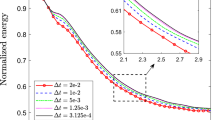
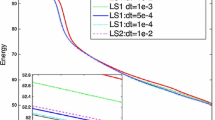
Abstract
Modeling interfacial dynamics with soluble surfactants in a multiphase system is a challenging task. Here, we consider the numerical approximation of a phase-field surfactant model with fluid flow. The nonlinearly coupled model consists of two Cahn–Hilliard-type equations and incompressible Navier–Stokes equation. With the introduction of two auxiliary variables, the governing system is transformed into an equivalent form, which allows the nonlinear potentials to be treated efficiently and semi-explicitly. By certain subtle explicit-implicit treatments to stress and convective terms, we construct first and second-order time marching schemes, which are extremely efficient and easy-to-implement, for the transformed governing system. At each time step, the schemes involve solving only a sequence of linear elliptic equations, and computations of phase-field variables, velocity and pressure are fully decoupled. We further establish a rigorous proof of unconditional energy stability for the first-order scheme. Numerical results in both two and three dimensions are obtained, which demonstrate that the proposed schemes are accurate, efficient and unconditionally energy stable. Using our schemes, we investigate the effect of surfactants on droplet deformation and collision under a shear flow, where the increase of surfactant concentration can enhance droplet deformation and inhibit droplet coalescence.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khatri, S., Tornberg, A.-K.: An embedded boundary method for soluble surfactants with interface tracking for two-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 256, 768–790 (2014)
Yang, X.: Numerical approximations for the Cahn–Hilliard phase field model of the binary fluid-surfactant system. J. Sci. Comput. 1–21 (2017)
Yang, X., Ju, L.: Linear and unconditionally energy stable schemes for the binary fluid–surfactant phase field model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 318, 1005–1029 (2017)
Fonseca, I., Morini, M., Slastikov, V.: Surfactants in foam stability: a phase-field model. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 183, 411–456 (2007)
Iglauer, S., Wu, Y., Shuler, P., Tang, Y., Goddard III, W.A.: New surfactant classes for enhanced oil recovery and their tertiary oil recovery potential. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 71, 23–29 (2010)
Liu, H., Zhang, Y.: Phase-field modeling droplet dynamics with soluble surfactants. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 9166–9187 (2010)
Lai, M.-C., Tseng, Y.-H., Huang, H.: Numerical simulation of moving contact lines with surfactant by immersed boundary method. Commun. Comput. Phys. 8, 735 (2010)
Liu, H., Ba, Y., Wu, L., Li, Z., Xi, G., Zhang, Y.: A hybrid lattice Boltzmann and finite difference method for droplet dynamics with insoluble surfactants. J. Fluid Mech. 837, 381–412 (2018)
Jacqmin, D.: Calculation of two-phase Navier–Stokes flows using phase-field modeling. J. Comput. Phys. 155, 96–127 (1999)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: A phase-field model and its numerical approximation for two-phase incompressible flows with different densities and viscosities. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32, 1159–1179 (2010)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of Allen–Cahn and Cahn–Hilliard equations. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst 28, 1669–1691 (2010)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Decoupled, energy stable schemes for phase-field models of two-phase incompressible flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53, 279–296 (2015)
James, A.J., Lowengrub, J.: A surfactant-conserving volume-of-fluid method for interfacial flows with insoluble surfactant. J. Comput. Phys. 201, 685–722 (2004)
Muradoglu, M., Tryggvason, G.: A front-tracking method for computation of interfacial flows with soluble surfactants. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 2238–2262 (2008)
Zhang, L., Kang, Q., Yao, J., Gao, Y., Sun, Z., Liu, H., Valocchi, A.J.: Pore scale simulation of liquid and gas two-phase flow based on digital core technology. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 1375–1384 (2015)
Booty, M., Siegel, M.: A hybrid numerical method for interfacial fluid flow with soluble surfactant. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 3864–3883 (2010)
Xu, J.-J., Ren, W.: A level-set method for two-phase flows with moving contact line and insoluble surfactant. J. Comput. Phys. 263, 71–90 (2014)
Zhang, Z., Xu, S., Ren, W.: Derivation of a continuum model and the energy law for moving contact lines with insoluble surfactants. Phys. Fluids 26, 062103 (2014)
Xu, J.-J., Li, Z., Lowengrub, J., Zhao, H.: A level-set method for interfacial flows with surfactant. J. Comput. Phys. 212, 590–616 (2006)
Xu, J.-J., Yang, Y., Lowengrub, J.: A level-set continuum method for two-phase flows with insoluble surfactant. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 5897–5909 (2012)
Kou, J., Sun, S.: Thermodynamically consistent modeling and simulation of multi-component two-phase flow with partial miscibility. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 331, 623–649 (2018)
Zhu, G., Yao, J., Li, A., Sun, H., Zhang, L.: Pore-scale investigation of carbon dioxide-enhanced oil recovery. Energy Fuels 31, 5324–5332 (2017)
Tóth, G.I., Kvamme, B.: Analysis of Ginzburg–Landau-type models of surfactant-assisted liquid phase separation. Phys. Rev. E 91, 032404 (2015)
Teng, C.-H., Chern, I.-L., Lai M.-C.: Simulating binary fluid-surfactant dynamics by a phase field model. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-Series B, Special issue for FAN2010 in honor of J. Thomas Beale (in press) (2012)
Yu, H., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations for a phase-field moving contact line model with variable densities and viscosities. J. Comput. Phys. 334, 665–686 (2017)
Yue, P., Feng, J.J., Liu, C., Shen, J.: A diffuse-interface method for simulating two-phase flows of complex fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 515, 293–317 (2004)
Kou, J., Sun, S.: An adaptive finite element method for simulating surface tension with the gradient theory of fluid interfaces. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 255, 593–604 (2014)
Zhu, G., Chen, H., Yao, J., Sun, S.: Efficient energy stable schemes for the hydrodynamics coupled phase-field model. Appl. Math. Model. 70, 82 (2018)
Laradji, M., Guo, H., Grant, M., Zuckermann, M.J.: The effect of surfactants on the dynamics of phase separation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 4, 6715 (1992)
Komura, S., Kodama, H.: Two-order-parameter model for an oil-water-surfactant system. Phys. Rev. E 55, 1722 (1997)
Theissen, O., Gompper, G.: Lattice–Boltzmann study of spontaneous emulsification. Eur. Phys. J. B Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 11, 91–100 (1999)
Van der Sman, R., Van der Graaf, S.: Diffuse interface model of surfactant adsorption onto flat and droplet interfaces. Rheol. Acta 46, 3–11 (2006)
Zhu, G., Kou, J., Sun, S., Yao, J., Li, A.: Decoupled, energy stable schemes for a phase-field surfactant model. Comput. Phys. Commun. 233, 67 (2018)
Engblom, S., Do-Quang, M., Amberg, G., Tornberg, A.-K.: On diffuse interface modeling and simulation of surfactants in two-phase fluid flow. Commun. Computat. Phys. 14, 879–915 (2013)
Garcke, H., Lam, K.F., Stinner, B.: Diffuse interface modelling of soluble surfactants in two-phase flow (2013). arXiv preprint arXiv:1303.2559
Pätzold, G., Dawson, K.: Numerical simulation of phase separation in the presence of surfactants and hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. E 52, 6908 (1995)
Teigen, K.E., Song, P., Lowengrub, J., Voigt, A.: A diffuse-interface method for two-phase flows with soluble surfactants. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 375–393 (2011)
Gu, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z.: An energy-stable finite-difference scheme for the binary fluid-surfactant system. J. Comput. Phys. 270, 416–431 (2014)
Yun, A., Li, Y., Kim, J.: A new phase-field model for a water–oil-surfactant system. Appl. Math. Comput. 229, 422–432 (2014)
Yang, X., Ju, L.: Efficient linear schemes with unconditional energy stability for the phase field elastic bending energy model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 315, 691–712 (2017)
Yang, X., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Shen, J.: Numerical approximations for a three-component Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model based on the invariant energy quadratization method. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 27, 1993–2030 (2017)
Alpak, F.O., Riviere, B., Frank, F.: A phase-field method for the direct simulation of two-phase flows in pore-scale media using a non-equilibrium wetting boundary condition. Comput. Geosci. 20, 881–908 (2016)
Frank, F., Liu, C., Alpak, F.O., Berg, S., Riviere, B.: Direct numerical simulation of flow on pore-scale images using the phase-field method. SPE J. (2018)
Zhu, G., Yao, J., Sun, H., Zhang, M., Xie, M., Sun, Z., Tao, L.: The numerical simulation of thermal recovery based on hydraulic fracture heating technology in shale gas reservoir. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 28, 305–316 (2016)
Liu, C., Shen, J.: A phase field model for the mixture of two incompressible fluids and its approximation by a Fourier-spectral method. Phys. D 179, 211–228 (2003)
Yang, X., Yu, H.: Linear, second order and unconditionally energy stable schemes for a phase-field moving contact line model (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.01311
Gao, M., Wang, X.-P.: A gradient stable scheme for a phase field model for the moving contact line problem. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 1372–1386 (2012)
Bao, K., Shi, Y., Sun, S., Wang, X.-P.: A finite element method for the numerical solution of the coupled Cahn–Hilliard and Navier–Stokes system for moving contact line problems. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 8083–8099 (2012)
Kou, J., Sun, S.: Thermodynamically consistent simulation of nonisothermal diffuse-interface two-phase flow with Peng–Robinson equation of state. J. Comput. Phys. 371, 581–605 (2018)
Kou, J., Sun, S., Wang, X.: Linearly decoupled energy-stable numerical methods for multicomponent two-phase compressible flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56, 3219–3248 (2018)
Copetti, M., Elliott, C.M.: Numerical analysis of the Cahn–Hilliard equation with a logarithmic free energy. Numer. Math. 63, 39–65 (1992)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: The scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) approach for gradient flows. J. Comput. Phys. 353, 407–416 (2018)
Cheng, Q., Shen, J., Yang, X.: Highly efficient and accurate numerical schemes for the epitaxial thin film growth models by using the SAV approach. J. Sci. Comput. 1–21 (2018)
Fjordholm, U.S., Mishra, S., Tadmor, E.: Well-balanced and energy stable schemes for the shallow water equations with discontinuous topography. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5587–5609 (2011)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Decoupled energy stable schemes for phase-field models of two-phase complex fluids. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36, B122–B145 (2014)
Chen, W., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: A positivity-preserving, energy stable numerical scheme for the Cahn–Hilliard equation with logarithmic potential (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.03225
Chen, W., Feng, W., Zhang, L., Cui, C., Ma, X., Sun, Z., Liu, F., Zhang, K.: A fractal discrete fracture network model for history matching of naturally fractured reservoirs. Fractals 27, 1940008 (2018)
Diegel, A.E., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Convergence analysis and error estimates for a second order accurate finite element method for the Cahn–Hilliard–Navier–Stokes system. Numer. Math. 137, 495–534 (2017)
Feng, X., He, Y., Liu, C.: Analysis of finite element approximations of a phase field model for two-phase fluids. Math. Comput. 76, 539–571 (2007)
Li, J., Yu, B., Wang, Y., Tang, Y., Wang, H.: Study on computational efficiency of composite schemes for convection–diffusion equations using single-grid and multigrid methods. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 10, JTST0009–JTST0009 (2015)
F. Moukalled, L. Mangani, M. Darwish, The finite volume method in computational fluid dynamics. An advanced introduction with OpenFOAM and Matlab, pp. 3–8 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Jun Yao and Guangpu Zhu acknowledge that this work is supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project (2016ZX05011-001), the NSF of China (51804325, 51504276, and 51674280). The work of Shuyu Sun and Jisheng Kou is supported by the KAUST research fund awarded to the Computational Transport Phenomena Laboratory at KAUST through the Grant BAS/1/1351-01-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G., Kou, J., Sun, S. et al. Numerical Approximation of a Phase-Field Surfactant Model with Fluid Flow. J Sci Comput 80, 223–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-00934-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-00934-1