Abstract
Purpose
Pulmonary vein antrum isolation (PVAI) guided by intracardiac echocardiography and a roaming circular mapping catheter is an effective treatment modality for atrial fibrillation. Unfortunately, the complexity of this technique leads to long procedure times and high fluoroscopy exposure. Single-catheter multipolar ablation holds the promise to reduce these parameters. This study examined the effect of the conventional point-by-point PVAI with that of single-catheter multipolar ablation on the procedural characteristics and clinical outcomes of atrial fibrillation ablation.
Methods
Referred patients underwent PVAI guided by a magnetic-based 3D mapping (CARTO 3® System; group 1) or duty-cycled multipolar AF ablation using the pulmonary vein ablation catheter (PVAC, group 2) between June 2010 and May 2011.
Results
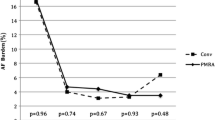
Data were analyzed from 19 patients in group 1 and 31 patients in group 2. There was no significant difference in the length of the procedure between the two groups (135 ± 26 vs 125 ± 25 min, P = 0.20). Patients who underwent ablation using PVAC spent significantly less time in the procedure room pre- and post-procedure than those who underwent conventional PVAI (205 ± 38 vs 179 ± 30 min, P = 0.02) and had a significantly shorter fluoroscopy exposure (50 ± 16 vs 36 ± 14 min, P = 0.003) and radiofrequency energy delivery time (54 ± 26 vs 32 ± 33 min, P = 0.02). No differences in safety and efficacy were seen between the groups.
Conclusions
Single-catheter multipolar AF ablation was associated with significantly lower fluoroscopy duration, radiofrequency energy delivery time, and the time the patient spent in the procedure room before and after ablation, although measured short-term clinical outcomes were similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin, E. J., Wolf, P. A., D’Agostino, R. B., Silbershatz, H., Kannel, W. B., & Levy, D. (1998). Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation, 98(10), 946–952.
Wolf, P. A., Mitchell, J. B., Baker, C. S., Kannel, W. B., & D’Agostino, R. B. (1998). Impact of atrial fibrillation on mortality, stroke, and medical costs. Archives of Internal Medicine, 158(3), 229–234.
Fuster, V., Ryden, L. E., Cannom, D. S., Crijns, H. J., Curtis, A. B., Ellenbogen, K. A., et al. (2006). ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation): Developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation, 114(7), e257–e354.
Dorian, P., Jung, W., Newman, D., Paquette, M., Wood, K., Ayers, G. M., et al. (2000). The impairment of health-related quality of life in patients with intermittent atrial fibrillation: Implications for the assessment of investigational therapy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 36(4), 1303–1309.
Crandall, M. A., Bradley, D. J., Packer, D. L., & Asirvatham, S. J. (2009). Contemporary management of atrial fibrillation: Update on anticoagulation and invasive management strategies. Mayo Clinic proceedings. Mayo Clinic, 84(7), 643–662.
Chung, M. K., Shemanski, L., Sherman, D. G., Greene, H. L., Hogan, D. B., Kellen, J. C., et al. (2005). Functional status in rate- versus rhythm-control strategies for atrial fibrillation: Results of the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Functional Status Substudy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 46(10), 1891–1899.
Corley, S. D., Epstein, A. E., DiMarco, J. P., Domanski, M. J., Geller, N., Greene, H. L., et al. (2004). Relationships between sinus rhythm, treatment, and survival in the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Study. Circulation, 109(12), 1509–1513.
Guglin, M., Chen, R., & Curtis, A. B. (2010). Sinus rhythm is associated with fewer heart failure symptoms: Insights from the AFFIRM trial. Heart Rhythm, 7(5), 596–601.
Haissaguerre, M., Jais, P., Shah, D. C., Takahashi, A., Hocini, M., Quiniou, G., et al. (1998). Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. The New England Journal of Medicine, 339(10), 659–666.
Chen, S. A., Hsieh, M. H., Tai, C. T., Tsai, C. F., Prakash, V. S., Yu, W. C., et al. (1999). Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins: Electrophysiological characteristics, pharmacological responses, and effects of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation, 100(18), 1879–1886.
Haissaguerre, M., Shah, D. C., Jais, P., Hocini, M., Yamane, T., Deisenhofer, I., et al. (2000). Electrophysiological breakthroughs from the left atrium to the pulmonary veins. Circulation, 102(20), 2463–2465.
Natale, A., Pisano, E., Shewchik, J., Bash, D., Fanelli, R., Potenza, D., et al. (2000). First human experience with pulmonary vein isolation using a through-the-balloon circumferential ultrasound ablation system for recurrent atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 102(16), 1879–1882.
Pappone, C., Oreto, G., Lamberti, F., Vicedomini, G., Loricchio, M. L., Shpun, S., et al. (1999). Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using a 3D mapping system. Circulation, 100(11), 1203–1208.
Marrouche, N. F., Dresing, T., Cole, C., Bash, D., Saad, E., Balaban, K., et al. (2002). Circular mapping and ablation of the pulmonary veins for treatment of atrial fibrillation. Impact of different catheter technologies. J Am Coll Cardiol, 40(3), 464–474.
Khaykin Y, Oosthuizen R, Zarnett L, Essebag V, Parkash R, Seabrook C, et al., Clinical predictors of arrhythmia recurrences following pulmonary vein antrum isolation for atrial fibrillation: Predicting arrhythmia recurrence post-PVAI. Journal of cardiovascular electrophysiology, 2011.
Hussein, A. A., Saliba, W. I., Martin, D. O., Bhargava, M., Sherman, M., Magnelli-Reyes, C., et al. (2011). Natural history and long-term outcomes of ablated atrial fibrillation. Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 4(3), 271–278.
Estner, H. L., Deisenhofer, I., Luik, A., Ndrepepa, G., von Bary, C., Zrenner, B., et al. (2006). Electrical isolation of pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation: reduction of fluoroscopy exposure and procedure duration by the use of a non-fluoroscopic navigation system (NavX). Europace, 8(8), 583–587.
Lakkireddy, D., Nadzam, G., Verma, A., Prasad, S., Ryschon, K., Di Biase, L., et al. (2009). Impact of a comprehensive safety program on radiation exposure during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A prospective study. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 24(2), 105–112.
Rotter, M., Takahashi, Y., Sanders, P., Haissaguerre, M., Jais, P., Hsu, L. F., et al. (2005). Reduction of fluoroscopy exposure and procedure duration during ablation of atrial fibrillation using a novel anatomical navigation system. European Heart Journal, 26(14), 1415–1421.
Khaykin, Y., Oosthuizen, R., Zarnett, L., Wulffhart, Z. A., Whaley, B., Hill, C., et al. (2011). CARTO-guided vs. NavX-guided pulmonary vein antrum isolation and pulmonary vein antrum isolation performed without 3-D mapping: effect of the 3-D mapping system on procedure duration and fluoroscopy time. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology: An International Journal of Arrhythmias and Pacing, 30(3), 233–240.
Knackstedt, C., Schauerte, P., & Kirchhof, P. (2008). Electro-anatomic mapping systems in arrhythmias. Europace, 10(Suppl 3), iii28–34.
Piorkowski, C., Hindricks, G., Schreiber, D., Tanner, H., Weise, W., Koch, A., et al. (2006). Electroanatomic reconstruction of the left atrium, pulmonary veins, and esophagus compared with the “true anatomy” on multislice computed tomography in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 3(3), 317–327.
Boersma, L. V., Wijffels, M. C., Oral, H., Wever, E. F., & Morady, F. (2008). Pulmonary vein isolation by duty-cycled bipolar and unipolar radiofrequency energy with a multielectrode ablation catheter. Heart Rhythm, 5(12), 1635–1642.
Scharf, C., Boersma, L., Davies, W., Kanagaratnam, P., Peters, N. S., Paul, V., et al. (2009). Ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation using multielectrode catheters and duty-cycled radiofrequency energy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 54(15), 1450–1456.
Wieczorek, M., Hoeltgen, R., Akin, E., Salili, A. R., Oral, H., & Morady, F. (2010). Results of short-term and long-term pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using duty-cycled bipolar and unipolar radiofrequency energy. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 21(4), 399–405.
Khaykin, Y., Skanes, A., Champagne, J., Themistoclakis, S., Gula, L., Rossillo, A., et al. (2009). A randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and safety of electroanatomic circumferential pulmonary vein ablation supplemented by ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms versus potential-guided pulmonary vein antrum isolation guided by intracardiac ultrasound. Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 2(5), 481–487.
Calkins, H., Brugada, J., Packer, D. L., Cappato, R., Chen, S. A., Crijns, H. J., et al. (2007). HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert Consensus Statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for personnel, policy, procedures and follow-up. A report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 4(6), 816–861.
Marrouche, N. F., Martin, D. O., Wazni, O., Gillinov, A. M., Klein, A., Bhargava, M., et al. (2003). Phased-array intracardiac echocardiography monitoring during pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Impact on outcome and complications. Circulation, 107, 2710–2716.
Kilicaslan, F., Verma, A., Saad, E., Rossillo, A., Davis, D. A., Prasad, S. K., et al. (2006). Transcranial doppler detection of microembolic signals during pulmonary vein antrum isolation: Implications for titration of radiofrequency energy. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17(5), 495–501.
Birnie, D., Healey, J. S., Krahn, A. D., Ahmad, K., Crystal, E., Khaykin, Y., et al. (2011). Prevalence and risk factors for cervical and lumbar spondylosis in interventional electrophysiologists. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(9), 957–960.
Bittner, A., Monnig, G., Zellerhoff, S., Pott, C., Kobe, J., Dechering, D., et al. (2011). Randomized study comparing duty-cycled bipolar and unipolar radiofrequency with point-by-point ablation in pulmonary vein isolation. Heart Rhythm, 8(9), 1383–1390.
Bulava, A., Hanis, J., Sitek, D., Osmera, O., Karpianus, D., Snorek, M., et al. (2010). Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A randomized comparison between multielectrode catheter and point-by-point ablation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology: PACE, 33(9), 1039–1046.
Tivig, C., Dang, L., Brunner-La Rocca, H. P., Ozcan, S., Duru, F., & Scharf, C. (2010). Duty-cycled unipolar/bipolar versus conventional radiofrequency ablation in paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. International journal of cardiology.
Herrera Siklody, C., Deneke, T., Hocini, M., Lehrmann, H., Shin, D. I., Miyazaki, S., et al. (2011). Incidence of asymptomatic intracranial embolic events after pulmonary vein isolation: Comparison of different atrial fibrillation ablation technologies in a multicenter study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 58(7), 681–688.
Deneke, T., Shin, D. I., Balta, O., Bunz, K., Fassbender, F., Mugge, A., et al. (2011). Postablation asymptomatic cerebral lesions: Long-term follow-up using magnetic resonance imaging. Heart rhythm.
Gaita, F., Leclercq, J. F., Schumacher, B., Scaglione, M., Toso, E., Halimi, F., et al. (2011). Incidence of silent cerebral thromboembolic lesions after atrial fibrillation ablation may change according to technology used: Comparison of irrigated radiofrequency, multipolar nonirrigated catheter and cryoballoon. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(9), 961–968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaykin, Y., Zarnett, L., Friedlander, D. et al. Point-by-point pulmonary vein antrum isolation guided by intracardiac echocardiography and 3D mapping and duty-cycled multipolar AF ablation: effect of multipolar ablation on procedure duration and fluoroscopy time. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 34, 303–310 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-012-9676-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-012-9676-3