Abstract
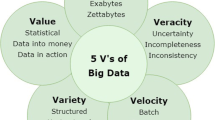
Secondary use of medical big data is increasingly popular in healthcare services and clinical research. Understanding the logic behind medical big data demonstrates tendencies in hospital information technology and shows great significance for hospital information systems that are designing and expanding services. Big data has four characteristics – Volume, Variety, Velocity and Value (the 4 Vs) – that make traditional systems incapable of processing these data using standalones. Apache Hadoop MapReduce is a promising software framework for developing applications that process vast amounts of data in parallel with large clusters of commodity hardware in a reliable, fault-tolerant manner. With the Hadoop framework and MapReduce application program interface (API), we can more easily develop our own MapReduce applications to run on a Hadoop framework that can scale up from a single node to thousands of machines. This paper investigates a practical case of a Hadoop-based medical big data processing system. We developed this system to intelligently process medical big data and uncover some features of hospital information system user behaviors. This paper studies user behaviors regarding various data produced by different hospital information systems for daily work. In this paper, we also built a five-node Hadoop cluster to execute distributed MapReduce algorithms. Our distributed algorithms show promise in facilitating efficient data processing with medical big data in healthcare services and clinical research compared with single nodes. Additionally, with medical big data analytics, we can design our hospital information systems to be much more intelligent and easier to use by making personalized recommendations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, C., Lin, I.-C., and Roan, J., Barriers to physicians’ adoption of healthcare information technology: an empirical study on multiple hospitals. J. Med. Syst. 36(3):1965–1977, 2012.
Poon, E. G., Jha, A. K., Christino, M., Honour, M. M., Fernandopulle, R., Middleton, B., Newhouse, J., Leape, L., Bates, D. W., and Blumenthal, D., Assessing the level of healthcare information technology adoption in the United States: a snapshot. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 6(1):1, 2006.
Miller, R. H., and Sim, I., Physicians’ use of electronic medical records: barriers and solutions. Health Aff. 23(2):116–126, 2004.
Blumenthal, D., Stimulating the adoption of health information technology. N. Engl. J. Med. 360(15):1477–1479, 2009.
Dean, J., and Ghemawat, S., Mapreduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Commun. ACM 51(1):107–113, 2008. doi:10.1145/1327452.1327492.
Dean, J., and Ghemawat, S., MapReduce: a flexible data processing tool. Commun. ACM 53(1):72–77, 2010. doi:10.1145/1629175.1629198.
Horiguchi, H., Yasunaga, H., Hashimoto, H., and Ohe, K., A user-friendly tool to transform large scale administrative data into wide table format using a mapreduce program with a pig latin based script. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 12:8, 2012. doi:10.1186/1472-6947-12-151.
Liu, B., Madduri, R. K., Sotomayor, B., Chard, K., Lacinski, L., Dave, U. J., Li, J. Q., Liu, C. C., and Foster, I. T., Cloud-based bioinformatics workflow platform for large-scale next-generation sequencing analyses. J. Biomed. Inform. 49:119–133, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2014.01.005.
Santana-Quintero, L., Dingerdissen, H., Thierry-Mieg, J., Mazumder, R., and Simonyan, V., HIVE-Hexagon: high-performance, parallelized sequence alignment for next-generation sequencing data analysis. PLoS One 9(6):11, 2014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099033.
Taylor, R. C., An overview of the Hadoop/MapReduce/HBase framework and its current applications in bioinformatics. BMC Bioinforma. 11:6, 2010. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-s12-s1.
Schatz, M. C., CloudBurst: highly sensitive read mapping with MapReduce. Bioinformatics 25(11):1363–1369, 2009. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp236.
Jun, L., and Peng, Z., Mining explainable user interests from scalable user behavior data. First Int. Conf. Inf. Technol. Quant. Manag. 17:789–796, 2013. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2013.05.101.
Wang, Z. H., Tu, L., Guo, Z., Yang, L. T., and Huang, B. X., Analysis of user behaviors by mining large network data sets. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 37:429–437, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.future.2014.02.015.
Shim, J. M., Schneider, J., and Curlin, F. A., Patterns of user disclosure of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) use. Med. Care 52(8):704–708, 2014.
Astin, J. A., Why patients use alternative medicine - results of a national study. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 279(19):1548–1553, 1998. doi:10.1001/jama.279.19.1548.
Gustafson, D. H., Hawkins, R., Boberg, E., Pingree, S., Serlin, R. E., Graziano, F., and Chan, C. L., Impact of a patient-centered, computer-based health information/support system. Am. J. Prev. Med. 16(1):1–9, 1999. doi:10.1016/s0749-3797(98)00108-1.
Powell, J., Inglis, N., Ronnie, J., and Large, S., The characteristics and motivations of online health information seekers: cross-sectional survey and qualitative interview study. J. Med. Internet Res. 13(1):11, 2011. doi:10.2196/jmir.1600.
Dowell, J., and Hudson, H., A qualitative study of medication-taking behaviour in primary care. Fam. Pract. 14(5):369–375, 1997. doi:10.1093/fampra/14.5.369.
Li, J.-S., Zhang, X.-G., Wang, H.-Q., Wang, Y., Wang, J.-M., and Shao, Q.-D., The meaningful use of EMR in Chinese hospitals: a case study on curbing antibiotic abuse. J. Med. Syst. 37(2):1–10, 2013.
Chaudhry, B., Wang, J., Wu, S., Maglione, M., Mojica, W., Roth, E., Morton, S. C., and Shekelle, P. G., Systematic review: impact of health information technology on quality, efficiency, and costs of medical care. Ann. Intern. Med. 144(10):742–752, 2006. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-144-10-200605160-00125.
Kobewka, D., Backman, C., Hendry, P., Hamstra, S. J., Suh, K. N., Code, C., and Forster, A. J., The feasibility of e-learning as a quality improvement tool. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 20(5):606–610, 2014. doi:10.1111/jep.12169.
Tian, Y., Zhou, T. S., Yao, Q., Zhang, M., and Li, J. S., Use of an agent-based simulation model to evaluate a mobile-based system for supporting emergency evacuation decision making. J. Med. Syst. 38(12):13, 2014. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0149-3.
Deidda, M., Lupianez-Villanueva, F., Codagnone, C., and Maghiros, I., Using data envelopment analysis to analyse the efficiency of primary care units. J. Med. Syst. 38(10):10, 2014. doi:10.1007/s10916-014-0122-1.
Hernan, M. A., With great data comes great responsibility publishing comparative effectiveness research in EPIDEMIOLOGY. Epidemiology 22(3):290–291, 2011. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e3182114039.
Weiss, N. S., The new world of data linkages in clinical epidemiology are we being brave or foolhardy? Epidemiology 22(3):292–294, 2011. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e318210aca5.
Sturmer, T., Funk, M. J., Poole, C., and Brookhart, M. A., Nonexperimental comparative effectiveness research using linked healthcare databases. Epidemiology 22(3):298–301, 2011. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e318212640c.
Chen, Y., Pavlov, D., and Canny, J. F., Large-scale behavioral targeting. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, Paris, France, 2009.
Ahmed, A., Low, Y., Aly, M., Josifovski, V., Smola, A. J., Scalable distributed inference of dynamic user interests for behavioral targeting. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, San Diego, California, USA, 2011
Kim, M., Jung, Y., Jung, D., and Hur, C., Investigating the congruence of crowdsourced information with official government data: the case of pediatric clinics. J. Med. Internet Res. 16(2):12, 2014. doi:10.2196/jmir.3078.
Alor-Hernandez, G., Perez-Gallardo, Y., Posada-Gomez, R., Cortes-Robles, G., Rodriguez-Gonzalez, A., and Aguilar-Laserre, A. A., iPixel: a visual content-based and semantic search engine for retrieving digitized mammograms by using collective intelligence. Inform. Health Soc. Care 37(3):159–176, 2012. doi:10.3109/17538157.2012.654840.
Gagnon, M. P., Ghandour, E. K., Talla, P. K., Simonyan, D., Godin, G., Labrecque, M., Ouimet, M., and Rousseau, M., Electronic health record acceptance by physicians: testing an integrated theoretical model. J. Biomed. Inform. 48:17–27, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2013.10.010.
Dunnebeil, S., Sunyaev, A., Blohm, I., Leimeister, J. M., and Krcmar, H., Determinants of physicians’ technology acceptance for e-health in ambulatory care. Int. J. Med. Inform. 81(11):746–760, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2012.02.002.
Thusoo, A., Sarma, J. S., Jain, N., Shao, Z., Chakka, P., Anthony, S., Liu, H., Wyckoff, P., and Murthy, R., Hive: a warehousing solution over a map-reduce framework. Proc. VLDB Endowment 2(2):1626–1629, 2009.
Inmon, W. H., Building the data warehouse. Wiley, New York, 2005.
Giacomelli, P., Apache mahout cookbook. Packt Publishing Ltd., 2013
Bonabeau, E., Decisions 2.0: the power of collective intelligence. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 50(2):45–52, 2009.
Ting, K.M., Precision and recall. In: Encyclopedia of machine learning. Springer, pp 781–781, 2010.
Yao Q, Wang Y, Li J-s Hospital information system integration based on cloud computing. In: 1st international workshop on cloud computing and information security. Atlantis Press, 2013.
Yoo, S., Kim, S., Kim, T., Baek, R.-M., Suh, C. S., Chung, C. Y., and Hwang, H., Economic analysis of cloud-based desktop virtualization implementation at a hospital. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 12(1):119, 2012.
Yao, Q., Han, X., Ma, X.-K., Xue, Y.-F., Chen, Y.-J., and Li, J.-S., Cloud-based hospital information system as a service for grassroots healthcare institutions. J. Med. Syst. 38(9):1–7, 2014.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 61173127), National High-tech R&D Program (No. 2013AA041201), and the Zhejiang University Top Disciplinary Partnership Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Transactional Processing Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Q., Tian, Y., Li, PF. et al. Design and Development of a Medical Big Data Processing System Based on Hadoop. J Med Syst 39, 23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0220-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0220-8