Abstract
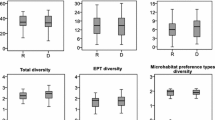
Suitable reservoirs and monitoring methods are needed to manage scarce water supplies in dry countries. We assessed here the impact on aquatic macroinvertebrates of the only dam on the Eerste River, which runs through the heart of a biodiversity hotspot, the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. The dam and associated activities, were the only forms of disturbance in this otherwise pristine area. We sampled over 20,000 macroinvertebrate individuals and illustrated some categorical effects of the impoundment and its effects on macroinvertebrate assemblages. Macroinvertebrate species diversity below the dam was only half of that in the pristine catchment area above the dam. Furthermore, Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera diversity and abundance dropped to almost zero as a result of the impoundment. In contrast, the abundance of the Diptera family Chironomidae increased substantially below the dam. These changes in macroinvertebrate diversity mirrored those recorded in biologically less diverse areas, but are of major concern in this biodiversity hotspot with its rich endemic fauna. We conclude that such an impoundment, while important for human welfare, results in a high price being paid in terms of loss of local biodiversity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JD (1995) Stream ecology: structure and function of running waters. Chapman and Hall, London
Armitage PD, Blackburn JH (1990) Environmental stability and communities of Chironomidae (Diptera) in a regulated river. Regul Rivers Res Manage 5:319–328. doi:10.1002/rrr.3450050404
Barow ME, McIntosh MD, Burky AJ, Way CM (2005) The influence of stream flow reduction on the energetics of Hawaiian torrenticolous aquatic insects, Telmatogeton Schiner and Pocanace Hendel. J Insect Conserv 9:175–185. doi:10.1007/s10841-005-4831-0
Basson MS, Van Niekerk PH, Van Rooyen JA (1997) Overview of water resources availability and utilisation in South Africa. DWAF Report No. PRSA/00/0197. Department of Water Affairs and Forestry and BKS (Pty) Ltd, Pretoria, South Africa
Bednarek A (2001) Undamming rivers: a review of the ecological impacts of dam removal. Environ Manage (N Y) 27:803–814. doi:10.1007/s002670010189
Born SM, Genskow KD, Filbert TL, Hernandez-Mora N, Keefer ML, White KA (1998) Socioeconomic and institutional dimensions of dam removals: the Wisconsin experience. Environ Manage (N Y) 22:359–370. doi:10.1007/s002679900111
Brasher AMD (2003) Impacts of human disturbances on biotic communities in Hawaiian streams. Bioscience 53:1052–1060. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[1052:IOHDOB]2.0.CO;2
Brittain JE, Saltveit SJ (1989) A review of the effect of river regulation on mayflies (Ephemeroptera). Regul Rivers Res Manage 3:191–204. doi:10.1002/rrr.3450030119
Brown CA, Dallas HF (1995) Eerste River, Western Cape: situation assessment of the riverine ecosystem. Final report, June 1995. Southern Waters Ecological Research and Consultancy, CSIR, Stellenbosch, South Africa
Chapman PM, Power EA, Burton GA Jr (1992) Integrative assessments in aquatic ecosystems. In: Burton GA Jr (ed) Sediment toxicity assessment. Lewis Boca Raton, Florida, pp 313–340
Chutter FM (1994) The rapid biological assessment of streams and rivers water quality by means of macroinvertebrate community in South Africa. Progress Report to the Water Research Commission, Pretoria, South Africa
Davies B, Day J (1998) Vanishing waters. University of Cape Town Press, Cape Town, South Africa
Dickens CWS, Graham PM (2002) The South African Scoring System (SASS5) Version 5 rapid bioassessment method for rivers. Afr J Aquat Sci 27:1–10
Doeg TJ, Koehn JD (1994) Effects of draining and desilting a small weir on downstream fish and macroinvertebrates. Regul Rivers Res Manage 9:263–277. doi:10.1002/rrr.3450090407
Drinkwater KF, Frank KT (1994) Effects of river regulation and diversion on marine fish and invertebrates. Aquat Conserv Freshw Mar Ecosyst 4:135–151. doi:10.1002/aqc.3270040205
Kevan PG (1999) Pollinators as bioindicators of the state of the environment: species, activity and diversity. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:373–393. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00044-4
King JM, Schael DM (2001) Assessing the ecological relevance of a spatially-nested geomorphological hierarchy for river management. WRC Report No 754/1/01 Freshwater Research Unit, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
Kondolf GM (1997) Hungry water: effects of dams and gravel mining on river channels. Environ Manage (N Y) 21:533–551. doi:10.1007/s002679900048
Ligon FK, Dietrich WE, Trush WJ (1995) Downstream ecological effects of dams. Bioscience 45:183–192. doi:10.2307/1312557
Loch DD, West JL, Perlmutter DG (1996) The effect of trout farm effluent on the taxa richness of benthic macroinvertebrates. Aquaculture 147:5–10. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01394-4
Logan P, Brooker MP (1983) The macroinvertebrate faunas of riffles and pools. Water Res 17:263–270. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(83)90179-3
Mackie GL (1998) Applied aquatic ecosystem concepts. University of Guelph Custom Coursepack
Madikizela BR, Dye AH, O’Keeffe JH (2001) Water quality and faunal studies in the Umzimvubu Catchment, Eastern Cape with particular emphasis on species as indicators of environmental change. WRC Report No.716/1/01. Freshwater Research Unit, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
Malmqvist B, Englund G (1996) Effects of hydropower-induced flow perturbations on Mayfly (Ephemeroptera) richness and abundance in North Swedish river rapids. Hydrobiologia 341:145–158. doi:10.1007/BF00018118
March JG, Benstead JP, Pringle CM, Scatena FN (2003) Damming tropical island streams: problems, solutions, and alternatives. Bioscience 53:1069–1078. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[1069:DTISPS]2.0.CO;2
McIntosh MD, Benbow ME, Burkey AJ (2002) Effects of stream diversion on riffle macroinvertebrate communities in a Maui, Hawaii, stream. River Res Appl 18:569–581. doi:10.1002/rra.694
Metcalf-Smith JL (1994) Biological water-quality assessment of rivers: use of macroinvertebrate communities. In: Calow P, Petts GE (eds) The rivers handbook, hydrological and ecological principles, vol 2. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 144–170
Mittermeier RA, Gil PR, Hoffmann M, Pilgrim J, Brooks T, Mittermeier CG et al (2004) Hotspots revisited. Cemex, Mexico City
Myers N, Mittermeier CG, Da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403:853–858. doi:10.1038/35002501
Nebeker AV (1971) Effect of high winter water temperatures on adult emergence of aquatic insects. Water Res 5:777–778. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(71)90100-X
Petts GE (1984) Impounded rivers: perspectives for ecological management. Wiley, Chichester, p 322
Poff NL, Allan JD, Bain MB, Karr JR, Prestegaard KL, Richter BD et al (1997) The natural flow regime. Bioscience 47:769–784. doi:10.2307/1313099
Quinn JM, Hickey CW (1990) Magnitude of effects of substrate particle size, recent flooding, and catchment development on benthic invertebrates. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 24:411–427
Resh VH (1995) The use of bentic macroinvertebrates and rapid assessment procedures for water quality monitoring in developing and newly industrialized countries. In: Davis WS, Simon T (eds) Biological assessment and criteria: tools for water resource planning and decision making. Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, pp 159–194
Resh VH, Rosenberg DM (1984) The ecology of aquatic insects. Praeger, New York
Roque FO, Trivinho-Strixino S, Strixino G, Agostinho RC, Fogo JC (2002) Benthic macroinvertebrates in streams of the Jarague State Park (Southeast of Brazil) considering multiple spatial scales. J Insect Conserv 7:63–72. doi:10.1023/A:1025505323668
Rosenberg DM (1998) A national aquatic ecosystem health program for Canada: we should go against the flow. Bull Entomol Soc Can 30:144–152
Rosenberg DM, Resh VH (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York
Rosenberg DM, Danks HV, Lehmkuhl DM (1986) Importance of insects in environmental impact assessment. Environ Manage (N Y) 10:773–783. doi:10.1007/BF01867730
Samways MJ, Taylor S (2004) Impacts of invasive alien plants on Red-listed South African dragonflies (Odonata). S Afr J Sci 100:78–80
Smith J, Samways MJ, Taylor S (2007) Assessing riparian quality using two complementary sets of bioindicators. Biodivers Conserv 16:2695–2713. doi:10.1007/s10531-006-9081-2
Stanford JA, Ward JV, Liss WJ, Frissell CA, Williams RN, Lichatowich JA et al (1996) A general protocol for restoration of regulated rivers. Regul Rivers Res Manage 12:391–413. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1646(199607)12:4/5<391::AID-RRR436>3.0.CO;2-4
Steytler NS, Samways MJ (1995) Biotope selection by adult male dragonflies (Odonata) at an artificial lake created for insect conservation in South Africa. Biol Conserv 72:381–386. doi:10.1016/0006-3207(94)00052-R
Turner CR (2000) A contribution to the study of the Table Mountain water beetles (Coleoptera) with special reference to the environmental impact of reservoirs. City Engineers Department, Cape Town
Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Sedell JR, Cushing CE (1980) The river continuum concept. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:130–137
Vigano L, Arillo A, Buffagni A, Camusso M, Ciannarella R, Crosa G et al (2002) Quality assessment of bed sediments of the Po River (Italy). Water Res 37:501–518. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00109-4
Ward JV (1992) Aquatic insect ecology: biology and habitat. Wiley, New York
Ward JV (1998) Riverine landscapes: biodiversity patterns, disturbance regimes, and aquatic conservation. Biol Conserv 83:269–278. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(97)00083-9
Ward JV, Stanford JA (1995) Ecological connectivity in alluvial river ecosystems and its disruption by flow regulation. Regul Rivers Res Manage 11:105–119. doi:10.1002/rrr.3450110109
Williams DD, Feltmate BW (1992) Aquatic insects. CAB International, Redwood Press, Melksham
Winston MR, Taylor CM, Pigg J (1991) Upstream extirpation of four minnow species due to damming of a prairie stream. Trans Am Fish Soc 120:98–105. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(1991)120<0098:UEOFMS>2.3.CO;2
Yeager BL (1994) Impacts of reservoirs on the aquatic environment of regulated rivers. Tennessee Valley Authority, Water Resources, Aquatic Biology Department, TVA/WR/AB-93/1, Norris, Tennessee, USA
Zwick P (1992) Stream habitat fragmentation—a threat to biodiversity. Biodivers Conserv 1:80–97. doi:10.1007/BF00731036
Acknowledgements
Adam Johnson kindly assisted with fieldwork. Financial support was from the National Research Foundation (NRF) and the University of Stellenbosch.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bredenhand, E., Samways, M.J. Impact of a dam on benthic macroinvertebrates in a small river in a biodiversity hotspot: Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. J Insect Conserv 13, 297–307 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-008-9173-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-008-9173-2