Abstract
Introduction
To assess tumor control and survival in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for 10 or more metastatic brain tumors.
Methods
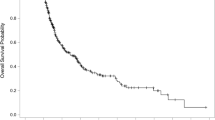
Patients were retrospectively identified. Clinical records were reviewed for follow-up data, and post-treatment MRI studies were used to assess tumor control. For tumor control studies, patients were separated based on synchronous or metachronous treatment, and control was assessed at 3-month intervals. The Kaplan–Meier method was employed to create survival curves, and regression analyses were employed to study the effects of several variables.
Results
Fifty-five patients were treated for an average of 17 total metastases. Forty patients received synchronous treatment, while 15 received metachronous treatment. Univariate analysis revealed an association between larger brain volumes irradiated with 12 Gy and decreased overall survival (p = 0.0406); however, significance was lost on multivariate analysis. Among patients who received synchronous treatment, the median percentage of tumors controlled was 100%, 91%, and 82% at 3, 6, and 9 months, respectively. Among patients who received metachronous treatment, the median percentage of tumors controlled after each SRS encounter was 100% at all three time points.
Conclusions
SRS can be used to treat patients with 10 or more total brain metastases with an expectation of tumor control and overall survival that is equivalent to that reported for patients with four or fewer tumors. Development of new metastases leading to repeat SRS is not associated with worsened tumor control or survival. Survival may be adversely affected in patients having a higher volume of normal brain irradiated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan AB, Kass JS, Ullrich NJ (2018) Brain Metastases. In: Ferri F (ed) Ferri’s clinical advisor 2019. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 236–237
Sawaya R, Bindal RK, Lang FF, Suki D (2012) Metastatic Brain Tumors. In: Kaye A, Laws E (eds) Brain tumors an encyclopedic approach, 3. Saunders/Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 864–892 rd
Grandhi R, Kondziolka D, Panczykowski D, Monaco EA, Kano H, Niranjan A et al (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery using the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion unit in the management of patients with 10 or more brain metastases. J Neurosurg 117:237–245
Hatiboglu MA, Tuzgen S, Akdur K, Chang EL (2016) Treatment of high numbers of brain metastases with Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a review. Acta Neurochir 158:625–634
Raldow AC, Chiang VL, Knisely JP, Yu JB (2013) Survival and Intracranial Control of Patients With 5 or More Brain Metastases Treated With Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Am J Clin Oncol 36:486–490
Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Baumert B, Combs SE, Kinhult S, Kros JM et al (2017) Diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases from solid tumors: guidelines from the European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO). Neuro-Oncology 19:162–174
Cohen-Inbar O, Sheehan JP (2016) The role of stereotactic radiosurgery and whole brain radiation therapy as primary treatment in the treatment of patients with brain oligometastases—a systematic review. J Radiosurg SBRT 4(2):79–88
Yamamoto M, Ide M, Nishio S, Urakawa Y (2002) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for numerous brain metastases: is this a safe treatment? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:1279–1283
Arvold ND, Lee EQ, Mehta MP, Margolin K, Alexander BM, Lin NU et al (2016) Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro-Oncology 18(8):1043–1065
Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Sato Y, Higuchi Y, Nariai T, Watanabe S et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases: a case-matched study comparing treatment results for patients with 2–9 versus 10 or more tumors. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):16–25
Kim CH, Im YS, Nam DH, Park K, Kim JH, Lee JI (2008) Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Ten or More Brain Metastases. J Korean Neurosurg 44:358–363
Rava P, Leonard K, Sioshansi S, Curran B, Wazer D, Cosgrove GR et al (2013) Survival among patients with 10 or more brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 119:457–462
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15:387–395
Bowden G, Kano H, Caparosa E, Park SH, Niranjan A, Flickinger J et al (2015) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for the management of cerebral metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. J Neurosurg 122:766–772
Chang WS, Kim HY, Chang JW, Park YG, Chang JH (2010) Analysis of radiosurgical results in patients with brain metastases according to the number of brain lesions: is stereotactic radiosurgery effective for multiple brain metastases? J Neurosurg 113(Suppl):73–78
Jairam V, Chiang VLS, Yu JB, Knisely J (2013) Role of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with more than four brain metastases. CNS Oncol 2:181–193
Jawahar A, Matthew RE, Minagar A, Shukla D, Zhang JH, Willis BK et al (2004) Gamma knife surgery in the management of brain metastases from lung carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of survival, local tumor control, and freedom from new brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 100:842–847
Park SH, Hwang SK, Kang DH, Lee SH, Park J, Hwang JH et al (2009) Gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases from lung cancer. J Clin Neurosci 16:626–629
Serizawa T, Iuchi T, Ono J, Saeki N, Osato K, Odaki M et al (2000) Gamma knife treatment for multiple metastatic brain tumors compared with whole-brain radiation therapy. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):32–36
Acknowledgements
No person other than the authors contributed to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals included in the study, whenever possible, taking into account the retrospective nature of the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrlich, M.I., Schiff, E., Knisely, J.P.S. et al. Tumor control and survival in patients with ten or more brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery: a retrospective analysis. J Neurooncol 143, 167–174 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03153-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03153-8