Abstract
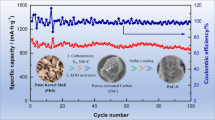
The most suitable activated carbon from three kinds of biomass wastes: walnut shell, peanut shell and pistachio hull is chosen to prepare the activated carbon–sulfur composites (AC-S) for rechargeable lithium–sulfur (Li–S) battery, due to the advantages of a relatively cheap, simple and non-toxic compositing progress. It indicates that the activated carbon (ACpe) derived from peanut shell owns flat, narrow and long shape macroporous structure with large micropores on its surface and is more suitable for the reaction in the Li–S battery. The ACpe/S composite containing about 57 wt% sulfur (sulfur loading of 0.83 mg cm− 2) shows a best initial discharge capacity of 943 mAhg− 1 at the rate of 0.2 C. It still retains a comparably high specific capacity of 619 mAh g− 1 with a coulombic efficiency of 95% after 100 cycles. This fact implies that the inherent flat pore construction of ACpe is beneficial for keep cycling stability for the lithium sulfur battery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.G. Bruce, S.A. Freunberger, L.J. Hardwick, J.-M. Tarascon, Li–O2 and Li–S batteries with high energy storage. Nat. Mater. 11, 19–29 (2012)
A. Manthiram, Y. Fu, Y.-S. Su, Challenges and prospects of lithium¨Csulfur batteries. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 1125–1134 (2012)
E. Peled, Lithium–Sulfur Battery: evaluation of dioxolane-based electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 136, 1621–1625 (1989)
M.K. Song, E.J. Cairns, Y. Zhang, Lithium–sulfur batteries with high specific energy: old challenges and new opportunities. Nanoscale 5, 2186–2204 (2013)
X. Ji, K.T. Lee, L.F. Nazar, A highly ordered nanostructured carbon-sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Mater. 8, 500–506 (2009)
X. Ji, L.F. Nazar, Advances in Li–S batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 9821–9826 (2010)
L. Suo, Y.S. Hu, H. Li, M. Armand, L. Chen, A new class of solvent-in-salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries. Nat. Commun. 4, 1481 (2013)
Z. Lin, Z. Liu, W. Fu, N.J. Dudney, C. Liang, Lithium Polysulfidophosphates: a Family of Lithium-Conducting Sulfur-Rich Compounds for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. Angew. Chem. 125, 7608–7611 (2013)
A. Manthiram, Y. Fu, S.H. Chung, C. Zu, Y.S. Su, Rechargeable Lithium–Sulfur Batteries, Chem. Rev. 114, 11751–11787 (2014)
D. Li, F. Han, S. Wang, F. Cheng, Q. Sun, W.C. Li, High Sulfur Loading Cathodes Fabricated Using Peapodlike, Large Pore Volume Mesoporous Carbon for Lithium–Sulfur Battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 5, 2208–2213 (2013)
J. Zhang, J. Xiang, Z. Dong, Y. Liu, Y. Wu, C. Xu, G. Du, Biomass derived activated carbon with 3D connected architecture for rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 116, 146–151 (2014)
Y.V. Mikhaylik, J.R. Akridge, Polysulfide shuttle study in the Li/S battery system, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151 (2004) A1969–A1976
T. Yim, M.S. Park, J.S. Yu, K.J. Kim, K.Y. Im, J.H. Kim, G. Jeong, Y.N. Jo, S.G. Woo, K.S. Kang, I. Lee, Y.J. Kim, Effect of chemical reactivity of polysulfide toward carbonate-based electrolyte on the electrochemical performance of Li–S batteries. Electrochim. Acta 107, 454–460 (2013)
C. Zu, A. Manthiram, Hydroxylated Graphene–Sulfur Nanocomposites for High-Rate Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 3, 1008–1012 (2013)
X. He, J. Ren, L. Wang, W. Pu, C. Jiang, C. Wan, Expansion and shrinkage of the sulfur composite electrode in rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 190, 154–156 (2009)
Z. Gao, Y. Zhang, N. Song, X. Li, Biomass-derived renewable carbon materials for electrochemical energy storage. Mater. Res. Lett. 5(2), 69–88 (2017)
Y. Zhang, Z. Gao, N. Song, X. Li, High-performance supercapacitors and batteries derived from activated banana-peel with porous structures. Electrochim. Acta 222, 1257–1266 (2016)
L. Zhou, T. Huang, A. Yu, Three-dimensional flower-shaped activated porous Carbon–Sulfur composites as cathode materials for Lithium–Sulfur batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 2442–2447 (2014)
M.K. Song, Y. Zhang, E.J. Cairns, A long-life, high-rate lithium/sulfur cell: a multifaceted approach to enhancing cell performance. Nano Lett. 13, 5891–5899 (2013)
X. Tao, J. Du, Y. Li, Y. Yang, Z. Fan, Y. Gan, X. Li, TaC nanowire/activated carbon microfiber hybrid structures from bamboo fibers. Adv. Energy Mater. 1(4), 534–539 (2011)
Z. Gao, N. Song, X. Li, Microstructural design of hybrid CoO@ NiO and graphene nano-architectures for flexible high performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(28), 14833–14844 (2015)
Z. Gao, N. Song, Y. Zhang, Y. Schwab, J. He, X. Li, Carbon nanotubes derived from yeast-fermented wheat flour and their energy storage application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(9), 11386–11396 (2018)
S. Uçar, M. Erdem, T. Tay, S. Karagöz, Preparation and characterization of activated carbon produced from pomegranate seeds by ZnCl2 activation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8890–8896 (2009)
C.D. Blasi, C. Branca, A. Galgano, Products and global weight loss rates of wood decomposition catalyzed by zinc chloride. Energy Fuels 22, 663–670 (2007)
C. Liang, N.J. Dudney, J.Y. Howe, Hierarchically structured sulfur/carbon nanocomposite material for high-energy lithium battery. Chem. Mater. 21, 4724–4730 (2009)
M. Gao, X. Xiong, W. Wang, S. Zhao, C. Li, H. Zhang, Z. Yu, Y. Huang, Discharge–charge process of the porous sulfur/carbon nanocomposite cathode for rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 248, 1149–1155 (2014)
X. Gu, Y. Wang, C. Lai, J. Qiu, S. Li, Y. Hou, W. Martens, N. Mahmood, S. Zhang, Microporous bamboo biochar for lithium–sulfur batteries, Nano Res. 8, 1–11
Y. Zhong, X. Xia, S. Deng, J. Zhan, R. Fang, Y. Xia, … J. Tu, Popcorn inspired porous macrocellular carbon: rapid puffing fabrication from rice and its applications in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv.Energy Mater. 8(1), 1701110 (2018)
Z.H. Chen, X.L. Du, J.B. He, F. Li, Y. Wang, Y.L. Li, S. Xin, Porous coconut shell carbon offering high retention and deep lithiation of sulfur for lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(39), 33855–33862 (2017)
J. Shim, K.A. Striebel, E.J. Cairns, The lithium/sulfur rechargeable cell effects of electrode composition and solvent on cell performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, A1321–A1325 (2002)
L. Xiao, Y. Cao, J. Xiao, B. Schwenzer, M.H. Engelhard, L.V. Saraf, Z. Nie, G.J. Exarhos, J. Liu, A soft approach to encapsulate sulfur: polyaniline nanotubes for lithium-sulfur batteries with long cycle life. Adv. Mater. 24, 1176–1181 (2012)
L. Ji, M. Rao, H. Zheng, L. Zhang, Y. Li, W. Duan, J. Guo, E.J. Cairns, Y. Zhang, Graphene oxide as a sulfur immobilizer in high performance lithium/sulfur cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 18522–18525 (2011)
Y. Zhang, Z. Gao, X. Li, Capillarity composited recycled paper/graphene scaffold for lithium–sulfur batteries with enhanced capacity and extended lifespan. Small 13(42), 1701927 (2017)
S.E. Cheon, K.S. Ko, J.H. Cho, S.W. Kim, E.Y. Chin, H.T. Kim, Rechargeable lithium sulfur battery II. Rate capability and cycle characteristics. J.Electrochem. Soc. 150, A800–A805 (2003)
Y. Qiu, W. Li, W. Zhao, G. Li, Y. Hou, M. Liu, L. Zhou, F. Ye, H. Li, Z. Wei, High-rate, ultralong cycle-life lithium/sulfur batteries enabled by nitrogen-doped graphene. Nano Lett. 14, 4821–4827 (2014)
B. Zhang, X. Qin, G. Li, X. Gao, Enhancement of long stability of sulfur cathode by encapsulating sulfur into micropores of carbon spheres. Energy Environ. Sci. 3, 1531–1537 (2010)
J. Gao, M.A. Lowe, Y. Kiya, H.c.D. Abrun a, Effects of liquid electrolytes on the charge¨Cdischarge performance of rechargeable lithium/sulfur batteries: electrochemical and in-situ X-ray absorption spectroscopic studies. J.Phys. Chem. C 115, 25132–25137 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11372267, 11102176 and 11602213), the National 863 Plan of China (SS2013AA032202) and the Graduate Innovation Program of Hunan Province (CX2013B259).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Xia, P., Lei, W. et al. Preparation of activated carbon derived from biomass and its application in lithium–sulfur batteries. J Porous Mater 26, 1325–1333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-019-00720-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-019-00720-2