Abstract
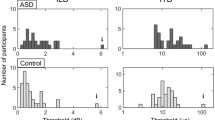
This study provides new evidence of deficient auditory cortical processing of speech in noise in autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Speech-evoked responses (~100–300 ms) in quiet and background noise were evaluated in typically-developing (TD) children and children with ASD. ASD responses showed delayed timing (both conditions) and reduced amplitudes (quiet) compared to TD responses. As expected, TD responses in noise were delayed and reduced compared to quiet responses. However, minimal quiet-to-noise response differences were found in children with ASD, presumably because quiet responses were already severely degraded. Moreover, ASD quiet responses resembled TD noise responses, implying that children with ASD process speech in quiet only as well as TD children do in background noise.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantara, J. I., Weisblatt, E. J., Moore, B. C., & Bolton, P. F. (2004). Speech-in-noise perception in high-functioning individuals with autism or asperger’s syndrome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 45(6), 1107–1114. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.t01-1-00303.x.
Banai, K., Hornickel, J. M., Skoe, E., Nicol, T., Zecker, S., & Kraus, N. (2009). Reading and subcortical auditory function. Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y.). doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp024.
Banai, K., Nicol, T., Zecker, S. G., & Kraus, N. (2005). Brainstem timing: Implications for cortical processing and literacy. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(43), 9850–9857. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2373-05.2005.
Bishop, D. V., Hardiman, M., Uwer, R., & von Suchodoletz, W. (2007). Maturation of the long-latency auditory ERP: Step function changes at start and end of adolescence. Developmental Science, 10(5), 565–575. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00619.x.
Boddaert, N., Chabane, N., Gervais, H., Good, C. D., Bourgeois, M., Plumet, M. H., et al. (2004). Superior temporal sulcus anatomical abnormalities in childhood autism: A voxel-based morphometry MRI study. NeuroImage, 23(1), 364–369. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.016.
Boucher, J. (2003). Language development in autism. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, 67(Suppl 1), S159–S163. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2003.08.016.
Bruneau, N., Bonnet-Brilhault, F., Gomot, M., Adrien, J. L., & Barthelemy, C. (2003). Cortical auditory processing and communication in children with autism: Electrophysiological/behavioral relations. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 51(1), 17–25. doi:10.1016/S0167-8760(03)00149-1.
Bruneau, N., Roux, S., Adrien, J. L., & Barthelemy, C. (1999). Auditory associative cortex dysfunction in children with autism: Evidence from late auditory evoked potentials (N1 wave-T complex). Clinical Neurophysiology, 110(11), 1927–1934. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(99)00149-2.
Ceponiene, R., Lepisto, T., Shestakova, A., Vanhala, R., Alku, P., Naatanen, R., et al. (2003). Speech-sound-selective auditory impairment in children with autism: They can perceive but do not attend. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(9), 5567–5572. doi:10.1073/pnas.0835631100.
Ceponiene, R., Shestakova, A., Balan, P., Alku, P., Yiaguchi, K., & Naatanen, R. (2001). Children’s auditory event-related potentials index sound complexity and “speechness”. The International Journal of Neuroscience, 109(3–4), 245–260.
Chawarska, K., Klin, A., Paul, R., & Volkmar, F. (2007). Autism spectrum disorder in the second year: Stability and change in syndrome expression. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 48(2), 128–138. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01685.x.
Connolly, J. F. (1993). The influence of stimulus intensity, contralateral masking and handedness on the temporal N1 and the T complex components of the auditory N1 wave. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 86(1), 58–68. doi:10.1016/0013-4694(93)90067-6.
Courchesne, E., Lincoln, A. J., Yeung-Courchesne, R., Elmasian, R., & Grillon, C. (1989). Pathophysiologic findings in nonretarded autism and receptive developmental language disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 19(1), 1–17. doi:10.1007/BF02212714.
Courchesne, E., & Pierce, K. (2005). Why the frontal cortex in autism might be talking only to itself: Local over-connectivity but long-distance disconnection. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15(2), 225–230. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2005.03.001.
Cunningham, J., Nicol, T., Zecker, S. G., Bradlow, A., & Kraus, N. (2001). Neurobiologic responses to speech in noise in children with learning problems: Deficits and strategies for improvement. Clinical Neurophysiology, 112(5), 758–767. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(01)00465-5.
Cunningham, J., Nicol, T., Zecker, S., & Kraus, N. (2000). Speech-evoked neurophysiologic responses in children with learning problems: Development and behavioral correlates of perception. Ear and Hearing, 21(6), 554–568. doi:10.1097/00003446-200012000-00003.
Ferri, R., Elia, M., Agarwal, N., Lanuzza, B., Musumeci, S. A., & Pennisi, G. (2003). The mismatch negativity and the P3a components of the auditory event-related potentials in autistic low-functioning subjects. Clinical Neurophysiology, 114(9), 1671–1680. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(03)00153-6.
Freitag, C. M. (2007). The genetics of autistic disorders and its clinical relevance: A review of the literature. Molecular Psychiatry, 12(1), 2–22. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001896.
Gage, N. M., Siegel, B., Callen, M., & Roberts, T. P. (2003a). Cortical sound processing in children with autism disorder: An MEG investigation. NeuroReport, 14(16), 2047–2051. doi:10.1097/00001756-200311140-00008.
Gage, N. M., Siegel, B., & Roberts, T. P. (2003b). Cortical auditory system maturational abnormalities in children with autism disorder: An MEG investigation. Brain Research, 144(2), 201–209. doi:10.1016/S0165-3806(03)00172-X.
Gorga, M. P., Abbas, P. J., & Worthington, D. W. (1985). Stimulus calibrations in ABR measurements. In J. T. Jacobson (Ed.), The auditory brainstem response (pp. 49–62). San Diego: College-Hill Press.
Groen, M. A., Alku, P., & Bishop, D. V. (2008). Lateralisation of auditory processing in Down syndrome: A study of T-complex peaks Ta and Tb. Biological Psychology, 79(2), 148–157. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.04.003.
Hall, J. W. (1992). Handbook of auditory evoked responses. Needham Heights: Allyn and Bacon.
Happe, F., Ronald, A., & Plomin, R. (2006). Time to give up on a single explanation for autism. Nature Neuroscience, 9(10), 1218–1220. doi:10.1038/nn1770.
Hardan, A. Y., Jou, R. J., Keshavan, M. S., Varma, R., & Minshew, N. J. (2004). Increased frontal cortical folding in autism: A preliminary MRI study. Psychiatry Research, 131(3), 263–268. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2004.06.001.
Hardan, A. Y., Muddasani, S., Vemulapalli, M., Keshavan, M. S., & Minshew, N. J. (2006). An MRI study of increased cortical thickness in autism. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 163(7), 1290–1292. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.163.7.1290.
Hayes, E. A., Warrier, C. M., Nicol, T. G., Zecker, S. G., & Kraus, N. (2003). Neural plasticity following auditory training in children with learning problems. Clinical Neurophysiology, 114(4), 673–684. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00414-5.
Herbert, M. R., Harris, G. J., Adrien, K. T., Ziegler, D. A., Makris, N., Kennedy, D. N., et al. (2002). Abnormal asymmetry in language association cortex in autism. Annals of Neurology, 52(5), 588–596. doi:10.1002/ana.10349.
Herbert, M. R., & Kenet, T. (2007). Brain abnormalities in language disorders and in autism. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 54(3), 563–583. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2007.02.007. vii.
Herbert, M. R., Ziegler, D. A., Deutsch, C. K., O’Brien, L. M., Kennedy, D. N., Filipek, P. A., et al. (2005). Brain asymmetries in autism and developmental language disorder: A nested whole-brain analysis. Brain, 128(Pt 1), 213–226. doi:10.1093/brain/awh330.
Hood, L. (1998). Clinical applications of the auditory brainstem response. Singular Publishing Group, Inc: San Diego.
Hoormann, J., Falkenstein, M., & Hohnsbein, J. (2000). Early attention effects in human auditory-evoked potentials. Psychophysiology, 37, 29–42. doi:10.1017/S0048577200981290.
Jacobson, J. T. (Ed.). (1985). The auditory brainstem response. San Diego: College-Hill Press.
Jansson-Verkasalo, E., Ceponiene, R., Kielinen, M., Suominen, K., Jantti, V., Linna, S. L., et al. (2003). Deficient auditory processing in children with Asperger syndrome, as indexed by event-related potentials. Neuroscience Letters, 338(3), 197–200. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)01405-2.
Johnstone, S. J., Barry, R. J., Anderson, J. W., & Coyle, S. F. (1996). Age-related changes in child and adolescent event-related potential component morphology, amplitude and latency to standard and target stimuli in an auditory oddball task. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 24(3), 223–238. doi:10.1016/S0167-8760(96)00065-7.
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Keller, T. A., & Minshew, N. J. (2004). Cortical activation and synchronization during sentence comprehension in high-functioning autism: Evidence of underconnectivity. Brain, 127(Pt 8), 1811–1821. doi:10.1093/brain/awh199.
King, C., Warrier, C. M., Hayes, E., & Kraus, N. (2002). Deficits in auditory brainstem pathway encoding of speech sounds in children with learning problems. Neuroscience Letters, 319(2), 111–115. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(01)02556-3.
Klatt, D. (1980). Software for cascade/parallel formant synthesizer. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 67, 971–975. doi:10.1121/1.383940.
Kraus, N., McGee, T. J., Zecker, S. G., Nicol, T., & Koch, D. B. (1996). Auditory neurophysiologic responses and discrimination deficits in children with learning problems. Science, 273, 971–973. doi:10.1126/science.273.5277.971.
Kuhl, P. K., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., & Dawson, G. (2005). Links between social and linguistic processing of speech in preschool children with autism: Behavioral and electrophysiological measures. Developmental Science, 8(1), F1–F12. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2004.00384.x.
Lavoie, B. A., Hine, J. E., & Thornton, R. D. (2008). The choice of distracting task can affect the quality of auditory evoked potentials recorded for clinical assessment. International Journal of Audiology, 47(7), 439–444. doi:10.1080/14992020802033109.
Le Couteur, A., Rutter, M., Lord, C., Rios, P., Robertson, S., Holdgrafer, M., et al. (1989). Autism diagnostic interview: A standardized investigator-based instrument. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 19(3), 363–387. doi:10.1007/BF02212936.
Lepisto, T., Kujala, T., Vanhala, R., Alku, P., Huotilainen, M., & Naatanen, R. (2005). The discrimination of and orienting to speech and non-speech sounds in children with autism. Brain Research, 1066(1–2), 147–157. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.10.052.
Lepisto, T., Silokallio, S., Nieminen-von Wendt, T., Alku, P., Naatanen, R., & Kujala, T. (2006). Auditory perception and attention as reflected by the brain event-related potentials in children with asperger syndrome. Clinical Neurophysiology, 117(10), 2161–2171. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2006.06.709.
Lincoln, A. J., Courchesne, E., Harms, L., & Allen, M. (1995). Sensory modulation of auditory stimuli in children with autism and receptive developmental language disorder: Event-related brain potential evidence. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 25(5), 521–539. doi:10.1007/BF02178298.
London, E. (2007). The role of the neurobiologist in redefining the diagnosis of autism. Brain Pathology (Zurich, Switzerland), 17(4), 408–411. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00103.x.
Lord, C., & Richler, J. (2006). Early diagnosis of children with autism spectrum disorders. In T. Charman & W. Stone (Eds.), Social and communication development in autism spectrum disorders: Early identification, diagnosis, & intervention (pp. 35–59). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Cook, E. H., Jr, Leventhal, B. L., DiLavore, P. C., et al. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(3), 205–223. doi:10.1023/A:1005592401947.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., Goode, S., Heemsbergen, J., Jordan, H., Mawhood, L., et al. (1989). Autism diagnostic observation schedule: A standardized observation of communicative and social behavior. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 19(2), 185–212. doi:10.1007/BF02211841.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., & Le Couteur, A. (1994). Autism diagnostic interview-revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24(5), 659–685. doi:10.1007/BF02172145.
Martin, B. A., Sigal, A., Kurtzberg, D., & Stapells, D. R. (1997). The effects of decreased audibility produced by high-pass noise masking on cortical event-related potentials to speech sounds/ba/and /da/. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 101(3), 1585–1599. doi:10.1121/1.418146.
McArthur, G. M., Bishop, D. V., & Proudfoot, M. (2003). Do video sounds interfere with auditory event-related potentials? Behavior Research Methods, Instruments and Computers: a journal of the Psychonomic Society Inc, 35(2), 329–333.
Minshew, N. J., & Williams, D. L. (2007). The new neurobiology of autism: Cortex, connectivity, and neuronal organization. Archives of Neurology, 64(7), 945–950. doi:10.1001/archneur.64.7.945.
Muller, R. A., Behen, M. E., Rothermel, R. D., Chugani, D. C., Muzik, O., Mangner, T. J., et al. (1999). Brain mapping of language and auditory perception in high-functioning autistic adults: A pet study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(1), 19–31. doi:10.1023/A:1025914515203.
Naatanen, R., & Picton, T. (1987). The N1 wave of the human electric and magnetic response to sound: A review and an analysis of the component structure. Psychophysiology, 24(4), 375–425. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.1987.tb00311.x.
Oades, R. D., Walker, M. K., Geffen, L. B., & Stern, L. M. (1988). Event-related potentials in autistic and healthy children on an auditory choice reaction time task. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 6(1), 25–37. doi:10.1016/0167-8760(88)90032-3.
Ponton, C., Eggermont, J. J., Khosla, D., Kwong, B., & Don, M. (2002). Maturation of human central auditory system activity: Separating auditory evoked potentials by dipole source modeling. Clinical Neurophysiology, 113(3), 407–420. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(01)00733-7.
Rapin, I., & Dunn, M. (2003). Update on the language disorders of individuals on the autistic spectrum. Brain and Development, 25(3), 166–172. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(02)00191-2.
Rojas, D. C., Bawn, S. D., Benkers, T. L., Reite, M. L., & Rogers, S. J. (2002). Smaller left hemisphere planum temporale in adults with autistic disorder. Neuroscience Letters, 328(3), 237–240. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00521-9.
Rojas, D. C., Camou, S. L., Reite, M. L., & Rogers, S. J. (2005). Planum temporale volume in children and adolescents with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35(4), 479–486. doi:10.1007/s10803-005-5038-7.
Russo, N., Nicol, T., Trommer, B., Zecker, S., & Kraus, N. (2009). Brainstem transcription of speech is disrupted in children with autism spectrum disorders. Developmental Science. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2008.00790.x.
Russo, N., Skoe, E., Trommer, B., Nicol, T., Zecker, S., Bradlow, A., et al. (2008). Deficient brainstem encoding of pitch in children with autism spectrum disorders. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119(8), 1720–1731. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2008.01.108.
Saalasti, S., Lepistö, T., Toppila, E., Kujala, T., Laakso, M., Nieminen-von Wendt, T., et al. (2008). Language abilities of children with asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(8), 1574–1580. doi:10.1007/s10803-008-0540-3.
Salmond, C. H., Vargha-Khadem, F., Gadian, D. G., de Haan, M., & Baldeweg, T. (2007). Heterogeneity in the patterns of neural abnormality in autistic spectrum disorders: Evidence from ERP and MRI. Cortex, 43(6), 686–699. doi:10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70498-2.
Semel, E., Wiig, E. H., & Secord, W. A. (2003). Clinical evaluation of language fundamentals (4th ed.). San Antonio, TX: Harcourt Assessment, Inc.
Seri, S., Cerquiglini, A., Pisani, F., & Curatolo, P. (1999). Autism in tuberous sclerosis: Evoked potential evidence for a deficit in auditory sensory processing. Clinical Neurophysiology, 110(10), 1825–1830. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(99)00137-6.
Shriberg, L. D., Paul, R., McSweeny, J. L., Klin, A. M., Cohen, D. J., & Volkmar, F. R. (2001). Speech and prosody characteristics of adolescents and adults with high-functioning autism and asperger syndrome. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research: JSLHR, 44(5), 1097–1115. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2001/087).
Siegal, M., & Blades, M. (2003). Language and auditory processing in autism. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(9), 378–380. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(03)00194-3.
Tager-Flusberg, H., & Caronna, E. (2007). Language disorders: Autism and other pervasive developmental disorders. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 54(3), 469–481. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2007.02.011. vi.
Tsatsanis, K. (2005). Neuropsychological aspects of autism and related conditions. In F. Volkmar, R. Paul, A. Klin, & D. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of autism and pervasive developmental disorders (Vol. 1, pp. 365–381). New York, NY: Wiley & Sons.
Volkmar, F. R., Lord, C., Bailey, A., Schultz, R. T., & Klin, A. (2004). Autism and pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 45(1), 135–170. doi:10.1046/j.0021-9630.2003.00317.x.
Warrier, C. M., Johnson, K. L., Hayes, E. A., Nicol, T., & Kraus, N. (2004). Learning impaired children exhibit timing deficits and training-related improvements in auditory cortical responses to speech in noise. Experimental Brain Research, 157(4), 431–441. doi:10.1007/s00221-004-1857-6.
Whitehouse, A. J. O., & Bishop, D. (2008). Do children with autism ‘switch off’ to speech sounds? An investigation using event-related potentials. Developmental Science, 11(4), 516–524. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2008.00697.x.
Whiting, K. A., Martin, B. A., & Stapells, D. R. (1998). The effects of broadband noise masking on cortical event-related potentials to speech sounds/ba/and/da/. Ear and Hearing, 19(3), 218–231. doi:10.1097/00003446-199806000-00005.
Wible, B., Nicol, T., & Kraus, N. (2002). Abnormal neural encoding of repeated speech stimuli in noise in children with learning problems. Clinical Neurophysiology, 113(4), 485–494. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00017-2.
Wible, B., Nicol, T., & Kraus, N. (2004). Atypical brainstem representation of onset and formant structure of speech sounds in children with language-based learning problems. Biological Psychology, 67, 299–317. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2004.02.002.
Wible, B., Nicol, T., & Kraus, N. (2005). Correlation between brainstem and cortical auditory processes in normal and language-impaired children. Brain, 128(Pt 2), 417–423. doi:10.1093/brain/awh367.
Wickelgren, I. (2005). Neurology. Autistic brains out of synch? Science [New York, N. Y (Dayton, Ohio)], 308(5730), 1856–1858.
Woerner, C., & Overstreet, K. (Eds.). (1999). Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence (WASI). San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH R01 DC01510. The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests. We would like to thank the children who participated in this study and their families; Trent Nicol, Gabriella Musacchia, and Daniel Abrams for assisting with peak picking; Trent Nicol and Erika Skoe for their contributions to this research, particularly in technical aspects of data processing and software development; Jane Hornickel for her assistance with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, N., Zecker, S., Trommer, B. et al. Effects of Background Noise on Cortical Encoding of Speech in Autism Spectrum Disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 39, 1185–1196 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-009-0737-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-009-0737-0