Abstract
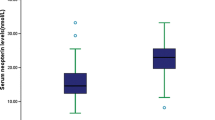
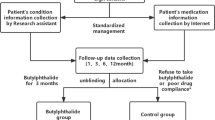
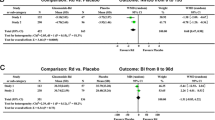
Ischaemic stroke represents one of the main causes of disability. According to the broad investigations, it is widely assumed that the contribution of inflammatory mediators is strongly involved in its pathogenesis. Hence, it seems that stroke treatment needs more efficient and inflammatory-targeted compounds to modulate inflammatory-related pathways. Such strategies paved the way to achieve better clinical outcomes along with conventional therapies. Boswellic acids (BAs), the main bioactive compounds of Boswellia sp. resin; are triterpenoids with well-documented anti-inflammatory properties. Compared with NSAIDs, BAs cross blood–brain barrier yet they do not cause serious gastrointestinal adverse effects. Considering BAs anti-inflammatory features, we conducted a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot trial of these compounds as a supplementary therapy. This trial randomized 80 ischaemic stroke patients (40–80-years old) with a 4–20 score according to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), within 72 h of neurological sign onset, in 1-month follow-up period. We assessed NIHSS as primary and plasma levels of TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IFN-γ, IP-10, MCP-1, 8-isoprostane, and PGE2 as secondary outcomes. According to NIHSS evaluation, patients who were allocated to BA group had a significant recovery in neurological function during the 1-month follow-up, compared with the placebo. The levels of plasma inflammatory markers were significantly decreased in BA group after 7 days of intervention in TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and PGE2. As a preliminary controlled trial in ischaemic stroke, BAs could improve clinical outcome in the early phases of stroke along with promising changes in plasma inflammatory factors.
Clinical trial registrationhttps://www.irct.ir Unique identifier: IRCT20170315033086N5. IRCT is a primary registry in the WHO registry network (https://www.who.int/ictrp/network/primary/en/)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-tawab M, Werz O, Schubert-Zsilavecz M (2011) Boswellia serrata: an overall assessment of in vitro, preclinical, pharmacokinetic and clinical data. Clin Pharmacokinet 50:349–369
Al Mamun A, Chauhan A, Yu H, Xu Y, Sharmeen R, Liu F (2018) Interferon regulatory factor 4/5 signaling impacts on microglial activation after ischemic stroke in mice. Eur J Neurosci 47:140–149
Albers GW, Amarenco P, Easton JD, Sacco RL, Teal P (2001) Antithrombotic and thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke. Chest 119:300s–320s
Amin M, Vakilian A, Mahmoodi MH, Hassanshahi G, Falahati-Pour SK, Dolatabadi MR, Nadimi AE (2017) Circulatory levels of C-X-C motif chemokine ligands 1, 9, and 10 are elevated in patients with ischemic stroke. Eurasian J Med 49:92–96
Ammon HP (2006) Boswellic acids in chronic inflammatory diseases. Planta Med 72:1100–1116
Ammon HP (2010) Modulation of the immune system by Boswellia serrata extracts and boswellic acids. Phytomedicine 17:862–867
Ammon HP (2016) Boswellic acids and their role in chronic inflammatory diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 928:291–327
Badria FA, Mikhaeil BR, Maatooq GT, Amer MM (2003) Immunomodulatory triterpenoids from the oleogum resin of Boswellia carterii Birdwood. Z Naturforsch C 58:505–516
Barone FC, Parsons AA (2000) Therapeutic potential of anti-inflammatory drugs in focal stroke. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9:2281–2306
Basic Kes V, Simundic AM, Nikolac N, Topic E, Demarin V (2008) Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke and their relation to early neurological deficit and stroke outcome. Clin Biochem 41:1330–1334
Bhushan S, Malik F, Kumar A, Isher HK, Kaur IP, Taneja SC, Singh J (2009) Activation of p53/p21/PUMA alliance and disruption of PI-3/Akt in multimodal targeting of apoptotic signaling cascades in cervical cancer cells by a pentacyclic triterpenediol from Boswellia serrata. Mol Carcinog 48:1093–1108
Bustamante A, Simats A, Vilar-Bergua A, Garcia-Berrocoso T, Montaner J (2016) Blood/brain biomarkers of inflammation after stroke and their association with outcome: from C-reactive protein to damage-associated molecular patterns. Neurotherapeutics 13:671–684
Chang LT, Yuen CM, Liou CW, Lu CH, Chang WN, Youssef AA, Yip HK (2010) Link between interleukin-10 level and outcome after ischemic stroke. NeuroImmunoModulation 17:223–228
Che X, Ye W, Panga L, Wu DC, Yang GY (2001) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expressed in neurons and astrocytes during focal ischemia in mice. Brain Res 902:171–177
Chen Y, Hallenbeck JM, Ruetzler C, Bol D, Thomas K, Berman NE, Vogel SN (2003) Overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in the brain exacerbates ischemic brain injury and is associated with recruitment of inflammatory cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:748–755
Chen CL, Young SH, Gan HH, Singh R, Lao AY, Baroque AC 2nd, Chang HM, Hiyadan JH, Chua CL, Advincula JM, Muengtaweepongsa S, Chan BP, De Silva HA, Towanabut S, Suwanwela NC, Poungvarin N, Chankrachang S, Wong KS, Eow GB, Navarro JC, Venketasubramanian N, Lee CF, Bousser MG (2013) Chinese medicine neuroaid efficacy on stroke recovery: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Stroke 44:2093–2100
Chen X, Zhuang X, Peng Z, Yang H, Chen L, Yang Q (2018) Intensive statin therapy for acute ischemic stroke to reduce the number of microemboli: a preliminary, randomized controlled study. Eur Neurol 80:163–170
Cuaz-Perolin C, Billiet L, Bauge E, Copin C, Scott-Algara D, Genze F, Buchele B, Syrovets T, Simmet T, Rouis M (2008) Antiinflammatory and antiatherogenic effects of the NF-kappaB inhibitor acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid in LPS-challenged ApoE−/− mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:272–277
Del Zoppo GJ (2010) Acute anti-inflammatory approaches to ischemic stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1207:143–148
Di Napoli M, Papa F (2003) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use is associated with reduced plasma concentration of C-reactive protein in patients with first-ever ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:2922–2929
Ding Y, Chen M, Wang M, Wang M, Zhang T, Park J, Zhu Y, Guo C, Jia Y, Li Y, Wen A (2014) Neuroprotection by acetyl-11-keto-beta-Boswellic acid, in ischemic brain injury involves the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Sci Rep 4:7002
Doll DN, Barr TL, Simpkins JW (2014) Cytokines: their role in stroke and potential use as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Aging Dis 5:294–306
Domac FM, Misirli H (2008) The role of neutrophils and interleukin-8 in acute ischemic stroke. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 13:136–141
Drieu A, Levard D, Vivien D, Rubio M (2018) Anti-inflammatory treatments for stroke: from bench to bedside. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 11:1756286418789854
Du Z, Liu Z, Ning Z, Liu Y, Song Z, Wang C, Lu A (2015) Prospects of boswellic acids as potential pharmaceutics. Planta Med 81:259–271
Dziedzic T (2015) Systemic inflammation as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Neurother 15:523–531
Enlimomab Acute Stroke Trial Investigators (2001) Use of anti-ICAM-1 therapy in ischemic stroke: results of the Enlimomab Acute Stroke Trial. Neurology 57:1428–1434
Etzel R (1996) Special extract of Boswellia serrata (H 15) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Phytomedicine 3:91–94
Forouzanfar F, Hosseinzadeh H, Ebrahimzadeh Bideskan A, Sadeghnia HR (2016) Aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Boswellia serrata protect against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Phytother Res 30:1954–1967
Gayathri B, Manjula N, Vinaykumar KS, Lakshmi BS, Balakrishnan A (2007) Pure compound from Boswellia serrata extract exhibits anti-inflammatory property in human PBMCs and mouse macrophages through inhibition of TNFalpha, IL-1beta, NO and MAP kinases. Int Immunopharmacol 7:473–482
Gerbeth K, Husch J, Fricker G, Werz O, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Abdel-Tawab M (2013) In vitro metabolism, permeation, and brain availability of six major boswellic acids from Boswellia serrata gum resins. Fitoterapia 84:99–106
Gupta I, Parihar A, Malhotra P, Singh GB, Ludtke R, Safayhi H, Ammon HP (1997) Effects of Boswellia serrata gum resin in patients with ulcerative colitis. Eur J Med Res 2:37–43
Gupta I, Gupta V, Parihar A, Gupta S, Ludtke R, Safayhi H, Ammon HP (1998) Effects of Boswellia serrata gum resin in patients with bronchial asthma: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, 6-week clinical study. Eur J Med Res 3:511–514
Hamidpour R, Hamidpour S, Hamidpour M, Shahlari M (2013) Frankincense (ru xiang; Boswellia species): from the selection of traditional applications to the novel phytotherapy for the prevention and treatment of serious diseases. J Tradit Complement Med 3:221–226
Hartmann RM, Fillmann HS, Martins MI, Meurer L, Marroni NP (2014) Boswellia serrata has beneficial anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in a model of experimental colitis. Phytother Res 28:1392–1398
Huang H, Al-Shabrawey M, Wang MH (2016) Cyclooxygenase- and cytochrome P450-derived eicosanoids in stroke. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 122:45–53
Huisa BN, Stemer AB, Zivin JA (2010) Atorvastatin in stroke: a review of SPARCL and subgroup analysis. Vasc Health Risk Manag 6:229–236
Husch J, Gerbeth K, Fricker G, Setzer C, Zirkel J, Rebmann H, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Abdel-Tawab M (2012) Effect of phospholipid-based formulations of Boswellia serrata extract on the solubility, permeability, and absorption of the individual boswellic acid constituents present. J Nat Prod 75:1675–1682
Intiso D, Zarrelli MM, Lagioia G, Di Rienzo F, Checchia De Ambrosio C, Simone P, Tonali P, Cioffi Dagger RP (2004) Tumor necrosis factor alpha serum levels and inflammatory response in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neurol Sci 24:390–396
Jeong HJ, Hong SH, Park HJ, Kweon DY, Lee SW, Lee JD, Kim KS, Cho KH, Kim HS, Kim KY, Kim HM (2002) Yangkyuk–Sanhwa–Tang induces changes in serum cytokines and improves outcome in focal stroke patients. Vascul Pharmacol 39:63–68
Jin R, Yang G, Li G (2010) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol 87:779–789
Jin R, Liu L, Zhang S, Nanda A, Li G (2013) Role of inflammation and its mediators in acute ischemic stroke. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 6:834–851
Kim JY, Kawabori M, Yenari MA (2014) Innate inflammatory responses in stroke: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Curr Med Chem 21:2076–2097
Kimmatkar N, Thawani V, Hingorani L, Khiyani R (2003) Efficacy and tolerability of Boswellia serrata extract in treatment of osteoarthritis of knee—a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial. Phytomedicine 10:3–7
Kirste S, Treier M, Wehrle SJ, Becker G, Abdel-Tawab M, Gerbeth K, Hug MJ, Lubrich B, Grosu AL, Momm F (2011) Boswellia serrata acts on cerebral edema in patients irradiated for brain tumors: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind pilot trial. Cancer 117:3788–3795
Kitagawa K, Hosomi N, Nagai Y, Kagimura T, Ohtsuki T, Origasa H, Minematsu K, Uchiyama S, Nakamura M, Matsumoto M (2017) Reduction in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in patients with ischemic stroke by statin treatment: Hs-CRP sub-study in J-STARS. J Atheroscler Thromb 24:1039–1047
Krams M, Lees KR, Hacke W, Grieve AP, Orgogozo JM, Ford GA (2003) Acute stroke therapy by inhibition of neutrophils (ASTIN): an adaptive dose-response study of UK-279,276 in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:2543–2548
Kuo PC, Yu IC, Scofield BA, Brown DA, Curfman ET, Paraiso HC, Chang FL, Yen JH (2017) 3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione as a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment of ischemic stroke through Nrf2 defense pathway. Brain Behav Immun 62:180–192
Kwan J, Horsfield G, Bryant T, Gawne-Cain M, Durward G, Byrne CD, Englyst NA (2013) IL-6 is a predictive biomarker for stroke associated infection and future mortality in the elderly after an ischemic stroke. Exp Gerontol 48:960–965
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M (2009) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med 7:97
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-κB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a001651
Liantao Z, Jing Z, Lingling L, Hua L (2019) Efficacy of fingolimod combined with alteplase in acute ischemic stroke and rehabilitation nursing. Pak J Pharm Sci 32:413–419
Lima IV, Bastos LF, Limborco-Filho M, Fiebich BL, De Oliveira AC (2012) Role of prostaglandins in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2012:946813
Liu X, Xia J, Wang L, Song Y, Yang J, Yan Y, Ren H, Zhao G (2009) Efficacy and safety of ginsenoside-Rd for acute ischaemic stroke: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II multicenter trial. Eur J Neurol 16:569–575
Mazzotta G, Sarchielli P, Caso V, Paciaroni M, Floridi A, Floridi A, Gallai V (2004) Different cytokine levels in thrombolysis patients as predictors for clinical outcome. Eur J Neurol 11:377–381
Mo X, Li T, Ji G, Lu W, Hu Z (2013) Peripheral polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation as a systemic inflammatory response in ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci 34:1509–1516
Montaner J (2005) Treatment with statins in the acute phase of ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Neurother 5:211–221
Montaner J, Chacon P, Krupinski J, Rubio F, Millan M, Molina CA, Hereu P, Quintana M, Alvarez-SABIN J (2008) Simvastatin in the acute phase of ischemic stroke: a safety and efficacy pilot trial. Eur J Neurol 15:82–90
Montaner J, Bustamante A, Garcia-Matas S, Martinez-Zabaleta M, Jimenez C, De La Torre J, Rubio FR, Segura T, Masjuan J, Canovas D, Freijo M, Delgado-Mederos R, Tejada J, Lago A, Bravo Y, Corbeto N, Giralt D, Vives-Pastor B, De Arce A, Moniche F, Delgado P, Ribo M (2016) Combination of thrombolysis and statins in acute stroke is safe: results of the STARS randomized trial (Stroke Treatment With Acute Reperfusion and Simvastatin). Stroke 47:2870–2873
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67:181–198
Muscari A, Puddu GM, Santoro N, Serafini C, Cenni A, Rossi V, Zoli M (2011) The atorvastatin during ischemic stroke study: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Clin Neuropharmacol 34:141–147
Nakase T, Moroi J, Ishikawa T (2018) Anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet effects of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in acute phase of ischemic stroke patients. Clin Transl Med 7:2
Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Afentoulis ME, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD (2006) Experimental stroke induces massive, rapid activation of the peripheral immune system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:654–665
Ormstad H, Aass HC, Lund-Sorensen N, Amthor KF, Sandvik L (2011) Serum levels of cytokines and C-reactive protein in acute ischemic stroke patients, and their relationship to stroke lateralization, type, and infarct volume. J Neurol 258:677–685
Poeckel D, Werz O (2006) Boswellic acids: biological actions and molecular targets. Curr Med Chem 13:3359–3369
Pongracz E, Kaposzta Z (2005) Antiplatelet therapy in ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Neurother 5:541–549
Raju NC, Yi Q, Nidorf M, Fagel ND, Hiralal R, Eikelboom JW (2012) Effect of colchicine compared with placebo on high sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with acute coronary syndrome or acute stroke: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Thromb Thrombolysis 33:88–94
Ramiro L, Simats A, Garcia-Berrocoso T, Montaner J (2018) Inflammatory molecules might become both biomarkers and therapeutic targets for stroke management. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 11:1756286418789340
Ravanfar P, Namazi G, Atigh M, Zafarmand S, Hamedi A, Salehi A, Izadi S, Borhani-Haghighi A (2016) Efficacy of whole extract of licorice in neurological improvement of patients after acute ischemic stroke. J Herb Med 6:12–17
Reising K, Meins J, Bastian B, Eckert G, Mueller WE, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Abdel-Tawab M (2005) Determination of boswellic acids in brain and plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 77:6640–6645
Russo NW, Petrucci G, Rocca B (2016) Aspirin, stroke and drug-drug interactions. Vascul Pharmacol 87:14–22
Seifert HA, Collier LA, Chapman CB, Benkovic SA, Willing AE, Pennypacker KR (2014) Pro-inflammatory interferon gamma signaling is directly associated with stroke induced neurodegeneration. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 9:679–689
Serebruany VL, Malinin AI, Eisert RM, Sane DC (2004) Risk of bleeding complications with antiplatelet agents: meta-analysis of 338,191 patients enrolled in 50 randomized controlled trials. Am J Hematol 75:40–47
Shaheen HA, Daker LI, Abbass MM, Abd El Fattah AA (2018) The relationship between the severity of disability and serum IL-8 in acute ischemic stroke patients. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg 54:26
Singh HV, Pandey A, Shrivastava AK, Raizada A, Singh SK, Singh N (2013) Prognostic value of neuron specific enolase and IL-10 in ischemic stroke and its correlation with degree of neurological deficit. Clin Chim Acta 419:136–138
Stamatovic SM, Shakui P, Keep RF, Moore BB, Kunkel SL, van Rooijen N, Andjelkovic AV (2005) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulation of blood–brain barrier permeability. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:593–606
Szczepanska-Szerej A, Kurzepa J, Wojczal J, Stelmasiak Z (2011) Simvastatin displays an antioxidative effect by inhibiting an increase in the serum 8-isoprostane level in patients with acute ischemic stroke: brief report. Clin Neuropharmacol 34:191–194
Tuttolomondo A, Di Sciacca R, Di Raimondo D, Serio A, D'Aguanno G, La Placa S, Pecoraro R, Arnao V, Marino L, Monaco S, Natale E, Licata G, Pinto A (2009) Plasma levels of inflammatory and thrombotic/fibrinolytic markers in acute ischemic strokes: relationship with TOAST subtype, outcome and infarct site. J Neuroimmunol 215:84–89
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Pecoraro R, Maida C, Arnao V, Della Corte V, Simonetta I, Corpora F, Di Bona D, Maugeri R, Iacopino DG, Pinto A (2016) Early high-dosage atorvastatin treatment improved serum immune-inflammatory markers and functional outcome in acute ischemic strokes classified as large artery atherosclerotic stroke: a randomized trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e3186
Wang X, Ellison JA, Siren AL, Lysko PG, Yue TL, Barone FC, Shatzman A, Feuerstein GZ (1998) Prolonged expression of interferon-inducible protein-10 in ischemic cortex after permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rat. J Neurochem 71:1194–1204
Woodruff TM, Thundyil J, Tang SC, Sobey CG, Taylor SM, Arumugam TV (2011) Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke. Mol Neurodegener 6:11
Wytrykowska A, Prosba-Mackiewicz M, Nyka WM (2016) IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 levels in gingival fluid and serum of patients with ischemic stroke. J Oral Sci 58:509–513
Zaremba J, Losy J (2001) Early TNF-alpha levels correlate with ischaemic stroke severity. Acta Neurol Scand 104:288–295
Zaremba J, Skrobanski P, Losy J (2001) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha is increased in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of ischaemic stroke patients and correlates with the volume of evolving brain infarct. Biomed Pharmacother 55:258–263
Zhang Y, Ning Z, Lu C, Zhao S, Wang J, Liu B, Xu X, Liu Y (2013) Triterpenoid resinous metabolites from the genus Boswellia: pharmacological activities and potential species-identifying properties. Chem Cent J 7:153
Zhang F, Yan C, Wei C, Yao Y, Ma X, Gong Z, Liu S, Zang D, Chen J, Shi FD, Hao J (2018) Vinpocetine inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent inflammation in acute ischemic stroke patients. Transl Stroke Res 9:174–184
Acknowledgements
This study was granted by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (SBMU) (number: 0308/25030-95/11/11). Our study benefited greatly from the efforts and critical comments of Mr. Hamid Fatemi. We would like to thank all stroke patients and Imam Hossein Hospital and Imam Khomeini Hospital Complex staffs specially Ms. Fatemeh Abbasi, and Ms. Mahnaz Varedi, chief nurses of stroke ward in the study centers for their cooperation. We are also grateful to Dr. Nahid Beladi Moghadam, Dr. Farhad Assarzadegan, Dr. Omid Hessami for their help. The authors wish to thank Pars Teb Lab staffs and Dr. Ali Kharaziyan for performing all routine laboratory tests. We also would like to thank all staff members of the IPD CRO Department for their cooperation and critical notes in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Ethical approval
All procedures involving human participants were carried out under Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (SBMU) ethics committee approval and supervision (Reference number: IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1395.409) and were compatible with Good Clinical Practice guidelines which is in association with the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) dated November 9, 2016 and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration, its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baram, S.M., Karima, S., Shateri, S. et al. Functional improvement and immune-inflammatory cytokines profile of ischaemic stroke patients after treatment with boswellic acids: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial. Inflammopharmacol 27, 1101–1112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00627-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00627-z