Abstract
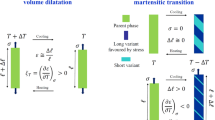
The elastocaloric effect and magnetic performance of Ni50Mn31.5Ti18Cu0.5 shape memory alloy were studied. The analysis of magnetic transformation shows that the transformation temperature of the alloy is close to room temperature. A large unloading rate can make the alloy showing smaller hysteresis and lower plastic deformation, and improve the superplasticity of the alloy. With the increase in loading stress, the cooling effect of the alloy is better. When the loading stress is 600 MPa, the ΔT of the alloy reaches 9 K. The alloy has good cycle stability during 100 cycles. Hence, the refrigeration performance of Ni50Mn31.5Ti18Cu0.5 alloy can be compared with many Ni-Mn-based alloys, which indicates that it is a promising elastocaloric refrigeration material.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, Z., Cong, D., Yuan, Y., Li, R., Zheng, H., Sun, X., Nie, Z., Ren, Y., Wang, Y.: Large room-temperature elastocaloric effect in a bulk polycrystalline Ni-Ti-Cu-Co alloy with low isothermal stress hysteresis. Appl. Mater. Today 21, (2020)
Li, Z., Li, Z., Lu, Y., Lu, X., Zuo, L.: Enhanced elastocaloric effect and refrigeration properties in a Si-doped Ni-Mn-In shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 117, 167–173 (2022)
Qu, Y.H., Cong, D.Y., Li, S.H., Gui, W.Y., Nie, Z.H., Zhang, M.H., Ren, Y., Wang, Y.D.: Simultaneously achieved large reversible elastocaloric and magnetocaloric effects and their coupling in a magnetic shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 151, 41–55 (2018)
Shen, Y., Sun, W., Wei, Z.Y., Shen, Q., Zhang, Y.F., Liu, J.: Orientation dependent elastocaloric effect in directionally solidified Ni-Mn-Sn alloys. Scripta Mater. 163, 14–18 (2019)
Manosa, L., Gonzalez-Alonso, D., Planes, A., Bonnot, E., Barrio, M., Tamarit, J.L., Aksoy, S., Acet, M.: Giant solid-state barocaloric effect in the Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape-memory alloy. Nat Mater 9(6), 478–481 (2010)
Chen, H., Xiao, F., Liang, X., Li, Z., Li, Z., Jin, X., Fukuda, T.: Giant elastocaloric effect with wide temperature window in an Al-doped nanocrystalline Ti–Ni–Cu shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 177, 169–177 (2019)
Chen, J., Lei, L., Fang, G.: Elastocaloric cooling of shape memory alloys: a review. Mater. Today Commun. 28, (2021).
Cong, D., Xiong, W., Planes, A., Ren, Y., Manosa, L., Cao, P., Nie, Z., Sun, X., Yang, Z., Hong, X., Wang, Y.: Colossal elastocaloric effect in ferroelastic Ni-Mn-Ti alloys. Phys Rev Lett 122(25), 255703 (2019)
Jankowska-Sumara, I., Gwizd, P., Majchrowski, A., Soszyński, A.: Electrocaloric effect in pure and Cr doped lead germanate single crystals. Mater. Chem. Phys. 242, (2020)
Kaur, S., Arora, M. Kumar, S., Malhi, P.S., Singh, M., Singh, A.: Abnormal electrocaloric effect near ambient temperature in MgO modified NBT-KBT. Mater. Today Commun. 30, (2022)
Devarajan, U., Esakki Muthu, S., Arumugam, S., Singh, S., Barman, S.R.: Investigation of the influence of hydrostatic pressure on the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Ni2−XMn1+XGa (X = 0, 0.15) Heusler alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 114(5), (2013)
Franco, V., Blázquez, J.S., Ipus, J.J., Law, J.Y., Moreno-Ramírez, L.M., Conde, A.: Magnetocaloric effect: from materials research to refrigeration devices. Prog. Mater Sci. 93, 112–232 (2018)
Hu, F., Wei, S., He, X., Li, Z., Xu, K., Cao, Y., Kang, Y.: Enhanced magnetocaloric effects driven by two successive magneto-structural transformations in Ni55.5Mn17.8Ga26.7 alloy under hydrostatic pressure. Solid State Commun. 300, (2019)
Aaltio, I., Fukuda, T., Kakeshita, T.: Elastocaloric cooling and heating using R-phase transformation in hot rolled Ni-Ti-Fe shape memory alloys with 2 and 4 at% Fe content. J. Alloy. Compd. 780, 930–936 (2019)
Kim, Y., Jo, M.-G., Park, J.-W., Park, H.-K., Han, H.N.: Elastocaloric effect in polycrystalline Ni 50 Ti 45.3 V 4.7 shape memory alloy. Scripta Mater. 144, 48–51 (2018)
Bechtold, C., Chluba, C., Lima de Miranda, R., Quandt, E.: High cyclic stability of the elastocaloric effect in sputtered TiNiCu shape memory films. Appl Phys Lett 101(9), 091903 (2012)
Ossmer, H., Lambrecht, F., Gültig, M., Chluba, C., Quandt, E., Kohl, M.: Evolution of temperature profiles in TiNi films for elastocaloric cooling. Acta Mater. 81, 9–20 (2014)
Zhu, X., Zhang, X., Qian, M., Zhong, S., Muhammad, I., Geng, L.: Enhanced elastocaloric stability in NiTi alloys under shear stress. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 838, (2022)
Guan, Z., Bai, J., Gu, J., Liang, X., Liu, D., Jiang, X., Huang, R., Zhang, Y., Esling, C., Zhao, X., Zuo, L.: First-principles investigation of B2 partial disordered structure, martensitic transformation, elastic and magnetic properties of all-d-metal Ni-Mn-Ti Heusler alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 68, 103–111 (2021)
Wang, L., Xuan, H., Liu, S., Cao, T., Xie, Z., Liang, X., Chen, F., Zhang, K., Feng, L., Han, P., Wu, Y.: Enhanced elastocaloric effect and mechanical properties of Gd-doped Ni–Mn–Sn-Gd ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 846, (2020)
Tang, X., Feng, Y., Wang, H., Wang, P.: Enhanced elastocaloric effect and cycle stability in B and Cu co-doping Ni-Mn-In polycrystals, Appl. Phys. Lett. 114(3), (2019)
Xiao, F., Fukuda, T., Kakeshita, T., Jin, X.: Elastocaloric effect by a weak first-order transformation associated with lattice softening in an Fe-31.2Pd (at.%) alloy. Acta Mater. 87, 8–14 (2015)
Xiao, F., Bucsek, A., Jin, X., Porta, M., Planes, A.: Giant elastic response and ultra-stable elastocaloric effect in tweed textured Fe-Pd single crystals. Acta Mater. 223, (2022)
Manosa, L., Jarque-Farnos, S., Vives, E., Planes, A.: large temperature span and giant refrigerant capacity in elastocaloric Cu-Zn-AI shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 103(21), 211904 (2013)
Xu, S., Huang, H.Y., Xie, J., Takekawa, S., Xu, X., Kainuma, R.: Giant elastocaloric effect covering wide temperature range in columnar-grained Cu71.5Al17.5Mn11 shape memory alloy. APL Mater. 4(10), 106106 (2016)
Zhao, D., Castán, T., Planes, A., Li, Z., Sun, W., Liu, J.: Enhanced caloric effect induced by magnetoelastic coupling in NiMnGaCu Heusler alloys: experimental study and theoretical analysis. Phys. Rev 96(22), 224105 (2017)
Huang, Y.J., Hu, Q.D., Liu, J., Zeng, L., Zhang, D.F., Li, J.G.: Banded-like morphology and martensitic transformation of dual-phase Ni–Mn–In magnetic shape memory alloy with enhanced ductility. Acta Mater. 61(15), 5702–5712 (2013)
Cao, T., Xuan, H., Liu, S., Wang, L., Xie, Z., Liang, X., Chen, F., Han, P., Wang, D., Du, Y.: Enhanced elastocaloric effect and mechanical properties of Fe-doped Ni–Mn–Al ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Intermetallics 112, (2019)
Zhao, D., Castán, T., Planes, A., Li, Z., Sun, W., Liu, J.: Enhanced caloric effect induced by magnetoelastic coupling in NiMnGaCu Heusler alloys: experimental study and theoretical analysis. Phys. Rev. B 96(22), (2017)
Zhao, D., Liu, J., Chen, X., Sun, W., Li, Y., Zhang, M., Shao, Y., Zhang, H., Yan, A.: Giant caloric effect of low-hysteresis metamagnetic shape memory alloys with exceptional cyclic functionality. Acta Mater. 133, 217–223 (2017)
Camarillo-Garcia, J.-P., Hernández-Navarro, F., Soto-Parra, D.E., Ríos-Jara, D., Flores-Zúñiga, H.: High sensitivity on caloric effects induced by stress or magnetic field in a polycrystalline Ni-Mn-In-Co-Cu shape-memory alloy. Scripta Mater. 166, 92–95 (2019)
Shi, W., Chen, F., Liu, J., Xuan, H., Zhang, R., Zhang, Q., Jiang, Y., Zhang, M.: The effect of hydrostatic pressure on martensitic transition and magnetocaloric effect of Mn44.7Ni43.5Sn11.8 ribbons. Solid State Commun. 308, (2020)
Zhao, D., Liu, J., Feng, Y., Sun, W., Yan, A.: Giant elastocaloric effect and its irreversibility in [001]-oriented Ni45Mn36.5In13.5Co5 meta-magnetic shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys Lett 110(2), 021906 (2017)
Li, Z., Li, Z., Yang, J., Li, D., Yang, B., Yan, H., Nie, Z., Hou, L., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Esling, C., Zhao, X., Zuo, L.: Large elastocaloric effect in a polycrystalline Ni45.7Co4.2Mn37.3Sb12.8 alloy with low transformation strain. Scr. Mater. 162, 486–491 (2019)
Huang, J.Y., Hu, Q.D., Bruno, N.M., Chen, J.H., Karaman, I., Ross, J.H., Jr., Li, G.J.: Giant elastocaloric effect in directionally solidified Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 105, 42–45 (2015)
Xiao, Y., Sun, W., Liu, J., Zhong, X., Liu, Z., Lu, M., Long, K., Zhang, H.: Room temperature elastocaloric effect in polycrystalline Ni51Mn34In8Sn7 alloy. Mater. Lett. 251, 1–4 (2019)
Lu, B., Liu, J.: Elastocaloric effect and superelastic stability in Ni-Mn-In-Co polycrystalline Heusler alloys: hysteresis and strain-rate effects. Sci Rep 7(1), 2084 (2017)
Eggeler, G., Hornbogen, E., Yawny, A., Heckmann, A., Wagner, M.: Structural and functional fatigue of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 378(1–2), 24–33 (2004)
Wagner, M., Sawaguchi, T., Kausträter, G., Höffken, D., Eggeler, G.: Structural fatigue of pseudoelastic NiTi shape memory wires. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 378(1–2), 105–109 (2004)
Yang, Z., Cong, D., Yuan, Y., Wu, Y., Nie, Z., Li, R., Wang, Y.: Ultrahigh cyclability of a large elastocaloric effect in multiferroic phase-transforming materials. Math Res Lett 7(4), 137–144 (2019)
Huang, X.-M., Zhao, Y., Yan, H.-L., Jia, N., Tang, S., Bai, J., Yang, B., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Esling, C., Zhao, X., Zuo, L.: A multielement alloying strategy to improve elastocaloric and mechanical properties in Ni–Mn-based alloys via copper and boron. Scripta Mater. 185, 94–99 (2020)
Funding
This work is supported by the China Scholarship Council (No. 201808140031), The Emerging Industry Leadership Talent Program of Shanxi Province (No.2019042), The Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No.201901D111267), and The Scientific and Technological Innovation Projects for Excellent Researchers of Shanxi Province (No. 201805D211042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, G., Li, C., Chen, M. et al. Elastocaloric Effect and Magnetic Properties of Ni50Mn31.5Ti18Cu0.5 Shape Memory Alloy. J Supercond Nov Magn 35, 1669–1676 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06280-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06280-y