Abstract
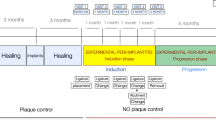
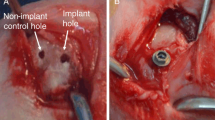
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of biofunctionalization with two TGF-β1 inhibitor peptides, P17 and P144, on osseointegration of CP-Ti dental implants. A total of 36 implants (VEGA, Klockner®) with 3.5 × 8 mm internal connection were used in this study, divided in three groups: (1) control group (n = 12), (2) implants which surfaces were biofunctionalized with P17 peptide inhibitor (n = 12), (3) implants with surfaces biofunctionalized by P144 peptide (n = 12). Three implants, one from each group, were inserted in both hemimandibles of 6 beagle dogs, 2 months after tooth extraction. Two animals were sacrificed at 2, 4 and 8 weeks post implant insertion, respectively. The samples were analyzed by Backscattering Scanning Electron Microscopy (BS-SEM) and histological analysis. Histomorphometric analysis of bone to implant contact (BIC), peri-implant bone fraction (BF) and interthread bone (IB) were carried out. Bone formation around implants measured by quantitative analysis, BS-SEM, was significantly higher in the P17-biofunctionalized implants, 4 and 8 weeks after the implantation. Histomorphometric analysis of BIC, BF and IB showed higher values in the P17-biofunctionalized group at initial stages of healing (2 weeks) and early osseointegration both at 4 and 8 weeks. For P144 biofunctionalized implants, the histomorphometric values obtained are also higher than control group. Accordingly, better results in the experimental groups were proven both by the quantitative and the qualitative analysis. Surface biofunctionalization with TGF-β1 inhibitor peptides, P17 and P144, resulted in better quantitative and qualitative parameters relative to implant osseointegration.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cornelini R, Rubini C, Fioroni M, Favero GA, Strocchi R, Piattelli A. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in the peri-implant soft tissues of healthy and failing dental implants. J Periodontol. 2003;74:446–50.
Schiller M, Javelaud D, Mauviel A. TGF-beta-induced SMAD signaling and gene regulation: consequences for extracellular matrix remodeling and wound healing. J Dermatol Sci. 2004;35:83–92.
Dotor J, López-Vázquez AB, Lasarte JJ, Sarobe P, García-Granero M, Riezu-Boj JI, et al. Identification of peptide inhibitors of transforming growth factor beta 1 using a phage-displayed peptide library. Cytokine 2007;39:106–15.
Vlacic-Zischke J, Hamlet SMM, Friis T, Tonetti MSS, Ivanovski S. The influence of surface microroughness and hydrophilicity of titanium on the up-regulation of TGFβ/BMP signalling in osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 2011;32:665–71.
Biguetti CC, Cavalla F, Silveira EM, Fonseca AC, Vieira AE, Tabanez AP, et al. Oral implant osseointegration model in C57Bl/6 mice: microtomographic, histological, histomorphometric and molecular characterization. J Appl Oral Sci Fac De Odontologia De Bauru USP. 2018;26:e20170601.
Anselme K, Linez P, Bigerelle M, Le Maguer D, Le Maguer A, Hardouin P, et al. The relative influence of the topography and chemistry of TiAl6V4 surfaces on osteoblastic cell behaviour. Biomaterials. 2000;21:1567–77.
Davidson PM, Özçelik H, Hasirci V, Reiter G, Anselme K. Microstructured Surfaces Cause Severe but Non-Detrimental Deformation of the Cell Nucleus. Adv Mater. 2009;21:3586–90.
Janssens K, ten Dijke P, Janssens S, Van Hul W. Transforming growth factor-beta1 to the bone. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:743–74.
Santiago B, Gutierrez-Cañas I, Dotor J, Palao G, Lasarte JJ, Ruiz J, et al. Topical application of a peptide inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta1 ameliorates bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis. J Investig Dermatol. 2005;125:450–5.
Branton MH, Kopp JB. TGF-beta and fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 1999;1:1349–65.
Aspenberg P, Jeppsson C, Wang JS, Boström M. Transforming growth factor beta and bone morphogenetic protein 2 for bone ingrowth: a comparison using bone chambers in rats. Bone. 1996;19:499–503.
Tieline L, Puolakkainen P, Pohjonen T, Rautavuori J, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P. The effect of transforming growth factor-beta1, released from a bioabsorbable self-reinforced polylactide pin, on a bone defect. Biomaterials. 2002;23:3817–23.
Nikolidakis D, Meijer GJ, Oortgiesen DAW, Walboomers XF, Jansen JA. The effect of a low dose of transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) on the early bone-healing around oral implants inserted in trabecular bone. Biomaterials. 2009;30:94–9.
Takeuchi K, Abe M, Hiasa M, Oda A, Amou H, Kido S, et al. TGF-β inhibition restores terminal osteoblast differentiation to suppress myeloma growth. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e9870.
Sevilla P, Cirera A, Dotor J, Gil FJ, Galindo-Moreno P, Aparicio C. In vitro cell response on CP-Ti surfaces functionalized with TGF-β1 inhibitory peptides. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29:73.
Gonzalo-Gil E, Galindo-Izquierdo M. Papel del factor de crecimiento transformador-beta (TGF-β) en la fisiopatología de la artritis reumatoide. Reumatol Clínica. 2014;10:174–9.
Sporn MB, Roberts AB. Transforming growth factor-beta: recent progress and new challenges. J Cell Biol. 1992;119:1017–21.
Barnard JA, Lyons RM, Moses HL. The cell biology of transforming growth factor beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1032:79–87.
Filvaroff E, Erlebacher A, Ye J, Gitelman SE, Lotz J, Heillman M, et al. Inhibition of TGF-beta receptor signaling in osteoblasts leads to decreased bone remodeling and increased trabecular bone mass. Development. 1999;126:4267–79.
Shen Z-JJ, Kim SK, Jun DY, Park W, Kim YH, Malter JS, et al. Antisense targeting of TGF-beta1 augments BMP-induced upregulation of osteopontin, type I collagen and Cbfa1 in human Saos-2 cells. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:1415–25.
Chang Y-C, Ho K-N, Feng S-W, Huang H-M, Chang C-H, Lin C-T, et al. Fibronectin-grafted titanium dental implants: an in vivo study. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1–11.
Mohammad KS, Chen CG, Balooch G, Stebbins E, McKenna CR, Davis H, et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of the TGF-beta type I receptor kinase has anabolic and anti-catabolic effects on bone. PLoS ONE 2009;4:e5275.
Ezquerro I-J, Lasarte J-J, Dotor J, Castilla-Cortázar I, Bustos M, Peñuelas I, et al. A synthetic peptide from transforming growth factor beta type III receptor inhibits liver fibrogenesis in rats with carbon tetrachloride liver injury. Cytokine. 2003;22:12–20.
Vicent S, Luis-Ravelo D, Antón I, García-Tuñón I, Borrás-Cuesta F, Dotor J, et al. A novel lung cancer signature mediates metastatic bone colonization by a dual mechanism. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2275–85.
Serratì S, Margheri F, Pucci M, Cantelmo AR, Cammarota R, Dotor J, et al. TGFbeta1 antagonistic peptides inhibit TGFbeta1-dependent angiogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:813–25.
Sevilla P, Gil J, Aparicio C. Relevant properties for immobilizing short peptides on biosurfaces. IRBM. 2017;38:256–65.
Serratì S, Margheri F, Pucci M, Cantelmo AR, Cammarota R, Dotor J, et al. TGFβ1 antagonistic peptides inhibit TGFβ1-dependent angiogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:813–25.
Lloyd-Williams P, Albericio F, Giralt E. Chemical approaches to the synthesis of peptides and proteins (new directions in organic & biological chemistry). Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC-Press, editor. CRC-Press; 1997.
Sevilla P, Vining KV, Dotor J, Rodriguez D, Gil FJ, Aparicio C. Surface immobilization and bioactivity of TGF-β1 inhibitor peptides for bone implant applications. J Biomed Mater Res - Part B Appl Biomater. 2016;104:385–94.
Gil FJ, Padrós A, Manero JM, Aparicio C, Nilsson M, Planell JA. Growth of bioactive surfaces on titanium and its alloys for orthopaedic and dental implants. Mater Sci Eng C. 2002;22:53–60.
Barba A, Diez-Escudero A, Maazouz Y, Rappe K, Espanol M, Montufar EB, et al. Osteoinduction by foamed and 3D-printed calcium phosphate scaffolds: effect of nanostructure and pore architecture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:41722–36.
Manresa C, Bosch M, Manzanares MC, Carvalho P, Echeverr JJ.A new standardized-automatic method for bone-to-implant contact histomorphometric analysis based on backscattered scanning electron microscopy images. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25:702–6.
Cardoso MV, Chaudhari A, Yoshida Y, Van Meerbeek B, Naert I, Duyck J. Bone tissue response to implant surfaces functionalized with phosphate-containing polymers. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25:91–100.
Godoy-Gallardo M, Manzanares-Céspedes MC, Sevilla P, Nart J, Manzanares N, Manero JM, et al. Evaluation of bone loss in antibacterial coated dental implants: an experimental study in dogs. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;69:538–45.
Arisan V, Anil A, Wolke JG, Özer K. The effect of injectable calcium phosphate cement on bone anchorage of titanium implants: an experimental feasibility study in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;39:463–8.
Schmitt CM, Koepple M, Moest T, Neumann K, Weisel T, Schlegel KA. In vivo evaluation of biofunctionalized implant surfaces with a synthetic peptide (P-15) and its impact on osseointegration. A preclinical animal study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27:1339–48.
Aparicio C, Padrós A, Gil, JJ. F-. In vivo evaluation of micro-rough and bioactive titanium dental implants using histometry and pull-out tests. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4:1672–82.
Vivan Cardoso M, Vandamme K, Chaudhari A, De Rycker J, Van Meerbeek B, Naert I, et al. Dental implant macro-design features can impact the dynamics of osseointegration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17(4):639–45.
Janner SFM, Gahlert M, Bosshardt DD, Roehling S, Milz S, Higginbottom F, et al. Bone response to functionally loaded, two-piece zirconia implants: a preclinical histometric study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29:277–89.
Iezzi G, Degidi M, Scarano A, Perrotti V, Piattelli A. Bone response to submerged, unloaded implants inserted in poor bone sites: a histological and histomorphometrical study of 8 titanium implants retrieved from man. J Oral Implantol. 2005;31:225–33.
Ivanoff CJ, Hallgren C, Widmark G, Sennerby L.Wennerberg A, Histologic evaluation of the bone integration of TiO2 blasted and turned titanium microimplants in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12:128–34. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11251662.
Ríos-Santos JV, Menjívar-Galán AM, Herrero-Climent M, Ríos-Carrasco B, Fernández-Palacín A, Perez RA. et al. Unravelling the effect of macro and microscopic design of dental implants on osseointegration: a randomised clinical study in minipigs. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(7):99.
Herrero-Climent M, Lázaro P, Vicente Rios J, Lluch S, Marqués-Calvo MS, Guillem-Martí J, et al. Influence of acid-etching after grit-blasted on osseointegration of titanium dental implants: In vitro and in vivo studies. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24:2047–55. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23625320
López-López J, Chimenos-Küstner E, Manzanares-Cespedes C, Muñoz-Sánchez J, Castañeda-Vega P, Jané-Salas E, et al. Histomorphological study of the bone regeneration capacity of platelet-rich plasma, bone marrow and tricalcium phosphate: experimental study on pigs. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:e620–7.
Pardali E, Dijke P. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling and tumor angiogenesis. Mol Cell. 2009;14:4848–61.
Hu XF, Wang L, Xiang G, Lei W, Feng YF. Angiogenesis impairment by the NADPH oxidase-triggered oxidative stress at the bone-implant interface: critical mechanisms and therapeutic targets for implant failure under hyperglycemic conditions in diabetes. Acta Biomater Acta Materialia Inc. 2018;73:470–87.
Delgado-Ruiz RA, Abboud M, Romanos G, Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Gomez-Moreno G, Calvo-Guirado JL. Peri-implant bone organization surrounding zirconia-microgrooved surfaces circularly polarized light and confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26:1328–37.
Zhao G, Raines AL, Wieland M, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD. Requirement for both micron- and submicron scale structure for synergistic responses of osteoblasts to substrate surface energy and topography. Biomaterials. 2007;28:2821–9.
Zhu H, Gomez M, Xiao J, Perale G, Betge F, Lyngstadaas SP. et al. Xenohybrid bone graft containing intrinsically disordered proteins shows enhanced in vitro bone formation. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(4):2263–74.
Harnett EM, Alderman J, Wood T. The surface energy of various biomaterials coated with adhesion molecules used in cell culture. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2007;55:90–7.
Yu Y, Zhu W, Xu L, Ming P, Shao S, Qiu J. Osseointegration of titanium dental implant under fluoride exposure in rabbits: Micro‐CT and histomorphometry study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30:1038–48.
Acknowledgements
The authors kindly acknowledge the collaboration of many individuals and institutions in the present manuscript. The present study was supported by the Research Cathedra Klockner-University of Granada. The experimental animals surgery and care was carried out with the valuable collaboration of Dr Albert Barba and Katrin Rappe of the surgical team in the Veterinary Faculty, Autonomous University of Barcelona; we would like to thank Ricardo Fernández and Allinson Olaechea for their participation during surgeries; the samples preparation and visualization was carried out by Ms Mónica Ortiz, from the Grup de Biomaterials, Biomecànica i Enginyeria de Teixits, Dept. de Ciència dels Materials i Enginyeria Metal·lúrgica and the Barcelona Research Center in MultiScale Science and Engineering, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC). Ms Eva Sanchez, from the Human Anatomy and Embryology lab in the Bellvitge campus of the University of Barcelona is kindly acknowledged by her technical support to the management of the undecalcified samples. The authors are grateful to the Spanish Government and European Union FEDER by the concession of the project RTI2018–098075-B-C22.
Funding
The present study was supported totally by the Research Cathedra Klockner-University of Granada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirera, A., Sevilla, P., Manzanares, M.C. et al. Osseointegration around dental implants biofunctionalized with TGFβ-1 inhibitor peptides: an in vivo study in beagle dogs. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 31, 62 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-020-06397-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-020-06397-3