BF, Howell SB (1999) A randomized controlled trial comparing intrathecal sustained-release cytarabine (DepoCyt) to intrathecal methotrexate in patients with neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors. Clin Canser Res 5:3394–3402
Gleissner B, Chamberlain MC (2006) Neoplastic meningitis. The Lancet Neurology 5:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70443-4
Chamberlain MC, Kormanik PA (1997) Prognostic significance of coexistent bulky metastatic central nervous system disease in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Arch Neurol 54:1364–1368
Yap HY, Yap BS, Rasmussen S, Levens ME, Hortobagyi GN, Blumenschein GR (1982) Treatment for meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer. Cancer 50:219–222
Balm M, Hammack J (1996) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: presenting features and prognostic factors. Arch Neurol 53:626–632
Fizazi K, Asselain B, Vincent-Salomon A, Jouve M, Dieras V, Palangie T, Beuzeboc P, Dorval T, Pouillart P (1996) Meningeal carcinomatosis in patients with breast carcinoma: Clinical features, prognostic factors, and results of a high-dose intrathecal methotrexate regimen. Cancer 77:1315–1323
Chamberlain MC, Tsao-Wei D, Groshen S (2004) Neoplastic meningitis-related encephalopathy Prognostic significance. Neurology 63:2159–2161
Bruna J, Gonzalez L, Miro J, Velasco R, Gil M, Tortosa A (2009) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: prognostic implications of clinical and cerebrospinal fluid features. Cancer 115:381–389
Clamon G, Doebbeling B (1987) Meningeal carcinomatosis from breast cancer: spinal cord vs. brain involvement. Breast Cancer Res Treat 9:213–217
Jayson GC, Howell A, Harris M, Morgenstern G, Chang J, Ryder WD, Grad, (1994) Carcinomatous meningitis in patients with breast cancer. An Aggressive Disease Variant 74:3135–3141. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19941215)74:12%3c3135:AID-CNCR35%3e3.0.CO;2-8
Lee SJ, Lee J-I, Nam D-H, Ahn YC, Han JH, Sun J-M, Ahn JS, Park K, Ahn M-J (2013) Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Impact on Survival and Correlated Prognostic Factors. J Thoracic Oncol 8:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182773f21
Park JH, Kim YJ, Lee JO, Lee KW, Kim JH, Bang SM, Chung JH, Kim JS, Lee JS (2012) Clinical outcomes of leptomeningeal metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer in the modern chemotherapy era. Lung Cancer 76:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.11.022
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Aoyagi K, Ono J, Saeki N, Iwadate Y, Hirai T, Takemoto S, Shibamoto Y (2017) Robustness of the neurological prognostic score in brain metastasis patients treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 127:1000–1006. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.JNS16528
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Cancer Center, Korea (1710871–2), and a grant of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, funded by the Ministry of Health & welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant No: 1731340–2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, Y., Gwak, HS., Park, E.Y. et al. Association of MRI findings with clinical characteristics and prognosis in patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from non-small cell lung cancer. J Neurooncol 143, 553–562 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03190-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03190-3