Abstract
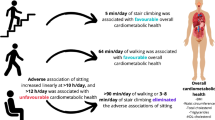
We aimed to estimate the associations between substituting 30-min/day of walking or moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) for 30 min/day of sitting and cardiovascular risk factors in a South Asian population free of cardiovascular disease. We collected information regarding sitting and physical activity from a representative sample of 6991 participants aged 20 years and above from New Delhi, India and Karachi, Pakistan enrolled in 2010–2011 in the Center for cArdio-metabolic Risk Reduction in South Asia study using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (short form). We conducted isotemporal substitution analyses using multivariable linear regression models to examine the cross-sectional associations between substituting MVPA and walking for sitting with cardiovascular risk factors. Substituting 30 min/day of MVPA for 30 min/day of sitting was associated with 0.08 mmHg lower diastolic blood pressure (β = −0.08 [− 0.15, − 0.0003]) and 0.13 mg/dl higher high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (β = 0.13 [0.04, 0.22]). Substituting 30 min/day of walking for 30 min/day of sitting was associated with 0.08 kg/m2 lower body mass index (β = −0.08 [− 0.15, − 0.02]), and 0.25 cm lower waist circumference (β = −0.25 [− 0.39, − 0.11]). In conclusion, substituting time engaged in more-active pursuits for time engaged in less-active pursuits was associated with modest but favorable cardiovascular risk factor improvements among South Asians.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M. K., Bhaskarapillai, B., Shivashankar, R., Mohan, D., Fatmi, Z. A., Pradeepa, R., et al. (2015). Socioeconomic status and cardiovascular risk in urban South Asia: The CARRS Study. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487315580891
Anjana, R. M., Pradeepa, R., Das, A. K., Deepa, M., Bhansali, A., Joshi, S. R., et al. (2014). Physical activity and inactivity patterns in India—Results from the ICMR-INDIAB study (Phase-1) [ICMR-INDIAB-5]. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 11, 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-11-26
Aravindalochanan, V., Kumpatla, S., Rengarajan, M., Rajan, R., & Viswanathan, V. (2014). Risk of diabetes in subjects with sedentary profession and the synergistic effect of positive family history of diabetes. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics, 16, 26–32. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2013.0140
Buman, M. P., Winkler, E. A., Kurka, J. M., Hekler, E. B., Baldwin, C. M., Owen, N., et al. (2014). Reallocating time to sleep, sedentary behaviors, or active behaviors: Associations with cardiovascular disease risk biomarkers, NHANES 2005–2006. American Journal of Epidemiology, 179, 323–334. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt292
Ekblom-Bak, E., Ekblom, O., Bergstrom, G., & Borjesson, M. (2015). Isotemporal substitution of sedentary time by physical activity of different intensities and bout lengths, and its associations with metabolic risk. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487315619734
Falconer, C. L., Page, A. S., Andrews, R. C., & Cooper, A. R. (2015). The potential impact of displacing sedentary time in adults with Type 2 diabetes. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 47, 2070–2075. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000651
Fishman, E. I., Steeves, J. A., Zipunnikov, V., Koster, A., Berrigan, D., Harris, T. A., et al. (2016). Association between objectively measured physical activity and mortality in NHANES. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000885
Forouzanfar, M. H., Alexander, L., Anderson, H. R., Bachman, V. F., Biryukov, S., Brauer, M., et al. (2015). Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet, 386, 2287–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00128-2
Hamer, M., Stamatakis, E., & Steptoe, A. (2014). Effects of substituting sedentary time with physical activity on metabolic risk. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 46, 1946–1950. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000317
Healy, G. N., Winkler, E. A., Brakenridge, C. L., Reeves, M. M., & Eakin, E. G. (2015). Accelerometer-derived sedentary and physical activity time in overweight/obese adults with type 2 diabetes: Cross-sectional associations with cardiometabolic biomarkers. PLoS ONE, 10, e0119140. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119140
IPAQ. (2004a). Retrieved 16 July 2018, from http://youthrex.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/IPAQ-TM.pdf
IPAQ. (2004b). Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)—Short Form. Retrieved 16 July 2018, from http://www.institutferran.org/documentos/scoring_short_ipaq_april04.pdf
Jd, V. D. B., Jhpm, V. D. V., Eac, D. E. W., Bosma, H., Savelberg, H., Schaper, N. C., et al. (2017). Replacement effects of sedentary time on metabolic outcomes: The Maastricht study. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 49, 1351–1358. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000001248
Johns, D. J., Hartmann-Boyce, J., Jebb, S. A., & Aveyard, P. (2014). Diet or exercise interventions vs combined behavioral weight management programs: A systematic review and meta-analysis of direct comparisons. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 114, 1557–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2014.07.005
Kamath, S. K., Hussain, E. A., Amin, D., Mortillaro, E., West, B., Peterson, C. T., et al. (1999). Cardiovascular disease risk factors in 2 distinct ethnic groups: Indian and Pakistani compared with American premenopausal women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 69, 621–631. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/69.4.621
Koolhaas, C. M., Dhana, K., Golubic, R., Schoufour, J. D., Hofman, A., van Rooij, F. J. A., et al. (2016). Physical activity types and coronary heart disease risk in middle-aged and elderly persons: The Rotterdam Study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 183, 729–738. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwv244
Lee, P. H., Macfarlane, D. J., Lam, T. H., & Stewart, S. M. (2011). Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 8, 115. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-8-115
Mekary, R. A., Lucas, M., Pan, A., Okereke, O. I., Willett, W. C., Hu, F. B., et al. (2013). Isotemporal substitution analysis for physical activity, television watching, and risk of depression. American Journal of Epidemiology, 178, 474–483. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kws590
Mekary, R. A., Willett, W. C., Hu, F. B., & Ding, E. L. (2009). Isotemporal substitution paradigm for physical activity epidemiology and weight change. American Journal of Epidemiology, 170, 519–527. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp163
Millett, C., Agrawal, S., Sullivan, R., Vaz, M., Kurpad, A., Bharathi, A. V., et al. (2013). Associations between active travel to work and overweight, hypertension, and diabetes in India: A cross-sectional study. PLOS Medicine, 10, e1001459. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001459
Misra, A., Nigam, P., Hills, A. P., Chadha, D. S., Sharma, V., Deepak, K. K., et al. (2012). Consensus physical activity guidelines for Asian Indians. Diabetes Technol Ther, 14, 83–98. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2011.0111
Moran, A., & Vedanthan, R. (2013). Cardiovascular disease prevention in South Asia gathering the evidence. Global heart, 8, 139–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gheart.2013.04.001
Nag, T., & Ghosh, A. (2013). Cardiovascular disease risk factors in Asian Indian population: A systematic review. Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Research, 4, 222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcdr.2014.01.004
Nair, M., Ali, M. K., Ajay, V. S., Shivashankar, R., Mohan, V., Pradeepa, R., et al. (2012). CARRS Surveillance study: Design and methods to assess burdens from multiple perspectives. BMC Public Health, 12, 701. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-701
Nethan, S., Sinha, D., & Mehrotra, R. (2017). Non communicable disease risk factors and their trends in India. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention: APJCP, 18, 2005–2010. https://doi.org/10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.7.2005
Prabhakaran, D., Jeemon, P., & Roy, A. (2016). Cardiovascular diseases in India: Current epidemiology and future directions. Circulation, 133, 1605–1620. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.114.008729
Quan, S. F., Howard, B. V., Iber, C., Kiley, J. P., Nieto, F. J., O’Connor, G. T., et al. (1997). The sleep heart health study: Design, rationale, and methods. Sleep, 20, 1077–1085.
Rastogi, T., Vaz, M., Spiegelman, D., Reddy, K. S., Bharathi, A. V., Stampfer, M. J., et al. (2004). Physical activity and risk of coronary heart disease in India. International Journal of Epidemiology, 33, 759–767. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyh042
Shenoy, S., Chawla, J. K., & Sandhu, J. S. (2014). Validation of short international physical activity questionnaire Punjabi version in India. Saudi Journal of Sports Medicine, 14, 77.
Siegel, K. R., Patel, S. A., & Ali, M. K. (2014). Non-communicable diseases in South Asia: Contemporary perspectives. British Medical Bulletin, 111, 31–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldu018
Stamatakis, E., Rogers, K., Ding, D., Berrigan, D., Chau, J., Hamer, M., et al. (2015). All-cause mortality effects of replacing sedentary time with physical activity and sleeping using an isotemporal substitution model: A prospective study of 201,129 mid-aged and older adults. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act, 12, 121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12966-015-0280-7
Tanasescu, M., Leitzmann, M. F., Rimm, E. B., Willett, W. C., Stampfer, M. J., & Hu, F. B. (2002). Exercise type and intensity in relation to coronary heart disease in men. JAMA, 288, 1994–2000. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.16.1994
Wellburn, S., Ryan, C. G., Azevedo, L. B., Ells, L., Martin, D. J., Atkinson, G., et al. (2015). Displacing Sedentary Time: Association with Cardiovascular Disease Prevalence. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000816
Willett, W., & Stampfer, M. J. (1986). Total energy intake: Implications for epidemiologic analyses. American Journal of Epidemiology, 124, 17–27.
Wilmot, E. G., Edwardson, C. L., Achana, F. A., Davies, M. J., Gorely, T., Gray, L. J., et al. (2012). Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia, 55, 2895–2905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2677-z
Yusuf, S., Hawken, S., Ounpuu, S., Dans, T., Avezum, A., Lanas, F., et al. (2004). Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): Case-control study. Lancet, 364, 937–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)17018-9
Zachariah, G., & Alex, A. (2017). Exercise for prevention of cardiovascular disease: Evidence-based recommendations. Journal of Clinical and Preventive Cardiology, 6, 109–114. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcpc.jcpc_9_17
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all CARRS participants and staff for the providing information for this study.
Funding
This project was funded in part by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Department of Health and Human Services, under Contract No. HHSN268200900026C, and the United Health Group, Minneapolis, MN, US.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jingkai Wei, Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Shifalika Goenka, Felipe Lobelo, Roopa Shivashankar, Muhammad Masood Kadir, Nikhil Tandon, Viswanathan Mohan, K. M. Venkat Narayan, Dorairaj Prabhakaran and Mohammed K. Ali declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights and Informed consent
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Anjana, R.M., Goenka, S. et al. Physical activity, sitting, and risk factors of cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional analysis of the CARRS study. J Behav Med 42, 502–510 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-018-9989-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-018-9989-5