Abstract
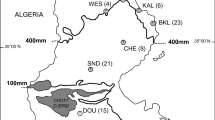
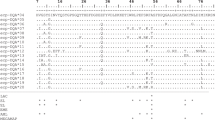
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are transmembrane proteins of the innate immune system, composed of the ectodomain involved in pathogen recognition and the intracellular Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain important for downstream signal transduction. Here, we analyze the genetic variability of TIR nucleotide and amino-acid sequences of the TLR2 gene in 243 brown hares from Europe and the Middle East and tested for the presence of selection signals and spatial structuring. TLR2 TIR domain sequences were PCR amplified and sequenced, while genotyping was performed by phasing. Genetic diversity indices were calculated in DnaSP and Arlequin, while presence of selection signals was tested using MEGA and the Datamonkey web server. The presence of spatial patterns in TIR sequence distribution was tested by spatial Principal Component Analysis (sPCA) in adegenet. A total of 13 haplotypes were revealed with haplotype diversity of 0.424, and nucleotide diversity (π) of 0.00138. Two spatial clusters were revealed: “Anatolia/Middle East” and “Europe”. In Anatolia the two most prevalent amino-acid variants, A and B (the latter being the most ancestral) were maintained at similar frequencies; but in Europe a shift in genotype frequencies was observed as well as a higher number of nonsynonymous substitutions giving rise to novel amino-acid protein variants originating from the evolutionarily younger protein variant. Molecular diversity (haplotype and nucleotide diversity) indices were significantly higher in the “Anatolia/Middle East” cluster. A signal of purifying selection was detected acting on the TIR sequences.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roach JC, Glusman G, Rowen L, Kaur A, Purcell MK, Smith KD, Hood LE, Aderem A (2005) The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(27):9577–9582
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11(5):373
Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T (2001) Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol 2(8):675
Kawai T, Akira S (2006) TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ 13(5):816
Barbalat R, Lau L, Locksley RM, Barton GM (2009) Toll-like receptor 2 on inflammatory monocytes induces type I interferon in response to viral but not bacterial ligands. Nat Immunol 10(11):1200
Gay NJ, Gangloff M (2007) Structure and function of Toll receptors and their ligands. Annu Rev Biochem 76:141–165
Farhat K, Riekenberg S, Heine H, Debarry J, Lang R, Mages J, Buwitt-Beckmann U, Röschmann K, Jung G, Wiesmüller KH, Ulmer AJ (2008) Heterodimerization of TLR2 with TLR1 or TLR6 expands the ligand spectrum but does not lead to differential signaling. J Leukoc Biol 83(3):692–701
Merx S, Zimmer W, Neumaier M, Ahmad-Nejad P (2006) Characterization and functional investigation of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the human TLR5 gene. Human mutat 27(3):293
Bhide MR, Mucha R, Mikula I, Kisova L, Skrabana R, Novak M (2009) Novel mutations in TLR genes cause hyporesponsiveness to Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis infection. BMC genet 10(1):21
Ben-Ali M, Barbouche MR, Bousnina S, Chabbou A, Dellagi K (2004) Toll-like receptor 2 Arg677Trp polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis in Tunisian patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11(3):625–626
O'Connell D (2007) Host response: genital herpes takes its toll. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(10):746
Mikami T, Miyashita H, Takatsuka S, Kuroki Y, Matsushima N (2012) Molecular evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors: evolutionary rate difference between their leucine-rich repeats and their TIR domains. Gene 503(2):235–243
Hughes AL, Packer B, Welch R, Chanock SJ, Yeager M (2005) High level of functional polymorphism indicates a unique role of natural selection at human immune system loci. Immunogenetics 57(11):821–827
Ferrer-Admetlla A, Bosch E, Sikora M, Marquès-Bonet T, Ramírez-Soriano A, Muntasell A, Navarro A, Lazarus R, Calafell F, Bertranpetit J, Casals F (2008) Balancing selection is the main force shaping the evolution of innate immunity genes. J Immunol 181(2):1315–1322
Mukherjee S, Sarkar-Roy N, Wagener DK, Majumder PP (2009) Signatures of natural selection are not uniform across genes of innate immune system, but purifying selection is the dominant signature. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(17):7073–7078
Majumder PP (2010) Pathogen pressure and molecular evolutionary genetics of innate immunity genes in humans. Ongoing Saga of Evolution. Springer, New Delhi, In Nature at Work
Chapman JR, Hellgren O, Helin AS, Kraus RH, Cromie RL, Waldenström J (2016) The evolution of innate immune genes: purifying and balancing selection on β-defensins in waterfowl. Mol Biol Evol 33(12):3075–3087
Areal H, Abrantes J, Esteves PJ (2011) Signatures of positive selection in Toll-like receptor (TLR) genes in mammals. BMC Evol Biol 11(1):368
Jann OC, Werling D, Chang JS, Haig D, Glass EJ (2008) Molecular evolution of bovine Toll-like receptor 2 suggests substitutions of functional relevance. BMC Evol Biol 8(1):288
Tschirren B, Råberg L, Westerdahl H (2011) Signatures of selection acting on the innate immunity gene Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) during the evolutionary history of rodents. J Evol Biol 24(6):1232–1240
Smith SA, Haig D, Emes RD (2014) Novel ovine polymorphisms and adaptive evolution in mammalian TLR2 suggest existence of multiple pathogen binding regions. Gene 540(2):217–225
Xu S, Tian R, Lin Y, Yu Z, Zhang Z, Niu X, Wang X, Yang G (2019) Widespread positive selection on cetacean TLR extracellular domain. Mol Immunol 106:135–142
Nakajima T, Ohtani H, Satta Y, Uno Y, Akari H, Ishida T, Kimura A (2008) Natural selection in the TLR-related genes in the course of primate evolution. Immunogenetics 60(12):727–735
Coetzer WG, Turner TR, Schmitt CA, Grobler JP (2018) Adaptive genetic variation at three loci in South African vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus pygerythrus) and the role of selection within primates. PeerJ 6:e4953
Barreiro LB, Ben-Ali M, Quach H, Laval G, Patin E, Pickrell JK, Bouchier C, Tichit M, Neyrolles O, Gicquel B, Kidd JR (2009) Evolutionary dynamics of human Toll-like receptors and their different contributions to host defense. PLoS Genet 5(7):e1000562
Seabury CM, Seabury PM, Decker JE, Schnabel RD, Taylor JF, Womack JE (2010) Diversity and evolution of 11 innate immune genes in Bos taurus taurus and Bos taurus indicus cattle. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(1):151–156
Mukherjee S, Ganguli D, Majumder PP (2014) Global footprints of purifying selection on toll-like receptor genes primarily associated with response to bacterial infections in humans. Genome Biol Evol 6(3):551–558
Wibbelt G, Frölich K (2005) Infectious diseases in European brown hare (Lepus europaeus). Wildl Biol Pract 17:86–93
Goüy de Bellocq J, Suchentrunk F, Baird SJ, Schaschl H (2009) Evolutionary history of an MHC gene in two leporid species: characterisation of Mhc-DQA in the European brown hare and comparison with the European rabbit. Immunogenetics 61(2):131
Campos JL, Goüy de Bellocq J, Schaschl H, Suchentrunk F (2011) MHC class II DQA gene variation across cohorts of brown hares (Lepus europaeus) from eastern Austria: testing for different selection hypotheses. Mamm Biol-Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 76(3):251–257
Smith S, Goüy de Bellocq J, Suchentrunk F, Schaschl H (2011) Evolutionary genetics of MHC class II beta genes in the brown hare Lepus europaeus. Immunogenetics 63(11):743–751
Koutsogiannouli EA, Moutou KA, Sarafidou T, Stamatis C, Spyrou V, Mamuris Z (2009) Major histocompatibility complex variation at class II DQA locus in the brown hare (Lepus europaeus). Mol Ecol 18(22):4631–4649
Koutsogiannouli EA, Moutou KA, Stamatis C, Walter L, Mamuris Z (2014) Genetic variation in the major histocompatibility complex of the European brown hare (Lepus europaeus) across distinct phylogeographic areas. Immunogenetics 66(6):379––392
Neves F, Águeda-Pinto A, Pinheiro A, Abrantes J, Esteves PJ (2019) Strong selection of the TLR2 coding region among the Lagomorpha suggests an evolutionary history that differs from other mammals. Immunogenetics 71(5–6):437–443
Awadi A, Ben Slimen H, Smith S, Kahlen J, Makni M, Suchentrunk F (2018) Genetic diversity of the toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in hare (Lepus capensis) populations from Tunisia. CR Biol 341(6):315–324
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, NY
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Human Genet 68(4):978–989
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25(11):1451–1452
Rousset F (2008) genepop’007: a complete re-implementation of the genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol ecol resour 8(1):103–106
Peakall RO, Smouse PE (2006) GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6(1):288–295
Excoffier L, Lischer HE (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10(3):564–567
Leigh JW, Bryant D (2015) popart: full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol Evol 6(9):1110–1116
Jombart T (2008) adegenet: a R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 24(11):1403–1405
RCore TE (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Jombart T, Devillard S, Dufour AB, Pontier D (2008) Revealing cryptic spatial patterns in genetic variability by a new multivariate method. Heredity 101(1):92
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549
Weaver S, Shank SD, Spielman SJ, Li M, Muse SV, Kosakovsky Pond SL (2018) Datamonkey 2.0: a modern web application for characterizing selective and other evolutionary processes. Mol Biol Evol 35(3):773–777
Yang J, Yan R, Roy A, Xu D, Poisson J, Zhang Y (2015) The I-TASSER Suite: protein structure and function prediction. Nat Methods 12(1):7
Roy A, Kucukural A, Zhang Y (2010) I-TASSER: a unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat Protoc 5(4):725
Xu Y, Tao X, Shen B, Horng T, Medzhitov R, Manley JL, Tong L (2000) Structural basis for signal transduction by the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domains. Nature 408(6808):111
Choi Y, Chan AP (2015) PROVEAN web server: a tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 31(16):2745–2747
Ve T, Williams SJ, Kobe B (2015) Structure and function of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR) domains. Apoptosis 20(2):250–261
Jebanathirajah JA, Peri S, Pandey A (2002) Toll and interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing proteins in plants: a genomic perspective. Trends Plant Sci 7(9):388–391
Turner JD (2003) A bioinformatic approach to the identification of bacterial proteins interacting with Toll—interleukin 1 receptor—resistance (TIR) homology domains. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 37(1):13–21
Hughes AL, Packer B, Welch R, Bergen AW, Chanock SJ, Yeager M (2003) Widespread purifying selection at polymorphic sites in human protein-coding loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(26):15754–15757
Kasapidis P, Suchentrunk F, Magoulas A, Kotoulas G (2005) The shaping of mitochondrial DNA phylogeographic patterns of the brown hare (Lepus europaeus) under the combined influence of Late Pleistocene climatic fluctuations and anthropogenic translocations. Mol Phylogenet Evol 34(1):55–66
Stamatis C, Suchentrunk F, Moutou KA, Giacometti M, Haerer G, Djan M, Vapa L, Vukovic M, Tvrtković N, Sert H, Alves PC, Mammuris Z (2009) Phylogeography of the brown hare (Lepus europaeus) in Europe: a legacy of south-eastern Mediterranean refugia? J Biogeogr 36(3):515–528
Djan M, Stefanović M, Veličković N, Lavadinović V, Alves PC, Suchentrunk F (2017) Brown hares (Lepus europaeus Pallas, 1778) from the Balkans: a refined phylogeographic model. Hystrix. Italian J Mammal 28(2):186–193
Stefanović M, Djan M, Veličković N, Beuković D, Lavadinović V, Zhelev CD, Demirbas Y, Paule L, Gedeon CI, Mamuris Z, Posautz A, Beiglbock C, Kubber-Heiss A, Suchentrunk F (2019) Positive selection and precipitation effects on the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6 gene in brown hares (Lepus europaeus) under a phylogeographic perspective. PLoS ONE 14(11):e0224902
Demirbaş Y, Albayrak İ, Koca AÖ, Stefanović M, Knauer F, Suchentrunk F (2019) Spatial genetics of brown hares (Lepus europaeus Pallas, 1778) from Turkey: different gene pool architecture on either side of the Bosphorus? Mammal Biol 94:77–85
O'Neill LA, Bowie AG (2007) The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 7(5):353
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282(5396):2085–2088
Verstak B, Arnot CJ, Gay NJ (2013) An alanine-to-proline mutation in the BB-loop of TLR3 Toll/IL-1R domain switches signalling adaptor specificity from TRIF to MyD88. J Immunol 191(12):6101–6109
Mahita J, Rv S (2018) Probing subtle conformational changes induced by phosphorylation and point mutations in the TIR domains of TLR 2 and TLR 3. Proteins: Struct, Funct, Bioinform 86(5):524–535
Tsai CJ, Del Sol A, Nussinov R (2009) Protein allostery, signal transmission and dynamics: a classification scheme of allosteric mechanisms. Mol BioSyst 5(3):207–216
Qiu Y, Ding Y, Zou L, Tan Z, Liu T, Fu X, Xu W (2013) Divergent roles of amino acid residues inside and outside the BB loop affect human Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2/2, TLR2/1 and TLR2/6 responsiveness. PLoS ONE 8(4):e61508
McKelvey AC, Lear TB, Dunn SR, Evankovich J, Londino JD, Bednash JS, Zhang Y, McVerry BJ, Liu Y, Chen BB (2016) RING finger E3 ligase PPP1R11 regulates TLR2 signaling and innate immunity. Elife 5:e18496
Conte GL, Hodgins KA, Yeaman S, Degner JC, Aitken SN, Rieseberg LH, Whitlock MC (2017) Bioinformatically predicted deleterious mutations reveal complementation in the interior spruce hybrid complex. BMC Genomics 18(1):970
Nyman T, Stenmark P, Flodin S, Johansson I, Hammarström M, Nordlund P (2008) The crystal structure of the human toll-like receptor 10 cytoplasmic domain reveals a putative signaling dimer. J Biol Chem 283(18):11861–11865
Acknowledgements
We thank all local hunters, Prof. Philip U. Alkon, PhD (Israel), Orsolya Vincze, PhD (Romania) and Sim Broekhuizen, PhD (The Netherlands) for helping collecting the samples. Partial financial support for this work was provided by Wildlife Research—Franz Suchentrunk (Project No. 1/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefanović, M., Djan, M., Veličković, N. et al. Purifying selection shaping the evolution of the Toll-like receptor 2 TIR domain in brown hares (Lepus europaeus) from Europe and the Middle East. Mol Biol Rep 47, 2975–2984 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05382-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05382-x