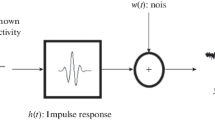
Abstract
The improvement of time resolution is commonly concerned in ultrasonic testing, while the reference signal significantly influences the decoupling and interpretation of multiple overlapped signals. In this paper, the frequency-domain sparse blind deconvolution (FSBD) method is proposed to enhance the time resolution of ultrasonic signals without using any reference signal. The matching pursuit (MP) algorithm is introduced to remove noise for signal reconstruction. On this basis, homomorphic transformation is applied to the de-noised signal, and the l1 and l2 norm constraints based on sparsity are combined to construct a frequency-domain objective function for improving time resolution. The multilayer specimens and small defect were quantitatively detected using the FSBD method by experiments. The results demonstrate that the to-be-measured object with a size of half-wavelength can be identified by decoupling the multiple overlapped signals. Finally, the FSBD method is compared with minimum entropy deconvolution and homomorphic deconvolution. The relationship between the number of scattered/reflected echoes K and the regularization parameter μ is discussed to solve reasonably the regularization problem.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, J., Demirli, R., Saniie, J.: Ultrasonic reflectivity function estimation using cepstrum sparse deconvolution. In: IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings, Tours (2016)
Wei, L., Huang, Z., Que, P.: Sparse deconvolution method for improving the time-resolution of ultrasonic NDE signals. NDT&E Int. 42(5), 430–434 (2009)
Chen, J., Bai, X., Yang, K., Ju, B.: An ultrasonic methodology for determining the mechanical and geometrical properties of a thin layer using a deconvolution technique. Ultrasonics 53(7), 1377–1383 (2013)
Praher, B., Steinbichler, G.: Ultrasound-based measurement of liquid-layer thickness: a novel time-domain approach. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 82, 166–177 (2017)
Dou, P., Wu, T., Peng, Z.: A time-domain ultrasonic approach for oil film thickness measurement with improved resolution and range. Meas. Sci. Technol. 31(7), 75006 (2020)
Honarvar, F., Sheikhzadeh, H., Moles, M., Sinclair, A.N.: Improving the time-resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of ultrasonic NDE signals. Ultrasonics 41(9), 755–763 (2004)
Hayward, G., Lewis, J.E.: Comparison of some non-adaptive deconvolution techniques for resolution enhancement of ultrasonic data. Ultrasonics 27(3), 155–164 (1989)
Sin, S.K., Chen, C.H.: A comparison of deconvolution techniques for the ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation of materials. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1(1), 3–10 (1992)
Chen, J., Wu, E., Wu, H., Zhou, H., Yang, K.: Enhancing ultrasonic time-of-flight diffraction measurement through an adaptive deconvolution method. Ultrasonics 96, 175–180 (2019)
Ma, Z.Y., Zhang, W., Luo, Z.B., Lin, L., Krishnaswamy, S.: Thickness determination of dual-layer coatings based on ultrasonic spectral filtering. Insight 60(4), 200–205 (2018)
Dong, J., Locquet, A., Citrin, D.S.: Depth resolution enhancement of terahertz deconvolution by autoregressive spectral extrapolation. Opt. Lett. 42(9), 1828 (2017)
Guo, J., Xin, Y.: Reconstructing outside pass-band data to improve time resolution in ultrasonic detection. NDT&E Int. 50, 50–57 (2012)
Shakibi, B., Honarvar, F., Moles, M.D.C., Caldwell, J., Sinclair, A.N.: Resolution enhancement of ultrasonic defect signals for crack sizing. NDT&E Int. 52, 37–50 (2012)
Chang, Y., Zi, Y., Zhao, J., Yang, Z., He, W., Sun, H.: An adaptive sparse deconvolution method for distinguishing the overlapping echoes of ultrasonic guided waves for pipeline crack inspection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 28(3), 35002 (2017)
Soussen, C., Idier, J., Carcreff, E., Simon, L., Potel, C.: Ultrasonic non destructive testing based on sparse deconvolution. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 353, 12010–12018 (2012)
Alessandrini, M., Maggio, S., Poree, J., De Marchi, L., Speciale, N., Franceschini, E., Bernard, O., Basset, O.: A restoration framework for ultrasonic tissue characterization. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 58(11), 2344–2360 (2011)
O’Brien, M.S., Sinclair, A.N., Kramer, S.M.: Recovery of a sparse spike time series by l1 norm deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 42(12), 3353 (1994)
Xin, J., Bilgutay, N.M.: Ultrasonic range resolution enhancement using l1 norm deconvolution. In: IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Baltimore (1993)
Jin, H., Chen, J., Yang, K.: A blind deconvolution method for attenuative materials based on asymmetrical Gaussian model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 140(2), 1184 (2016)
Li, X., Li, X., Liang, W., Chen, L.: ℓ0−norm regularized minimum entropy deconvolution for ultrasonic NDT & E. NDT&E Int. 47, 80–87 (2012)
Donoho, D.: On minimum entropy deconvolution. In: Applied Time Series Analysis II, pp. 565–609. Academic Press, New York (1981)
Delebarre, C., Bruneel, C., Miquet, P.: Digital signal processing method for multilayered media thickness measurement. In: IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Chicago (1988)
Nasr, R., Falou, O., Shahin, A., Hysi, E., Wirtzfeld, L.A., Berndl, E., Kolios, M.C.: Mean scatterer spacing estimation using cepstrum-based continuous wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 67(6), 1118–1126 (2020)
Adam, D., Michailovich, O.: Blind deconvolution of ultrasound sequences using nonparametric local polynomial estimates of the pulse. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49(2), 118–131 (2002)
Taylor, J.R.B., Mijares Chan, J.J., Thomas, G.: Wavelet-based blind deconvolution of near-field ultrasound scans. IET Image Process. 9(8), 672–679 (2015)
De Macedo, I.A.S., De Figueiredo, J.J.S., De Sousa, M.C., Nascimento, M.J.S.: Estimation of the seismic wavelet through homomorphic deconvolution and well log data: application on well-to-seismic tie procedure. Geophys. Prospect. 68(4), 1328–1340 (2020)
Abedi, M.M., Torabi, S.: Improving homomorphic wavelet estimation by compensating for residual NMO stretching on stack section. Appl. Geophys. 12(4), 598–604 (2015)
Park, Y., Choi, A., Kim, K.: Monaural sound localization based on reflective structure and homomorphic deconvolution. Sensors 17(10), 2189 (2017)
Dackermann, U., Smith, W.A., Alamdari, M.M., Li, J., Randall, R.B.: Cepstrum-based damage identification in structures with progressive damage. Struct. Health Monit. 18(1), 87–102 (2018)
Carcreff, E., Bourguignon, S., Idier, J., Simon, L.: A linear model approach for ultrasonic inverse problems with attenuation and dispersion. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 61(7), 1191–1203 (2014)
Zhang, G.M., Harvey, D.M., Braden, D.R.: Signal denoising and ultrasonic flaw detection via overcomplete and sparse representations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124(5), 2963–2972 (2008)
Qi, A., Zhang, G., Dong, M., Ma, H., Harvey, D.M.: An artificial bee colony optimization based matching pursuit approach for ultrasonic echo estimation. Ultrasonics 88, 1–8 (2018)
Wu, B., Li, H., Huang, Y.: Sparse recovery of multiple dispersive guided-wave modes for defect localization using a Bayesian approach. Struct. Health Monit. 18(4), 1235–1252 (2019)
Xu, C., Yang, Z., Qiao, B., Chen, X.: Traveling distance estimation for dispersive Lamb waves through sparse Bayesian learning strategy. Smart Mater. Struct. 28(8), 85008 (2019)
Zhao, M., Zhou, W., Huang, Y., Li, H.: Sparse Bayesian learning approach for propagation distance recognition and damage localization in plate-like structures using guided waves. Struct. Health Monit. 20(1), 3–24 (2020)
Fortineau, J.P., Vander, M.F., Fortineau, J., Feuillard, G.: Efficient algorithm for discrimination of overlapping ultrasonic echoes. Ultrasonics 73, 253–261 (2017)
Zhang, G.M., Zhang, C.Z., Harvey, D.M.: Sparse signal representation and its applications in ultrasonic NDE. Ultrasonics 52(3), 351–363 (2012)
Ruiz-Reyes, N., Vera-Candeas, P., Curpián-Alonso, J., Mata-Campos, R., Cuevas-Martínez, J.C.: New matching pursuit-based algorithm for SNR improvement in ultrasonic NDT. NDT&E Int. 38(6), 453–458 (2005)
Kim, S., Koh, K., Lustig, M., Boyd, S., Gorinevsky, D.: An interior-point method for large-scale l1-regularized least squares. IEEE J-STSP 4(1), 606–617 (2007)
Jin, S.J., Sun, X., Ma, T.T., Ding, N., Lei, M.K., Lin, L.: Quantitative detection of shallow subsurface defects by using mode-converted waves in time-of-flight diffraction technique. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 39(2), 33 (2020)
Wooh, S.C., Wei, C.: A homomorphic deconvolution technique for improved ultrasonic imaging of thin composite laminates. In: Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation, vol. 17, pp. 807–814. Plenum Press, New York (1998)
Hou, R., Xia, Y., Bao, Y., Zhou, X.: Selection of regularization parameter for l1-regularized damage detection. J. Sound Vib. 423, 141–160 (2018)
Wang, J., Wang, S., Yuan, S., Li, J., Yin, H.: Stochastic spectral inversion for sparse-spike reflectivity by presetting the number of non-zero spikes as a prior sparsity constraint. J. Geophys. Eng. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2132/11/1/015010
Kundu, D.: Estimating the number of sinusoids and its performance analysis. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 60(4), 347–362 (1998)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51905079, 52075078) and the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (Grant No. XLYC1902082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Lin, L. & Jin, S.J. Improving Time Resolution of Ultrasonic Signals with Frequency-Domain Sparse Blind Deconvolution (FSBD) Method. J Nondestruct Eval 41, 37 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-022-00869-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-022-00869-y