Abstract
Emotional intelligence (EI) has been found to generally predict subjective wellbeing (SWB) indicators such as life satisfaction and happiness. Concerning the specific abilities of trait EI, i.e., mood attention, emotional clarity and mood repair, research has largely demonstrated that emotional clarity and mood repair are the strongest predictors of SWB indicators, whereas mood attention has been relegated to a secondary role. To clarify previous inconsistencies, we tested EI by means of the bifactor model because it allows for a better comprehension of the complex nature of EI. The current paper was composed of two studies: Study 1 examined the prediction of SWB indicators by EI and its dimensions in the bifactor model; and Study 2 analysed the differences in EI and SWB indicators across university students and employees. Results of Study 1 demonstrated that the structure of EI is best represented by the bifactor model with a general e(motional)-factor and three specific emotional abilities. Mood attention was a negative predictor of SWB indicators, whereas mood repair was a positive predictor, and emotional clarity was non-significant. Study 2 showed that employees and university students did not differed in how EI predicted SWB indicators. These findings evidenced a shift in the study and measurement of EI. Further implications of this paper are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atienza, F. L., Pons, D., Balaguer, I., & García-Merita, M. L. (2000). Psychometric properties of the satisfaction with life scale in adolescents. Psicothema,12, 314–319.
Augusto-Landa, J. M., López-Zafra, E., De Antoñana, R. M., & Pulido, M. (2006). Perceived emotional intelligence and life satisfaction among university teachers. Psicothema,18, 152–157.
Augusto-Landa, J. M., Pulido-Martos, M., & López-Zafra, E. (2011). Does perceived emotional intelligence and optimism/pessimism predict psychological well-being? Journal of Happiness Studies,12, 463–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-010-9209-7.
Baltes, P. B., & Baltes, M. M. (1990). Psychological perspectives on successful aging: The model of selective optimization with compensation. In P. B. Baltes & M. M. Baltes (Eds.), Successful aging: Perspectives from the behavioral sciences (pp. 1–34). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Bar-On, R. (2006). The bar-on model of emotional-social intelligence (ESI). Psicothema,18, 13–25.
Beaujean, A. (2015). John Carroll’s views on intelligence: Bi-factor vs. higher-order models. Journal of Intelligence,3(4), 121–136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence3040121.
Boden, M. T., & Thompson, R. J. (2015). Facets of emotional awareness and associations with emotion regulation and depression. Emotion,15, 399–410. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000057.
Byrne, B. M. (1994). Structural equation modeling with EQS and EQS/windows: Basic concepts, applications, and programming. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Carroll, J. B. (1996). A three-stratum theory of intelligence: Spearman’s contribution. In I. Dennis & P. Tapsfield (Eds.), Human abilities: Their nature and measurement (pp. 1–17). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Carstensen, L. L., Pasupathi, M., Mayr, U., & Nesselroade, J. R. (2000). Emotional experience in everyday life across the adult life span. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,79, 644–655. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.79.4.644.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling,14, 464–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705510701301834.
Chen, F. F., Bai, L., Lee, J. M., & Jing, Y. (2016a). Culture and the structure of affect: A bifactor modeling approach. Journal of Happiness Studies,17, 1801–1824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-015-9671-3.
Chen, F. F., Jing, Y., Hayes, A., & Lee, J. M. (2013). Two concepts or two approaches? A bifactor analysis of psychological and subjective well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies,14, 1033–1068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-012-9367-x.
Chen, Y., Peng, Y., & Fang, P. (2016b). Emotional intelligence mediates the relationship between age and subjective well-being. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development,83(2), 91–107. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415016648705.
Cucina, J., & Byle, K. (2017). The bifactor model fits better than the higher-order model in more than 90% of comparisons for mental abilities test batteries. Journal of Intelligence,5(3), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence5030027.
Cummins, R. A. (2003). Normative life satisfaction: Measurement issues and a homeostatic model. Social Indicators Research,64, 225–256. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024712527648.
Damasio, B. F., Hauck-Filho, N., & Koller, S. H. (2016). Measuring meaning in life: An empirical comparison of two well-known measures. Journal of Happiness Studies,17, 431–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-014-9602-8.
Delhom, I., Gutierrez, M., Lucas-Molina, B., & Meléndez, J. C. (2017). Emotional intelligence in older adults: psychometric properties of the TMMS-24 and relationship with psychological well-being and life satisfaction. International Psychogeriatrics,29, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610217000722.
Diener, E. D. (1984). Subjective well-being. Psychological Bulletin,95(3), 542–575. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.95.3.542.
Diener, E. D., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment,49, 71–75. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa4901_13.
Diener, E. D., Oishi, S., & Lucas, R. E. (2003). Personality, culture, and subjective well-being: Emotional and cognitive evaluations of life. Annual Review of Psychology,54, 403–425. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145056.
Extremera, N., & Fernández-Berrocal, P. (2014). The subjective happiness scale: Translation and preliminary psychometric evaluation of a Spanish version. Social Indicators Research,119, 473–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0497-2.
Extremera, N., Ruiz-Aranda, D., Pineda-Galán, C., & Salguero, J. M. (2011a). Emotional intelligence and its relation with hedonic and eudaimonic well-being: A prospective study. Personality and Individual Differences,51(1), 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2011.02.029.
Extremera, N., Salguero, J. M., & Fernández-Berrocal, P. (2011b). Trait meta-mood and subjective happiness: A 7-week prospective study. Journal of Happiness Studies,12, 509–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-010-9233-7.
Fan, H. Y., Jackson, T., Yang, X. G., Tang, W. Q., & Zhang, J. F. (2010). The factor structure of the Mayer–Salovey–Caruso emotional intelligence test V 2.0 (MSCEIT): A meta-analytic structural equation modeling approach. Personality and Individual Differences,48(7), 781–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.02.004.
Fernández-Berrocal, P., Extremera, N., & Ramos, N. (2004). Validity and reliability of the Spanish modified version of the trait meta-mood scale. Psychological Reports,94, 751–755. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.94.3.751-755.
Fiori, M., Antonietti, J.-P., Mikolajczak, M., Luminet, O., Hansenne, M., & Rossier, J. (2014). What is the ability emotional intelligence test (MSCEIT) good for? An evaluation using item response theory. PLoS ONE,9(6), e98827. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098827.
Fontaine, J. R. J. (2016). Comment: Redefining emotional intelligence based on the componential emotion approach. Emotion Review,8(4), 332–333.
Frisby, C. L., & Beaujean, A. A. (2015). Testing Spearman’s hypotheses using a bi-factor model with WAIS-IV/WMS-IV standardization data. Intelligence,51, 79–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2015.04.007.
Gohm, C. L. (2003). Mood regulation and emotional intelligence: Individual differences. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,84, 594–607. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.84.3.594.
Goldman, S. L., Kraemer, D. T., & Salovey, P. (1996). Beliefs about mood moderate the relationship of stress to illness and symptom reporting. Journal of Psychosomatic Research,41, 115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(96)00119-5.
Gutiérrez-Cobo, M. J., Cabello, R., & Fernández-Berrocal, P. (2017). The three models of emotional intelligence and performance in a hot and cool go/no-go task in undergraduate students. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience,11, 33. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00033.
Hodzic, S., Scharfen, J., Ripoll, P., Holling, H., & Zenasni, F. (2018). How efficient are emotional intelligence trainings: A meta-analysis. Emotion Review,10(2), 138–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073917708613.
Hughes, D. J., & Batey, M. (2017). Using personality questionnaires for selection. In H. Goldstein, E. Pulakos, J. Passmore, & C. Semedo (Eds.), The wiley blackwell handbook of the psychology of recruitment, selection and retention. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell.
Jovanović, V. (2015). A bifactor model of subjective well-being: A re-examination of the structure of subjective well-being. Personality and Individual Differences,87, 45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.07.026.
Kenny, D. A., Kaniskan, B., & McCoach, D. B. (2015). The performance of RMSEA in models with small degrees of freedom. Sociological Methods and Research,44, 486–507. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124114543236.
Keyes, C. L. M., & Grzywacz, J. G. (2005). Health as a complete state: The added value in work performance and healthcare costs. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine,47, 523–532. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.jom.0000161737.21198.3a.
Keyes, C. L. M., & Waterman, M. B. (2003). Dimensions of well-being and mental health in adulthood. In M. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C. L. M. Keyes, & K. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development throughout the life course (pp. 477–497). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (3rd ed.). New York: The Guilford Press.
Koydemir, S., Şimşek, Ö. F., Schütz, A., & Tipandjan, A. (2013). Differences in how trait emotional intelligence predicts life satisfaction: The role of affect balance versus social support in India and Germany. Journal of Happiness Studies,14, 51–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-011-9315-1.
Lauriola, M., & Iani, L. (2017). Peronality, positivity and happiness: A mediation analysis using a bifactor model. Journal of Happiness Studies,18, 1659–1682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-016-9792-3.
Lench, H. C., Darbor, K. E., & Berg, L. A. (2013). Functional perspectives on emotion, behavior, and cognition. Behavioral Sciences,3, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs3040536.
Lischetzke, T., Eid, M., & Diener, E. D. (2012). Perceiving one’s own and others’ feelings around the world: The relations of attention to and clarity of feelings with subjective well-being across nations. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology,43, 1249–1267. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022111429717.
Lucas, R. E., & Gohm, C. (2000). Age and sex differences in subjective well-being across cultures. In E. Diener & E. M. Suh (Eds.), Culture and subjective well-being (pp. 291–317). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Luo, D., Petrill, S. A., & Thompson, L. A. (1994). An exploration of genetic g: Hierarchical factor analysis of cognitive data from the Western Reserve Twin Project. Intelligence,18(3), 335–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-2896(94)90033-7.
Lyubomirsky, S. (2001). Why are some people happier than others? The role of cognitive and motivational processes in well-being. American Psychologist,56(3), 239–249. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.56.3.239.
Lyubomirsky, S., & Lepper, H. S. (1999). A measure of subjective happiness: Preliminary reliability and construct validation. Social Indicators Research,46, 137–155. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006824100041.
Maul, A. (2012). The validity of the Mayer–Salovey–Caruso emotional intelligence test (MSCEIT) as a measure of emotional intelligence. Emotion Review,4, 394–402. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073912445811.
Mayer, J. D., Caruso, D. R., & Salovey, P. (2016). The ability model of emotional intelligence: Principles and updates. Emotion Review,8(4), 290–300. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073916639667.
Mayer, J. D., & Salovey, P. (1997). What is emotional intelligence? In P. Salovey & D. Sluyter (Eds.), Emotional development and emotional intelligence: Implications for educators (pp. 3–31). New York: Basic Books.
Mayer, J. D., & Stevens, A. A. (1994). An emerging understanding of the reflective (meta-) experience of mood. Journal of Research in Personality,28, 351–373. https://doi.org/10.1006/jrpe.1994.1025.
Meredith, W. (1993). Measurement invariance, factor analysis and factorial invariance. Psychometrika,58(4), 525–543.
Mestre, J. M., MacCann, C., Guil, R., & Roberts, R. D. (2016). Models of cognitive ability and emotion can better inform contemporary emotional intelligence frameworks. Emotion Review,8(4), 322–330. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073916650497.
Miao, C., Humphrey, R. H., & Qian, S. (2017). A meta-analysis of emotional intelligence and work attitudes. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology,90, 177–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/joop.12167.
Mikolajczak, M., Luminet, O., Leroy, C., & Roy, E. (2007). Psychometric properties of the trait emotional intelligence questionnaire: Factor structure, reliability, construct, and incremental validity in a French-speaking population. Journal of Personality Assessment,88, 338–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223890701333431.
Muthén, L., & Muthén, B. O. (2012). Mplus user’s guide (6th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Nickerson, C., Diener, E., & Schwarz, N. (2011). Positive affect and college success. Journal of Happiness Studies,12, 717–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-010-9224-8.
Parker, J. D., Creque, R. E., Barnhart, D. L., Harris, J. I., Majeski, S. A., Wood, L. M., et al. (2004). Academic achievement in high school: Does emotional intelligence matter? Personality and Individual Differences,37, 1321–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2004.01.002.
Petrides, K. V., Furnham, A., & Mavroveli, S. (2007). Trait emotional intelligence. Moving forward in the field of EI. In G. Matthews (Ed.), Emotional intelligence. Knowns and unknowns (Series in affective science). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Reise, S. P., Moore, T. M., & Haviland, M. G. (2010). Bifactor models and rotations: Exploring the extent to which multidimensional data yield univocal scale scores. Journal of Personality Assessment,92, 544–559. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2010.496477.
Reise, S. P., Scheines, R., Widaman, K. F., & Haviland, M. G. (2013). Multidimensionality and structural coefficient bias in structural equation modeling: A bifactor perspective. Educational and Psychological Measurement,73(1), 5–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164412449831.
Roberts, R. D., Schulze, R., & MacCann, C. (2008). The measurement of emotional intelligence: A decade of progress? In G. Boyle, G. Matthews, & D. Saklofske (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of personality theory and assessment (pp. 461–482). New York: SAGE.
Rodriguez, A., Reise, S. P., & Haviland, M. G. (2016). Evaluating bifactor models: Calculating and interpreting statistical indices. Psychological Methods,21, 137–150. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000045.
Rogoza, R., Truong, T. K. H., Różycka-Tran, J., Piotrowski, J., & Żemotel-Piotrowska, M. (2018). Psychometric properties of the MHC-SF: An integration of the existing measurement approaches. Journal of Clinical Psychology,74, 1742–1758. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.22626.
Salovey, P., & Mayer, J. D. (1990). Emotional intelligence. Imagination, Cognition and Personality,9(3), 185–211. https://doi.org/10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG.
Salovey, P., Mayer, J. D., Goldman, S. L., Turvey, C., & Palfai, T. P. (1995). Emotional attention, clarity, and repair: Exploring emotional intelligence using the trait meta-mood scale. In J. W. Pennebaker (Ed.), Emotion, disclosure, and health (pp. 125–154). Washington: American Psychological Association.
Salovey, P., Stroud, L. R., Woolery, A., & Epel, E. S. (2002). Perceived emotional intelligence, stress reactivity, and symptom reports: Further explorations using the trait meta-mood scale. Psychology and Health,17, 611–627. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870440290025812.
Sánchez-Álvarez, N., Extremera, N., & Fernández-Berrocal, P. (2015). The relation between emotional intelligence and subjective well-being: A meta-analytic investigation. Journal of Positive Psychology,11, 276–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2015.1058968.
Spearman, C. (1923). The nature of “intelligence” and principles of cognition. London: MacMillan.
Szczygieł, D., & Mikolajczak, M. (2017). Why are people high in emotional intelligence happier? They make the most of their positive emotions. Personality and Individual Differences,117, 177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.05.051.
Thoresen, C. J., Kaplan, S. A., Barsky, A. P., Warren, C. R., & de Chermont, K. (2003). The affective underpinnings of job perceptions and attitudes: A meta-analytic review and integration. Psychological Bulletin,129, 914–945. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.129.6.914.
Urquijo, I., Extremera, N., & Villa, A. (2016). Emotional intelligence, life satisfaction, and psychological well-being in graduates: The mediating effect of perceived stress. Applied Research in Quality of Life,11, 1241–1252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-015-9432-9.
Van de Schoot, R., Lugtig, P., & Hox, J. (2012). A checklist for testing measurement invariance. European Journal of Developmental Psychology,9(4), 486–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2012.686740.
Van Praag, B. M., Frijters, P., & Ferrer-i-Carbonell, A. (2003). The anatomy of subjective well-being. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization,51, 29–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2681(02)00140-3.
Wechsler, D. (1997). Wechsler adult intelligence scale III (3rd ed.). San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation.
Wilson, T. D., & Gilbert, D. T. (2005). Affective forecasting: Knowing what to want. Current Directions in Psychological Science,14, 131–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00355.x.
Wood, J. V., Heimpel, S. A., & Michela, J. L. (2003). Savoring versus dampening: Self-esteem differences in regulating positive affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,85, 566–580. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.3.566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
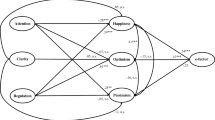
Measurement part of the structural equation models presented on Figs. 1 and 2. The estimates from Study 1 and Study 2 are separated by brackets. Following tables present standardised factor loadings obtained from: the Trait Meta-Mood Scale-24 (Table 5); Satisfaction with Life Scale (Table 6); and Subjective Happiness Scale (Table 7).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blasco-Belled, A., Rogoza, R., Torrelles-Nadal, C. et al. Emotional Intelligence Structure and Its Relationship with Life Satisfaction and Happiness: New Findings from the Bifactor Model. J Happiness Stud 21, 2031–2049 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-019-00167-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-019-00167-x