Abstract
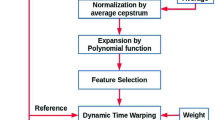
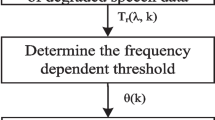
This paper presents a proposed approach for cancelable biometric recognition related to speaker identification. Both comb and inverse comb filters are used to distort speech signals intentionally prior to and after feature extraction. The objective of this approach is to generate protected templates of speech signals representing speakers without subjecting the original speech signals or features to violations of attackers. Both comb and inverse comb filters are used for this purpose. In addition, a satisfactory performance represented in the speaker identification rate is retained. In case the database of speaker features is compromised, it is possible to change the comb or inverse comb filter orders to generate new features for the same speakers. Simulation results reveal the possibility to identify speakers from their deteriorated speech signals, which proves the robustness of the proposed cancelable speaker identification system. The reason of choosing the comb filter is that it is a multi-band filter with multiple nulls in its frequency response. Hence, its inversion is difficult due to the nulling effect. This characteristic can induce non-invertible distortion in speech signals.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Samie, F. E. (2017). Information security for automatic speaker identification. International Journal of Speech Technology., 20, 977–1004.
Al-Nuaimy, W., El-Bendary, M. A. M., Shafik, A., Shawki, F., Abou-El-azm, A. E., El-Fishawy, N. A., et al. (2011). An SVD audio watermarking approach using chaotic encrypted image. Digital Signal Process, 21(6), 764–779.
Asaker A. A., Sharkawy, Z. F. E. L., Nassar, S., Ayad, N., Zahran, O. & Abd EL-Samie F. E. (2020). A novel cancellable Iris template generation based on salting approach. Multimedia Tools and Applications.
Chauhan, N. & Chandra, M. (2017). Speaker recognition and verification using artificial neural network. In International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET).
Chen, H., & Chen, H. (2010). A hybrid scheme for securing fingerprint templates. International Journal of Information Security, 9, 353–361.
Chuang, C. T., Chang, T., Chiang, Y. T., & Chang, F. R. (2016). Heart rate monitoring using a slow–fast adaptive comb filter to eliminate motion artifacts. Journal of Medical and Biometric Engineering, 36, 833–842.
Dolecek, G. J. (2017). Advances in multirate systems. Springer, pp. 59–81.
Fredrickson, S. E. & Tarassenko L. (1995). Text-independent speaker recognition using neural network techniques. In 4th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, pp. 13 18.
Furui, S. An overview of speaker recognition technology. Automatic Speech and Speaker Recognition, pp. 31–56.
Furui, S. (1996). An overview of speaker recognition technology. The Kluwer International Series in Engineering and Computer Science, 355, 31–55.
Hossain, M., Ahmed, B., Asrafi, M. (2007). A real Time Speaker Identification using artificial Network. In 10th international conference on Computer and Information Technology 2007, ICCIT2008, pp. 1–5, Dec. 2007, Dhaka.
Jimenez, M. G. C., Romero, D. E. T & Dolecek, G.J. (2015). Comb filters characteristics and applications. Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, Third Edition, pp. 4062–4071.
Kuo, S. M., Lee, B. H. & Tain, W. Real-time digital signal processing implementations and applications. Second Edition.
Nair, P. G. & Nair, R. (2015). Efficient speaker identification using artificial neural network. IJECT l6(1).
Nikolic, M., & Lutovac, M. (2011). Sharpening of the multistage modified comb filters. Serbian Journal of Electrical Engineering, 8(2), 281–291.
Park, J.S. (2013). Advanced technologies, embedded and multimedia for human-centric computing. pp. 31–36.
Pilt, K., Meigas, K., Karai, D. & Kaik, J. (2009). PPG signal processing for pulse delay computing by using adaptive comb filter. World Congress on Medical Physical and Biometric Engineering, pp. 1653–1656.
Poostchi, M., Kamkar, I. & Mohebbi, J. (2010). Soft computing in industrial applications. 75:165–173.
Kumar. J., Prabhakar, OP. & Sahu, N. S. (2014). Comparative analysis of different feature extraction and classifier techniques for speaker identification systems: a review. 2(1).
Prochazka, A., Uhlir, J., Rayner, P. J. W., & Kingsbury, N. J. (1998). Signal Analysis and Prediction. New York: Birkhauser Inc.
Saha, G., Kumar, P. & Chakroborty, S. (2004). A comparative study of feature extraction algorithms on ANN based speaker model for speaker recognition applications. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing, ICONIP 2004:Neural Information Processing, pp. 1192–1197.
Shafik, A., Elhalafawy, S. M., Diab, S. M., Sallam, B. M., & Abd El-samie, F. E. (2009). A wavelet based approach for speaker identification from degraded speech. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS), 1(3), 53–60.
Soliman, R. F., Amin, M., & Abd El-Samie, F. E. (2020). Cancelable Iris recognition system based on comb filter. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 79, 2521–2541.
Soliman, N. F., Mostfa, Z., Abd El-Samie, F. E., & Abdalla, M. I. (2017). Performance enhancement of speaker identification systems using speech encryption and cancelable features. International Journal of Speech Technology, 20(4), 977–1004.
Tirumala, S. S., Shahamiri, S. R., Garhwal, A. S., & Wang, R. (2017). Speaker identification features extraction methods a systematic review. Expert Systems with Applications, 90, 250–271.
Trang, H., Loc, T.H., Nam, H.B.H. (2014). Proposed combination of PCA and MFCC feature extraction in speech recognition system. International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC 2014).
Wang, W., Li, S. Yang, J. Liu, Z. & Zhou, W.O. (2016). Feature extraction of underwater target in auditory sensation area based on MFCC., IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monir, M., Kareem, M., El-Dolil, S.M. et al. Cancelable speaker identification based on cepstral coefficients and comb filters. Int J Speech Technol 25, 471–492 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-021-09804-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-021-09804-4