Abstract
Current treatment for high risk and recurrent medulloblastoma (MB) and supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors (stPNET) has a very poor prognosis in children. High dose chemotherapy (HDCT) and autologous stem cell rescue have improved survival rates. We present 19 patients (thirteen classified in the high risk group and six patients with recurrent disease) that received HDCT and autologous stem cell rescue.
In the high risk group [Med Pediatr Oncol 38 (2002) 83], all patients underwent neurosurgical debulking. Standard chemotherapy was prescribed in 10 patients. Radiotherapy was given to 4 patients (all older than 4 years old). In the recurrence disease group [Childs Nerv Syst 15 (1999) 498], five patients underwent surgery. Radiotherapy was given to those who were not previously irradiated. The HDCT in twelve patients consisted of busulfan 4 mg/kg/day, orally over 4 days in 6-hourly divided doses and melphalan at a dose of 140 mg/m2/day by intravenous infusion over 5 min on day −1. Three patients additionally received thiotepa 250 mg/m2/day intravenously over 2 days and four patients additionally received topotecan 2 mg/m2/day over 5 days by intravenous infusion over 30 min. The other seven patients received busulfan and thiotepa at the same doses.
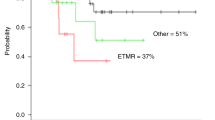
Patient’s stem cells were mobilized with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor at a dose of 12 μg/kg twice daily subcutaneously for four consecutive days. Cryopreserved peripheral blood progenitor cells were re-infused 48 h after completion of chemotherapy. With a median follow-up of 34 months (range 5–93) eight complete responses and one partial response were observed. Three patients died of treatment-related toxicities (15%). The 2 year event-free survival was 37.67 ± 14% in all patients and 57 ± 15% for the high risk group.
Therefore we conclude that HDCT may improve survival rates in patients with high risk/recurrent MB and stPNET despite treatment toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IJ Dunkel JM Boyett A Yates M Rosenblum JH Garvin SuffixJr BC Bostrom et al. (1998) ArticleTitleHigh-dose carboplatin, thiotepa, and etoposide with autologous stem cell rescue for patients with recurrent medulloblastoma J Clin Oncol 16 222–228
WP Mason A Grovas S Halpern IJ Dunkel J Garvin G Heller et al. (1998) ArticleTitleIntensive chemotherapy and bone marrow rescue for young children with newly diagnosed malignant brain tumors J Clin Oncol 16 210–221
IJ Dunkel JL Finlay (2002) ArticleTitleHigh-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue for brain tumors Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 41 197–204
ML Graham JE Herndon Suffix2nd JR Casey S Chaffee GH Ciocci JP Krischer et al. (1997) ArticleTitleHigh-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem-cell rescue in patients with recurrent and high risk pediatric brain tumors J Clin Oncol 15 1814–1823
C Kalifa D Valteau B Pizer G Vassal J Grill O Hartmann (1999) ArticleTitleHigh-dose chemotherapy in childhood brain tumours Child’s Nerv Syst 15 498–505
S Guruangan IJ Dunkel S Goldman JH Garvin M Rosenblum JM Boyett et al. (1998) ArticleTitleMyeloablative chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow rescue in young children with recurrent malignant brain tumors. J Clin Oncol 16 IssueID7 2486–2493
MA Díaz MG Vicent L Madero (1999) ArticleTitleHigh-dose busulfan/melphalan as conditioning for autologous PBPC transplantation in pediatric patients with solid tumors Bone Marrow Transplant 11 1157–1159
C Kalifa O Hartmann F Demeocq G Vassal D Couanet MJ Terrier-Lacombe et al. (1992) ArticleTitleHigh-dose busulfan and thiotepa with autologous bone marrow transplantation in childhood malignant brain tumors: a phase II study. Bone Marrow Trasplant 9 IssueID4 227–233
J Laurent CH Chang M Cohen (1985) ArticleTitleA classification system for primitive neuroectodermal tumors (medulloblastoma) of the posterior fossa Cancer 56 1807–1809
D Jenkin C Danjoux M Greenberg (1998) ArticleTitleSubsequent quality of life for children irradiated for a brain tumor before age four years Med Pediatr Oncol 318 506–511
JL Finlay Grovas Am J Garvin I Dunkel L Bayer D Pucetti S Halpern R Drachtman S Goldman O Tugal S Jayabose M Weinblatt I Sadhev JC Allen (1995) ArticleTitleThe “head start’’ regimen for children less than 6 years of age newly-diagnosed with malignant brain tumors. Med Pediatr Oncol 25 IssueID4 250
P Marec-Berare A Jouvet P Thiesse C Kalifa F Koz D Frappaz (2002) ArticleTitleSupratentorial embryonal tumors in children under 5 years of age: an SFOP study of treatment with postoperative chemotherapy alone Med Pediatr Oncol 38 83–90
P Zeltzer J Boyett J Finlay A Albright L Rorke J Milstein et al. (1999) ArticleTitleMetastasis stage, adjuvant treatment, and residual tumor are prognostic factors for medulloblatoma in children: conclusions from the Children’s Cancer Group 921 randomized phase III study J Clin Oncol 17 832–845
R Mulhern J Kepner P Thomas F Armstrong H Friedman L Kun (1998) ArticleTitleNeuropsychologic functioning of survivors of childhood medulloblastoma randomized to received conventional or reduced-dose craniospinal irradiation: a Pediatric Oncologic Group study J Clin Oncol 16 1723–1728
S Schmandt J Kühl (1998) ArticleTitleChemotherapy as prophylaxis and treatment of meningosis in children less than 3 years of age with medulloblastoma J Neuro-Oncol 38 187–192
SB Lansky MA List LL Lansky C Ritter-Sterr D Miller (1987) ArticleTitleThe measurement of performance in childhood cancer patients Cancer 60 1651–1656
J Sevilla M Gonzalez-Vicent L Madero F García-Sanchez MA Diaz (2002) ArticleTitleGranulocyte colony-stimulating factor alone at 12 μg/kg twice a day for 4 days for peripheral blood progenitor cell priming in pediatric patients Bone Marrow Transplant 30 417–420
A Trotti R Byhardt J Stetz C Gwede B Corn K Fu L Gunderson B McCormick M Morrisintegral T Rich W Shipley W Curran (2000) ArticleTitleCommon toxicity criteria: version 2.0 an improved reference for grading the acute effects of cancer treatment: impact of radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47 IssueID1 13–47 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00559-3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3itlCjsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10758303
EL Kaplan P Meier (1958) ArticleTitleNon-parametric estimation from incomplete observations J Am Stat Assoc 3 457–481
L Madero MG Vicent J Sevilla M Prudencio F Rodríguez MA Díaz (2002) ArticleTitleEngraftment syndrome in children undergoing autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 30 355–358
JC Allon F Epstein (1982) ArticleTitleMedulloblastoma and other primary malignant neuroectodermal tumor of the CNS: the effect of age and the patients extent of disease on prognosis J Neurosurg 57 446–451
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Martínez, A., Lassaletta, A., González-Vicent, M. et al. High-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue for children with high risk and recurrent medulloblastoma and supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors. J Neurooncol 71, 33–38 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-4527-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-4527-4