Abstract
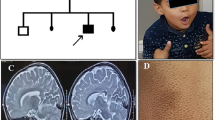
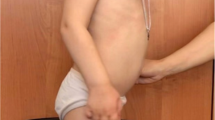
Multiple Sulfatase Deficiency (MSD) is a rare autosomal recessive disease in which the activities of all sulfatases are reduced; its estimated prevalence is 1:1.4 million births. The disease is caused by mutations in SUMF1, which encodes an enzyme involved in the post-translational modification of sulfatases. The MSD phenotype is a combination of the clinical features found in diseases resulting from a deficiency of the individual sulfatases; i.e., mucopolysaccharidosis II, IIIA, IIID, IVA and VI, metachromatic leukodystrophy, X-linked ichthyosis, and the X-linked recessive form of chondrodysplasia punctata. We describe herein the first case of a Brazilian patient with MSD. The case was initially diagnosed as having mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS), due to skeletal alterations, coarse facial features, and urinary excretion of dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate. Later, after a detailed biochemical investigation, the diagnosis of MSD was established. The analysis of the SUMF1 showed the patient was a compound heterozygote for two novel mutations (p.R349G and p.F244S). This case illustrates the challenges in the diagnosis of a disease considered rare, such as MSD. We point out that the availability of therapy for certain MPS disorders necessitates correct disease assignment, and the need to exclude the likelihood of MSD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
al Aqeel A, Ozand PT, Brismar J, Gascon GG, Brismar G, Nester M, Sakati N (1992) Saudi variant of multiple sulfatase deficiency. J Child Neurol 7(Suppl):S12–S21
Cosma MP, Pepe S, Parenti G, Settembre C, Annunziata I, Wade-Martins R, Di Domenico C, Di Natale P, Mankad A, Cox B, Uziel G, Mancini GM, Zammarchi E, Donati MA, Kleijer WJ, Filocamo M, Carrozzo R, Carella M, Ballabio A (2004) Molecular and functional analysis of SUMF1 mutations in multiple sulfatase deficiency. Hum Mutat 23(6):576–581
Dierks T, Schmidt B, Borissenko LV, Peng J, Preusser A, Mariappan M, von Figura K (2003) Multiple sulfatase deficiency is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the human C(alpha)-formylglycine generating enzyme. Cell 113:435–444
Dierks T, Dickmanns A, Preusser-Kunze A, Schmidt B, Mariappan M, von Figura K, Ficner R, Rudolph MG (2005) Molecular basis for multiple sulfatase deficiency and mechanism for formylglycine generation of the human formylglycine-generating enzyme. Cell 121(4):541–552
Dierks T, Schlotawa L, Frese MA, Radhakrishnan K, von Figura K, Schmidt B (2008) Molecular basis of multiple sulfatase deficiency, mucolipidosis II/III and Niemann-Pick C1 disease—Lysosomal storage disorders caused by defects of non-lysosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta; Dec 10. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 19124046
Hopwood JJ, Ballabiao A (2001) Multiple sulfatase deficiency and the nature of the sulfatase family. In: Scriver CR, Baudet AL, Sly WS (eds) The metabolic and molecular basis of inherited disease, vol III, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 3725–3732
Mancini GMS, van Diggelen OP, Hujimans JG, Stroin H, de Coo RFM (2001) Pitfalls in the diagnosis of multiple sulfatase deficiency. Neuropediatrics 32:38–40
Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF (1999) Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 281:249–254
Parenti G, Meroni G, Ballabio A (1997) The sulfatase gene family. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7(3):386–391
PolyPhen. http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph
Preusser-Kunze A, Mariappan M, Schmidt B, Gande SL, Mutenda K, Wenzel D, von Figura K, Dierks T (2005) Molecular characterization of the human Calpha-formylglycine-generating enzyme. J Biol Chem 280(15):14900–14910
Sandberg S, Charnas L, Braunlin E, Bjoraker K, Deanching M, Hoganson G, Rimell R, Whitley C (2007) Treatment of multiple sulfatase deficiency with recombinant human arylsulfatase B. Mol Genet Metab 92(4):31
Schlotawa L, Steinfeld R, von Figura K, Dierks T, Gärtner J (2008) Molecular analysis of SUMF1 mutations: stability and residual activity of mutant formylglycine-generating enzyme determine disease severity in multiple sulfatase deficiency. Hum Mutat 29(1):205–218
Yiş U, Pepe S, Kurul SH, Ballabio A, Cosma MP, Dirik E (2008) Multiple sulfatase deficiency in a Turkish family resulting from a novel mutation. Brain Dev 30(5):374–377
Acknowledgements
The authors declare that they have no conflicting financial interests. The authors would like to thank Dr. Roberto Giugliani, Dr. Simone Fagondes, Dr. Diane Marinho, and Dr. Jefferson Becker for their help in evaluating this patient; they would also like to thank the MPS-BRAZIL Network for its support for the metabolic investigation. This study was conducted with the support of FIPE/HCPA and CNPq/Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Artigalás, O.A., da Silva, L.R., Burin, M. et al. Multiple sulfatase deficiency: clinical report and description of two novel mutations in a Brazilian patient. Metab Brain Dis 24, 493–500 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-009-9151-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-009-9151-8