Abstract
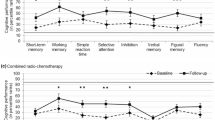
Preservation of cognition is an important outcome measure in eloquent area glioma surgery. Glioma patients may have pre-operative deficits in one or more cognitive domains which could deteriorate post-operatively. It is assumed that these impairments recover within 3 months; some studies however, still detected cognitive decline. Longer follow-up is necessary to elucidate the conclusive effects of surgery. 45 patients with gliomas (low- and high-grade, but without contrast enhancement at diagnosis) in eloquent areas were assessed pre-operatively, 3 months and 1 year post-operatively with a neuropsychological test-protocol. Patients’ performance was compared to normal population and between test-moments. Univariate analyses were performed between cognitive change and tumor-characteristics (localization, grade, volume, extent of resection [EOR]) and treatment-related factors (radio-/chemotherapy). Pre- and post-operatively, impairments were found in all cognitive domains; language, memory, attention and executive functions (p < 0.05). Post-operatively, permanent improvement was observed on a memory test (verbal recall: t = −1.931, p = 0.034), whereas deterioration was found on a language test (category fluency: t = 2.517, p = 0.030). Between 3 months and 1 year, patients improved on 2 language tests (naming: t = −2.781, p = 0.026 and letter fluency: t = −1.975, p = 0.047). There was no influence of tumor- or treatment-related factors on cognitive change. The findings underline the importance of cognitive testing at longer term post-operatively, as cognitive recovery took longer than 3 months, especially within the language domain. However, this longitudinal follow-up study showed that glioma surgery is possible without major long-term damage of cognitive functions. Tumor characteristics and EOR are no additional risk factors for cognitive outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanai N, Berger MS (2012) Recent surgical management of gliomas. Adv Exp Med Biol 746:12–25
De Witt Hamer PC, Robles SG, Zwinderman AH, Duffau H, Berger MS (2012) Impact of intraoperative stimulation brain mapping on glioma surgery outcome: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 30(20):2559–2565
Santini B, Talacchi A, Squintani G, Casagrande F, Capasso R, Miceli G (2012) Cognitive outcome after awake surgery for tumors in language areas. J Neurooncol 108(2):319–326
Talacchi A, Santini B, Savazzi S, Gerosa M (2010) Cognitive effects of tumour and surgical treatment in glioma patients. J Neurooncol. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0417-0
Satoer D, Vork J, Visch-Brink E, Smits M, Dirven C, Vincent A (2012) Cognitive functioning early after surgery of gliomas in eloquent areas. J Neurosurg 117(5):831–838
Sanai N, Chang S, Berger MS (2011) Low-grade gliomas in adults. J Neurosurg 115(5):948–965
Tucha O, Smely C, Preier M, Becker G, Paul GM, Lange KW (2003) Preoperative and postoperative cognitive functioning in patients with frontal meningiomas. J Neurosurg 98(1):21–31. doi:10.3171/jns.2003.98.1.0021
Duffau H, Gatignol P, Mandonnet E, Capelle L, Taillandier L (2008) Intraoperative subcortical stimulation mapping of language pathways in a consecutive series of 115 patients with Grade II glioma in the left dominant hemisphere. J Neurosurg 109:461–471
Teixidor P, Gatignol P, Leroy M, Masuet-Aumatell C, Capelle L, Duffau H (2007) Assessment of verbal working memory before and after surgery for low-grade glioma. J Neurooncol 81(3):305–313. doi:10.1007/s11060-006-9233-y
Bello L, Gallucci M, Fava M, Carrabba G, Giussani C, Acerbi F, Baratta P, Songa V, Conte V, Branca V, Stocchetti N, Papagno C, Gaini SM (2007) Intraoperative subcortical language tract mapping guides surgical removal of gliomas involving speech areas. Neurosurgery 60(1):67–80 discussion 80–62
Ilmberger J, Ruge M, Kreth FW, Briegel J, Reulen HJ, Tonn JC (2008) Intraoperative mapping of language functions: a longitudinal neurolinguistic analysis. J Neurosurg 109(4):583–592
Sacko O, Lauwers-Cances V, Brauge D, Sesay M, Brenner A, Roux FE (2011) Awake craniotomy vs surgery under general anesthesia for resection of supratentorial lesions. Neurosurgery 68(5):1192–1198 discussion 1198–1199
Sarubbo S, Latini F, Panajia A, Candela C, Quatrale R, Milani P, Fainardi E, Granieri E, Trapella G, Tugnoli V, Cavallo MA (2011) Awake surgery in low-grade gliomas harboring eloquent areas: 3-year mean follow-up. Neurol Sci 32(5):801–810
Le Rhun E, Delbeuck X, Devos P, Pasquier F, Dubois F (2009) Cognitive disorders and adult grade II and III gliomas: analysis of a series of 15 patients (Troubles cognitifs dans les gliomes de grade II et III de l’adulte : a propos d’une serie de 15 patients). Neurochirurgie 55(3):303–308. doi:10.1016/j.neuchi.2008.08.111
Bennett TL (2001) Neuropsychological evaluation in rehabilitation planning and evaluation of functional skills. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 16(3):237–253
Duffau H (2005) Intraoperative cortico-subcortical stimulations in surgery of low-grade gliomas. Expert Rev Neurother 5(4):473–485. doi:10.1586/14737175.5.4.473
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC et al (1993) The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(5):365–376
Naidich TP, Hof PR, Gannon PJ, Yousry TA, Yousry I (2001) Anatomic substrates of language: emphasizing speech. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 11(2):305–341
Graetz S, De Blesser P, Willmes K (1991) Akense Afasie Test, Dutch edn. Swets and Zeitlinger, Lisse
Kaplan E, Goodglass H, Weintraub S (2001) Boston naming test. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, Tokyo
Luteijn F, Barelds DPF (2004) Groninger Intelligentie Test II (GIT II). Pearson, Amsterdam
Schmand B, Groenink SC, Van den Dungen M (2008) Letterfluency: psychometrische eigenschappen en Nederlandse normen. Tijdschr Gerontol Geriatr 39(2):65–77
Van der Elst W, van Boxtel MP, van Breukelen GJ, Jolles J (2005) Rey’s verbal learning test: normative data for 1,855 healthy participants aged 24–81 years and the influence of age, sex, education, and mode of presentation. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 11(3):290–302
Lezak MD (2004) Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford University Press, New York
Verhage F (1964) Intelligentie en leeftijd: Onderzoek bij Nederlanders van 12 tot 77 jaar Van Gorkum, Assen
Kim H, Kim J, Kim DY, Heo J (2011) Differentiating between aphasic and nonaphasic stroke patients using semantic verbal fluency measures with administration time of 30 s. Eur Neurol 65(2):113–117
Gehring K, Sitskoorn MM, Gundy CM, Sikkes SA, Klein M, Postma TJ, van den Bent MJ, Beute GN, Enting RH, Kappelle AC, Boogerd W, Veninga T, Twijnstra A, Boerman DH, Taphoorn MJ, Aaronson NK (2009) Cognitive rehabilitation in patients with gliomas: a randomized, controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 27(22):3712–3722. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.5765
Mandonnet E, Delattre JY, Tanguy ML, Swanson KR, Carpentier AF, Duffau H, Cornu P, Van Effenterre R, Alvord EC Jr, Capelle L (2003) Continuous growth of mean tumor diameter in a subset of grade II gliomas. Ann Neurol 53(4):524–528
Correa DD, Shi W, Thaler HT, Cheung AM, DeAngelis LM, Abrey LE (2008) Longitudinal cognitive follow-up in low grade gliomas. J Neurooncol 86(3):321–327. doi:10.1007/s11060-007-9474-4
Weintraub S, Rogalski E, Shaw E, Sawlani S, Rademaker A, Wieneke C, Mesulam MM (2013) Verbal and nonverbal memory in primary progressive aphasia: the Three Words-Three Shapes Test. Behav Neurol 26:67–76
Gruber O, Goschke T (2004) Executive control emerging from dynamic interactions between brain systems mediating language, working memory and attentional processes. Acta Psychol (Amst) 115:105–121
Menke R, Meinzer M, Kugel H, Deppe M, Baumgartner A, Schiffbauer H, Thomas M, Kramer K, Lohmann H, Floel A, Knecht S, Breitenstein C (2009) Imaging short- and long-term training success in chronic aphasia. BMC Neurosci 10:118
Saur D, Lange R, Baumgaertner A, Schraknepper V, Willmes K, Rijntjes M, Weiller C (2006) Dynamics of language reorganization after stroke. Brain 129(Pt 6):1371–1384
Yoshii Y, Tominaga D, Sugimoto K, Tsuchida Y, Hyodo A, Yonaha H, Kushi S (2008) Cognitive function of patients with brain tumor in pre- and post-operative stage. Surg Neurol 69(1):51–61 discussion 61
Gehring K, Aaronson NK, Gundy CM, Taphoorn MJ, Sitskoorn MM (2011) Predictors of neuropsychological improvement following cognitive rehabilitation in patients with gliomas. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 17(2):256–266
Hahn CA, Dunn RH, Logue PE, King JH, Edwards CL, Halperin EC (2003) Prospective study of neuropsychologic testing and quality-of-life assessment of adults with primary malignant brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 55(4):992–999. doi:S0360301602042050
Taphoorn MJ, Klein M (2004) Cognitive deficits in adult patients with brain tumours. Lancet Neurol 3(3):159–168
Costello A, Shallice T, Gullan R, Beaney R (2004) The early effects of radiotherapy on intellectual and cognitive functioning in patients with frontal brain tumours: the use of a new neuropsychological methodology. J Neurooncol 67(3):351–359
Satoer D, Vincent A, Smits M, Dirven C, Visch-Brink E (2013) Spontaneous speech of patients with gliomas in eloquent areas before and early after surgery. Acta Neurochir 155:685–692
Sanai N, Berger (2008) Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery 62(4):753–764. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000318159.21731.cf discussion 264–756
Bosma I, Reijneveld JC, Klein M, Douw L, van Dijk BW, Heimans JJ, Stam CJ (2009) Disturbed functional brain networks and neurocognitive function in low-grade glioma patients: a graph theoretical analysis of resting-state MEG. Nonlinear Biomed Phys 3(1):9
Klein M, Heimans JJ, Aaronson NK, van der Ploeg HM, Grit J, Muller M, Postma TJ, Mooij JJ, Boerman RH, Beute GN, Ossenkoppele GJ, van Imhoff GW, Dekker AW, Jolles J, Slotman BJ, Struikmans H, Taphoorn MJ (2002) Effect of radiotherapy and other treatment-related factors on mid-term to long-term cognitive sequelae in low-grade gliomas: a comparative study. Lancet 360(9343):1361–1368
Taphoorn MJ, Heimans JJ, Snoek FJ, Lindeboom J, Karim AB (1994) Quality of life and neuropsychological functions in long-term low-grade glioma survivors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 29(5):1201–1202
Scoccianti S, Detti B, Cipressi S, Iannalfi A, Franzese C, Biti G (2012) Changes in neurocognitive functioning and quality of life in adult patients with brain tumors treated with radiotherapy. J Neurooncol 108(2):291–308
Drane DL, Meador KJ (2002) Cognitive and behavioral effects of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Behav 3(5S):49–53
Brady MC, Kelly H, Godwin J, Enderby P (2012) Speech and language therapy for aphasia following stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD000425
Duffau H (2007) Contribution of cortical and subcortical electrostimulation in brain glioma surgery: methodological and functional considerations. Neurophysiol Clin 37(6):373–382
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the European Low Grade Glioma Network for elaborate discussion on this work at the 2013 Annual ELLGN meeting in Ghent, Belgium.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satoer, D., Visch-Brink, E., Smits, M. et al. Long-term evaluation of cognition after glioma surgery in eloquent areas. J Neurooncol 116, 153–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1275-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1275-3