Abstract
Context
Characterized by intensive urban sprawl and continuous cropland shrinkage, the unprecedented urbanization process has profoundly reshaped China’s landscape over the past four decades. However, the interaction between urban expansion and cropland loss in China at a finer spatiotemporal resolution remains unclear.
Objectives
This study aims to quantify and compare the rates, patterns, dynamics, and interactions of urban expansion and cropland loss in 14 Chinese cities during 1980–2015.
Methods
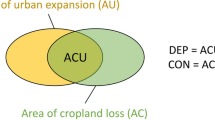
Multiple landscape metrics were calculated to quantify the magnitudes, rates, and patterns of urban expansion and cropland loss for each city. The standard deviation ellipse analysis and two quantitative indices (the dependence and the contribution of urban expansion on cropland loss) were used to characterize the relationship between urban expansion and cropland loss.
Results
The pattern of rapid urban expansion and extensive cropland loss was observed across all selected cities (except for Harbin), with the averaged expansion area of 764.17 km2 and averaged loss area of 650.83 km2 per city. The primary mode of urbanization was the edge-expansion (6889.22 km2, 60.01%), followed by the infilling (2767.32 km2, 24,11%) and the outlying (1822.72 km2, 15.88%). Urban expansion was identified to be the dominant driver of cropland loss, accounting for 84.99% of the newly expanded urban land and 74.36% of the lost cropland in total, thus leading to a more spatially irregular and fragmented distribution of the cropland.
Conclusions
The balance between urbanization and land protection is still challenging. Here we advocate more effective policy-driven practices to protect China’s existing cropland for food security and sustainable development goals.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkama R, Cescatti A (2016) Biophysical climate impacts of recent changes in global forest cover. Science 351(6273):600–604
Bai X, Shi P, Liu Y (2014) Society: realizing China’s urban dream. Nat News 509(7499):158
Chen B, Nie Z, Chen Z, Xu B (2017) Quantitative estimation of 21st-century urban greenspace changes in Chinese populous cities. Sci Total Environ 609:956–965
Cheng L, Xia N, Jiang P, Zhong L, Pian Y, Duan Y, Huang Q, Li M (2015) Analysis of farmland fragmentation in China Modernization Demonstration Zone since “Reform and Openness”: a case study of South Jiangsu Province. Sci Rep 5:11797
d’Amour CB, Reitsma F, Baiocchi G, Barthel S, Güneralp B, Erb KH, Haberl H, Creutzig F, Seto KC (2017) Future urban land expansion and implications for global croplands. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(34):8939–8944
Deng X, Huang J, Rozelle S, Zhang J, Li Z (2015) Impact of urbanization on cultivated land changes in China. Land Use Policy 45:1–7
Ding C, Lichtenberg E (2011) Land and urban economic growth in China. J Reg Sci 51(2):299–317
Fei W, Zhao S (2019) Urban land expansion in China’s six megacities from 1978 to 2015. Sci Total Environ 664:60–71
Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309(5734):570–574
Forman R (2014) Land mosaics: the ecology of landscapes and regions 1995. Springer, Berlin
Gao X, Cheng W, Wang N, Liu Q, Ma T, Chen Y, Zhou C (2019) Spatio-temporal distribution and transformation of cropland in geomorphologic regions of China during 1990–2015. J Geog Sci 29(2):180–196
Gong J (2002) Clarifying the standard deviational ellipse. Geogr Anal 34(2):155–167
Gong P, Liang S, Carlton EJ, Jiang Q, Wu J, Wang L, Remais JV (2012) Urbanisation and health in China. The Lancet 379(9818):843–852
Gong P, Wang J, Yu L, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Liang L, Niu Z, Huang X, Fu H, Liu S, Li C, Li X, Fu W, Liu C, Xu Y, Wang X, Cheng Q, Hu L, Yao W, Zhang H, Zhu P, Zhao Z, Zhang H, Zheng Y, Ji L, Zhang Y, Chen H, Yan A, Guo J, Yu L, Wang L, Liu X, Shi T, Zhu M, Chen Y, Yang G, Tang P, Xu B, Giri C, Clinton N, Zhu Z, Chen J, Chen J (2013) Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: first mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM + data. Int J Remote Sens 34(7):2607–2654
Gong J, Jiang C, Chen W, Chen X, Liu Y (2018) Spatiotemporal dynamics in the cultivated and built-up land of Guangzhou: insights from zoning. Habitat Int 82:104–112
Gong P, Chen B, Li X, Liu H, Wang J, Bai Y, Chen J, Chen X, Fang L, Feng S, Feng Y, Gong Y, Gu H, Huang H, Huang X, Jiao H, Kang Y, Lei G, Li A, Li X, Li X, Li Y, Li Z, Li Z, Liu C, Liu C, Liu M, Liu S, Mao W, Miao C, Ni H, Pan Q, Qi S, Ren Z, Shan Z, Shen S, Shi M, Song Y, Su M, Ping Suen H, Sun B, Sun F, Sun J, Sun L, Sun W, Tian T, Tong X, Tseng Y, Tu Y, Wang H, Wang L, Wang X, Wang Z, Wu T, Xie Y, Yang J, Yang J, Yuan M, Yue W, Zeng H, Zhang K, Zhang N, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Zhao F, Zheng Y, Zhou Q, Clinton N, Zhu Z, Xu B (2019a) Mapping essential urban land use categories in China (EULUC-China): preliminary results for 2018. Sci Bull 65(3):182–187
Gong P, Liu H, Zhang M, Li C, Wang J, Huang H, Clinton N, Ji L, Li W, Bai Y, Chen B, Xu B, Zhu Z, Yuan C, Suen HP, Guo J, Xua N, Lia W, Zhao Y, Yang J, Yu C, Wang X, Fu H, Yu L, Dronova I, Hui F, Cheng X, Shi X, Xiao F, Liu Q, Song L (2019b) Stable classification with limited sample: transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci Bull 64(6):370–373
Gong P, Li X, Wang J, Bai Y, Chen B, Hu T, Liu X, Xu B, Yang J, Zhang W, Zhou Y (2020) Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens Environ 236:111510
Grimm NB, Faeth SH, Golubiewski NE, Redman CL, Wu J, Bai X, Briggs JM (2008) Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 319(5864):756–760
He C, Liu Z, Tian J, Ma Q (2014) Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: a multiscale landscape perspective. Glob Change Biol 20(9):2886–2902
He C, Gao B, Huang Q, Ma Q, Dou Y (2017) Environmental degradation in the urban areas of China: evidence from multi-source remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 193:65–75
Hu Y, Kong X, Zheng J, Sun J, Wang L, Min M (2018) Urban expansion and farmland loss in Beijing during 1980–2015. Sustainability 10(11):3927
Imhoff ML, Bounoua L, Ricketts T, Loucks C, Harriss R, Lawrence WT (2004) Global patterns in human consumption of net primary production. Nature 429(6994):870
Jiang L, Deng X, Seto KC (2012) Multi-level modeling of urban expansion and cultivated land conversion for urban hotspot counties in China. Landsc Urban Plan 108(2–4):131–139
Ju H, Zhang Z, Zhao X, Wang X, Wu W, Yi L, Wen Q, Liu F, Xu J, Hu S, Zuo L (2018) The changing patterns of cropland conversion to built-up land in China from 1987 to 2010. J Geog Sci 28(11):1595–1610
Kalnay E, Cai M (2003) Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 423(6939):528
Kennedy CM, Oakleaf JR, Theobald DM, Baruch-Mordo S, Kiesecker J (2019) Managing the middle: a shift in conservation priorities based on the global human modification gradient. Glob Change Biol 25(3):811–826
Kuang W (2011) Simulating dynamic urban expansion at regional scale in Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan Metropolitan Area. J Geog Sci 21(2):317
Kuang W, Chi W, Lu D, Dou Y (2014) A comparative analysis of megacity expansions in China and the US: patterns, rates and driving forces. Landsc Urban Plan 132:121–135
Kuang W, Liu J, Dong J, Chi W, Zhang C (2016) The rapid and massive urban and industrial land expansions in China between 1990 and 2010: a CLUD-based analysis of their trajectories, patterns, and drivers. Landsc Urban Plan 145:21–33
Le Quéré C, Andrew RM, Canadell JG, Sitch S, Korsbakken JI, Peters GP, Manning AC, Boden TA, Tans PP, Houghton RA, Keeling RF, Alin S, Andrews OD, Anthoni P, Barbero L, Bopp L, Chevallier F, Chini LP, Ciais P, Currie K, Delire C, Doney SC, Friedlingstein P, Gkritzalis T, Harris I, Hauck J, Haverd V, Hoppema M, Klein Goldewijk K, Jain AK, Kato E, Körtzinger A, Landschützer P, Lefèvre N, Lenton A, Lienert S, Lombardozzi D, Melton JR, Metzl N, Millero F, Monteiro PMS, Munro DR, Nabel JEMS, Nakaoka S, O'Brien K, Olsen A, Omar AM, Ono T, Pierrot D, Poulter B, Rödenbeck C, Salisbury J, Schuster U, Schwinger J, Séférian R, Skjelvan I, Stocker BD, Sutton AJ, Takahashi T, Tian H, Tilbrook B, van der Laan-Luijkx IT, van der Werf GR, Viovy N, Walker AP, Wiltshire AJ, Zaehle S (2016) Global carbon budget 2016. Earth Syst Sci Data 8(2):605–649
Lefever DW (1926) Measuring geographic concentration by means of the standard deviational ellipse. Am J Sociol 32(1):88–94
Li X, Yeh AG-O (2004) Analyzing spatial restructuring of land use patterns in a fast growing region using remote sensing and GIS. Landsc Urban Plan 69(4):335–354
Li C, Li J, Wu J (2013a) Quantifying the speed, growth modes, and landscape pattern changes of urbanization: a hierarchical patch dynamics approach. Landsc Ecol 28(10):1875–1888
Li J, Li C, Zhu F, Song C, Wu J (2013b) Spatiotemporal pattern of urbanization in Shanghai, China between 1989 and 2005. Landsc Ecol 28(8):1545–1565
Li X, Zhou W, Ouyang Z (2013c) Forty years of urban expansion in Beijing: what is the relative importance of physical, socioeconomic, and neighborhood factors? Appl Geogr 38:1–10
Li Y, Cong C, Wang Y, Liu Y (2014) Urban-rural transformation and farmland conversion in China: the application of the environmental Kuznets Curve. J Rural Stud 36:311–317
Liang C, Penghui J, Manchun L, Liyan W, Yuan G, Yuzhe P, Nan X, Yuewei D, Qiuhao H (2015) Farmland protection policies and rapid urbanization in China: a case study for Changzhou City. Land Use Policy 48:552–566
Lichtenberg E, Ding C (2008) Assessing farmland protection policy in China. Land Use Policy 25(1):59–68
Liu J, Tian H, Liu M, Zhuang D, Melillo JM, Zhang Z (2005) China’s changing landscape during the 1990 s: large-scale land transformations estimated with satellite data. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021649
Liu X, Li X, Chen Y, Tan Z, Li S, Ai B (2010) A new landscape index for quantifying urban expansion using multi-temporal remotely sensed data. Landsc Ecol 25(5):671–682
Liu Y, Fang F, Li Y (2014) Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 40:6–12
Liu G, Zhang L, You H (2015a) Spatiotemporal dynamics of arable land in the Nanjing metropolitan region, China. Environ Earth Sci 73(11):7183–7191
Liu T, Liu H, Qi Y (2015b) Construction land expansion and cultivated land protection in urbanizing China: insights from national land surveys, 1996–2006. Habitat Int 46:13–22
Liu F, Zhang Z, Shi L, Zhao X, Xu J, Yi L, Liu B, Wen Q, Hu S, Wang X, Zuo L, Li N, Li M (2016) Urban expansion in China and its spatial-temporal differences over the past four decades. J Geogr Sci 26(10):1477–1496
Liu F, Zhang Z, Zhao X, Wang X, Zuo L, Wen Q, Yi L, Xu J, Hu S, Liu B (2019) Chinese cropland losses due to urban expansion in the past four decades. Sci Total Environ 650:847–857
Long H, Ge D, Zhang Y, Tu S, Qu Y, Ma L (2018) Changing man-land interrelations in China’s farming area under urbanization and its implications for food security. J Environ Manag 209:440–451
Mao D, Wang Z, Wu J, Wu B, Zeng Y, Song K, Yi K, Luo L (2018) China’s wetlands loss to urban expansion. Land Degrad Dev 29(8):2644–2657
McDonald RI, Kareiva P, Forman RT (2008) The implications of current and future urbanization for global protected areas and biodiversity conservation. Biol Conserv 141(6):1695–1703
McGarigal K (2014) FRAGSTATS help. Documentation for FRAGSTATS 4
McKinney ML (2002) Urbanization, biodiversity, and conservation: the impacts of urbanization on native species are poorly studied, but educating a highly urbanized human population about these impacts can greatly improve species conservation in all ecosystems. Bioscience 52(10):883–890
Qiu B, Li H, Tang Z, Chen C, Berry J (2020) How cropland losses shaped by unbalanced urbanization process? Land Use Policy 96:104715
Satterthwaite D, McGranahan G, Tacoli C (2010) Urbanization and its implications for food and farming. Philos Trans R Soc B: Biol Sci 365(1554):2809–2820
Schneider A, Mertes C (2014) Expansion and growth in Chinese cities, 1978–2010. Environ Res Lett 9(2):024008
Seto KC, Fragkias M (2005) Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban land-use change in four cities of China with time series landscape metrics. Landsc Ecol 20(7):871–888
Seto KC, Ramankutty N (2016) Hidden linkages between urbanization and food systems. Science 352(6288):943–945
Seto KC, Güneralp B, Hutyra LR (2012) Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(40):16083–16088
Song W (2014) Decoupling cultivated land loss by construction occupation from economic growth in Beijing. Habitat Int 43:198–205
Song W, Pijanowski BC, Tayyebi A (2015) Urban expansion and its consumption of high-quality farmland in Beijing, China. Ecol Ind 54:60–70
Song J, Ye J, Zhu E, Deng J, Wang K (2016) Analyzing the impact of highways associated with farmland loss under rapid urbanization. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 5(6):94
Song X-P, Hansen MC, Stehman SV, Potapov PV, Tyukavina A, Vermote EF, Townshend JR (2018) Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 560(7720):639
Song Y, Chen B, Kwan M-P (2020) How does urban expansion impact people’s exposure to green environments? A comparative study of 290 Chinese cities. J Clean Prod 246:119018
Su S, Jiang Z, Zhang Q, Zhang Y (2011) Transformation of agricultural landscapes under rapid urbanization: a threat to sustainability in Hang-Jia-Hu region, China. Appl Geogr 31(2):439–449
Sun Y, Zhao S (2018) Spatiotemporal dynamics of urban expansion in 13 cities across the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration from 1978 to 2015. Ecol Ind 87:302–313
Sun Z, You L, Müller D (2018) Synthesis of agricultural land system change in China over the past 40 years. Taylor & Francis, Milton Park
Tan M, Li X, Xie H, Lu C (2005) Urban land expansion and arable land loss in China—a case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 22(3):187–196
The National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China (1998) The law of land administration of the People’s Republic of China
The State Council of the People’s Republic of China (1994) Regulations on the protection of prime farmland
Theobald DM, Kennedy C, Chen B, Oakleaf J, Baruch-Mordo S, Kiesecker J (2020) Earth transformed: detailed mapping of global human modification from 1990 to 2017. Earth Sys Sci Data 12(3):1953–1972
Tian G, Jiang J, Yang Z, Zhang Y (2011) The urban growth, size distribution and spatio-temporal dynamic pattern of the Yangtze River Delta megalopolitan region, China. Ecol Model 222(3):865–878
Tu Y, Chen B, Yu L, Xin Q, Gong P, Xu B (2019) Urban-expansion driven farmland loss follows with the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: evidence from temporal analysis in Beijing, China. Geoinformatics in sustainable ecosystem and society. Springer, Berlin, pp 394–412
Tu Y, Chen B, Zhang T, Xu B (2020a) Regional mapping of essential urban land use categories in China: a segmentation-based approach. Remote Sens 12(7):1058
Tu Y, Lang W, Yu L, Li Y, Jiang J, Qin Y, Wu J, Chen T, Xu B (2020b) Improved mapping results of 10 m resolution land cover classification in Guangdong, China using multisource remote sensing data with google Earth engine. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 13:5384–5397
Turner BL, Lambin EF, Reenberg A (2007) The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(52):20666–20671
van Vliet J (2019) Direct and indirect loss of natural area from urban expansion. Nat Sustain 2(8):755–763
Wahnschafft R, Wei F (2015) Urban China: toward efficient, inclusive, and sustainable urbanization The World Bank and the Development Research Center of the State Council, People’s Republic of China World Bank, Washington, DC. In: Natural resources forum, vol 39. Wiley Online Library, pp 151–152
Wang L, Li C, Ying Q, Cheng X, Wang X, Li X, Hu L, Liang L, Yu L, Huang H, Gong P (2012) China’s urban expansion from 1990 to 2010 determined with satellite remote sensing. Chin Sci Bull 57(22):2802–2812
Wang B, Shi W, Miao Z (2015) Confidence analysis of standard deviational ellipse and its extension into higher dimensional Euclidean space. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0118537
Weng Q (2002) Land use change analysis in the Zhujiang Delta of China using satellite remote sensing, GIS and stochastic modelling. J Environ Manag 64(3):273–284
Wilson EH, Hurd JD, Civco DL, Prisloe MP, Arnold C (2003) Development of a geospatial model to quantify, describe and map urban growth. Remote Sens Environ 86(3):275–285
Wu J (2014) Urban ecology and sustainability: the state-of-the-science and future directions. Landscape and Urban Planning 125:209–221
Wu J, Xiang W-N, Zhao J (2014) Urban ecology in China: historical developments and future directions. Landsc Urban Plan 125:222–233
Wu W, Zhao S, Zhu C, Jiang J (2015) A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc Urban Plan 134:93–106
Xiao R, Liu Y, Huang X, Shi R, Yu W, Zhang T (2018) Exploring the driving forces of farmland loss under rapidurbanization using binary logistic regression and spatial regression: a case study of Shanghai and Hangzhou Bay. Ecol Ind 95:455–467
Xu Y, Yu L, Peng D, Zhao J, Cheng Y, Liu X, Li W, Meng R, Xu X, Gong P (2020) Annual 30-m land use/land cover maps of China for 1980–2015 from the integration of AVHRR, MODIS and Landsat data using the BFAST algorithm. Sci China Earth Sci 63:1390–1407
Yang C, Zhang C, Li Q, Liu H, Gao W, Shi T, Liu X, Wu G (2020) Rapid urbanization and policy variation greatly drive ecological quality evolution in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area of China: a remote sensing perspective. Ecol Ind 115:106373
Yeh A, Xu J, Yi H (2006) The fourth wave of urbanization in China. City Plan Rev 30(10):13–18
Yu Q, Hu Q, van Vliet J, Verburg PH, Wu W (2018) GlobeLand30 shows little cropland area loss but greater fragmentation in China. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 66:37–45
Zhang Q, Ban Y, Liu J, Hu Y (2011) Simulation and analysis of urban growth scenarios for the Greater Shanghai Area, China. Comput Environ Urban Syst 35(2):126–139
Zhang Z, Wang B, Buyantuev A, He X, Gao W, Wang Y, Yang Z (2019) Urban agglomeration of Kunming and Yuxi cities in Yunnan, China: the relative importance of government policy drivers and environmental constraints. Landsc Ecol 34:663–679
Zhao S, Da L, Tang Z, Fang H, Song K, Fang J (2006) Ecological consequences of rapid urban expansion: Shanghai, China. Front Ecol Environ 4(7):341–346
Zhao S, Zhou D, Zhu C, Qu W, Zhao J, Sun Y, Huang D, Wu W, Liu S (2015) Rates and patterns of urban expansion in China’s 32 major cities over the past three decades. Landsc Ecol 30(8):1541–1559
Zuo L, Zhang Z, Carlson KM, MacDonald GK, Brauman KA, Liu Y, Zhang W, Zhang H, Wu W, Zhao X, Wang X, Liu B, Yi L, Wen Q, Liu F, Xu J, Hu S, Sun F, Gerber JS, West PC (2018) Progress towards sustainable intensification in China challenged by land-use change. Nat Sustain 1(6):304–313
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China under the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFA0600104), the National Key Scientific and Technological Infrastructure project “Earth System Science Numerical Simulator Facility” (EarthLab), and donations from Delos Living LLC and the Cyrus Tang Foundation to Tsinghua University. The authors would like to thank the four anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions, which have greatly improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, Y., Chen, B., Yu, L. et al. How does urban expansion interact with cropland loss? A comparison of 14 Chinese cities from 1980 to 2015. Landscape Ecol 36, 243–263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-020-01137-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-020-01137-y