Abstract
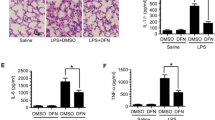
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by the dysregulated host immune response to infection characterized by excessive secretion of inflammatory factors. AZD4547 is a selective inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptors that participates in the inflammatory response. The aim of this study was to investigate the inflammation-targeting effects and related molecular mechanisms of AZD4547 in sepsis using a cecal ligation and puncture model and RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. AZD4547 improved the survival of CLP mice and exhibited a robust protective function against lung damage histologically. Pretreatment with AZD4547 significantly alleviated the expression of the pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MMP9, and CXCL10 both in vivo and in vitro. In addition, AZD4547 suppressed the proliferative activity of macrophages in lung tissue and RAW264.7 macrophages. In addition, the LPS-induced phosphorylation of key proteins of NF-κB/MAPK/STAT3 pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages, such as p65, IκB-α, Erk1/2, JNK, and STAT3 proteins, could be inhibited by AZD4547 pretreatment. In conclusion, AZD4547 exerts a protective effect against excessive inflammatory damage in septic mice and may have the potential for use as an effective drug for the management of sepsis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleischmann, C., A. Scherag, N.K. Adhikari, C.S. Hartog, T. Tsaganos, P. Schlattmann, D.C. Angus, K. Reinhart, and Trialists International Forum of Acute Care. 2016. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. current estimates and limitations. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 193 (3): 259–272. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC.
Rahmel, T. 2018. SSC international guideline 2016 - management of sepsis and septic shock. Anästhesiologie, Intensivmedizin, Notfallmedizin, Schmerztherapie 53 (2): 142–148. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-114639.
Chousterman, B.G., F.K. Swirski, and G.F. Weber. 2017. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Seminars in Immunopathology 39 (5): 517–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-017-0639-8.
Gavine, P.R., L. Mooney, E. Kilgour, A.P. Thomas, K. Al-Kadhimi, S. Beck, C. Rooney, et al. 2012. AZD4547: an orally bioavailable, potent, and selective inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase family. Cancer Research 72 (8): 2045–2056. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3034.
Fitzpatrick, E.A., X. Han, Z. Xiao, and L.D. Quarles. 2018. Role of fibroblast growth Factor-23 in innate immune responses. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9: 320. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00320.
Han, X., L. Li, J. Yang, G. King, Z. Xiao, and L.D. Quarles. 2016. Counter-regulatory paracrine actions of FGF-23 and 1,25(OH)2 D in macrophages. FEBS Letters 590 (1): 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12040.
Paik, P.K., R. Shen, M.F. Berger, D. Ferry, J.C. Soria, A. Mathewson, C. Rooney, N.R. Smith, M. Cullberg, E. Kilgour, D. Landers, P. Frewer, N. Brooks, and F. André. 2017. A phase Ib open-label multicenter study of AZD4547 in patients with advanced squamous cell lung cancers. Clinical Cancer Research 23 (18): 5366–5373. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0645.
Jang, J., H.K. Kim, H. Bang, S.T. Kim, S.Y. Kim, S.H. Park, H.Y. Lim, W.K. Kang, J. Lee, and K.M. Kim. 2017. Antitumor effect of AZD4547 in a fibroblast growth factor receptor 2-amplified gastric cancer patient-derived cell model. Translational Oncology 10 (4): 469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2017.03.001.
Dejager, L., I. Pinheiro, E. Dejonckheere, and C. Libert. 2011. Cecal ligation and puncture: the gold standard model for polymicrobial sepsis? Trends in Microbiology 19 (4): 198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2011.01.001.
Smith, K.M., J.D. Mrozek, S.C. Simonton, D.R. Bing, P.A. Meyers, J.E. Connett, and M.C. Mammel. 1997. Prolonged partial liquid ventilation using conventional and high-frequency ventilatory techniques: gas exchange and lung pathology in an animal model of respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 25 (11): 1888–1897.
Davies, L.C., M. Rosas, P.J. Smith, D.J. Fraser, S.A. Jones, and P.R. Taylor. 2011. A quantifiable proliferative burst of tissue macrophages restores homeostatic macrophage populations after acute inflammation. European Journal of Immunology 41 (8): 2155–2164. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201141817.
Oeckinghaus, A., M.S. Hayden, and S. Ghosh. 2011. Crosstalk in NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Nature Immunology 12 (8): 695–708. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2065.
Ivashkiv, L.B. 2011. Inflammatory signaling in macrophages: transitions from acute to tolerant and alternative activation states. European Journal of Immunology 41 (9): 2477–2481. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201141783.
Moreno, R.P., B. Metnitz, L. Adler, A. Hoechtl, P. Bauer, P.G. Metnitz, and Saps Investigators. 2008. Sepsis mortality prediction based on predisposition, infection and response. Intensive Care Medicine 34 (3): 496–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-007-0943-1.
Linder, A., and J.A. Russell. 2014. An exciting candidate therapy for sepsis: Ulinastatin, a urinary protease inhibitor. Intensive Care Medicine 40 (8): 1164–1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-014-3366-9.
Kumar, V. 2018. Targeting macrophage immunometabolism: dawn in the darkness of sepsis. International Immunopharmacology 58: 173–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.005.
Cavaillon, J.M., and M. Adib-Conquy. 2005. Monocytes/macrophages and sepsis. Critical Care Medicine 33 (12 Suppl): S506–S509.
Weber, G.F., and F.K. Swirski. 2014. Immunopathogenesis of abdominal sepsis. Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery 399 (1): 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-013-1129-7.
Helming, L. 2011. Inflammation: cell recruitment versus local proliferation. Current Biology 21 (14): R548–R550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.06.005.
Punyadeera, C., E.M. Schneider, D. Schaffer, H.Y. Hsu, T.O. Joos, F. Kriebel, M. Weiss, and W.F. Verhaegh. 2010. A biomarker panel to discriminate between systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis and sepsis severity. Journal of Emergencies, Trauma, and Shock 3 (1): 26–35. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2700.58666.
Herzig, D.S., L. Luan, J.K. Bohannon, T.E. Toliver-Kinsky, Y. Guo, and E.R. Sherwood. 2014. The role of CXCL10 in the pathogenesis of experimental septic shock. Critical Care 18 (3): R113. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc13902.
Wang, M., Q. Zhang, X. Zhao, G. Dong, and C. Li. 2014. Diagnostic and prognostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1 for sepsis in the emergency department: an observational study. Critical Care 18 (6): 634. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-014-0634-6.
Rahman, M., S. Zhang, M. Chew, I. Syk, B. Jeppsson, and H. Thorlacius. 2013. Platelet shedding of CD40L is regulated by matrix metalloproteinase-9 in abdominal sepsis. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 11 (7): 1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12273.
Uwe, S. 2008. Anti-inflammatory interventions of NF-kappaB signaling: potential applications and risks. Biochemical Pharmacology 75 (8): 1567–1579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2007.10.027.
Blackwell, T.S., F.E. Yull, C.L. Chen, A. Venkatakrishnan, T.R. Blackwell, D.J. Hicks, L.H. Lancaster, J.W. Christman, and L.D. Kerr. 2000. Multiorgan nuclear factor kappa B activation in a transgenic mouse model of systemic inflammation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 162 (3 Pt 1): 1095–1101. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.162.3.9906129.
Hayden, M.S., and S. Ghosh. 2008. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132 (3): 344–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.020.
Arthur, J.S., and S.C. Ley. 2013. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nature Reviews. Immunology 13 (9): 679–692. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3495.
Pizzino, G., A. Bitto, G. Pallio, N. Irrera, F. Galfo, M. Interdonato, A. Mecchio, F. de Luca, L. Minutoli, F. Squadrito, and D. Altavilla. 2015. Blockade of the JNK signalling as a rational therapeutic approach to modulate the early and late steps of the inflammatory cascade in polymicrobial sepsis. Mediators of Inflammation 2015: 591572. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/591572.
Zhao, J., H. Yu, Y. Liu, S.A. Gibson, Z. Yan, X. Xu, A. Gaggar, P.K. Li, C. Li, S. Wei, E.N. Benveniste, and H. Qin. 2016. Protective effect of suppressing STAT3 activity in LPS-induced acute lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 311 (5): L868–L880. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00281.2016.
Severgnini, M., S. Takahashi, L.M. Rozo, R.J. Homer, C. Kuhn, J.W. Jhung, G. Perides, M. Steer, P.M. Hassoun, B.L. Fanburg, B.H. Cochran, and A.R. Simon. 2004. Activation of the STAT pathway in acute lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 286 (6): L1282–L1292. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00349.2003.
Song, Z., X. Zhao, Y. Gao, M. Liu, M. Hou, H. Jin, and Y. Cui. 2015. Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide ameliorates trauma-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting JAK/STAT signaling pathway in rats. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 78 (5): 980–987. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000000602.
Acknowledgments
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Wenzhou Medical University.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671968) and the Medical Innovation Discipline of Zhejiang Province (Critical Care Medicine, Y2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
The expression of FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 in RAW264.7 cells (a) and lung tissues (b) was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. (PNG 279 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Wang, F., Li, H. et al. Inhibition of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor by AZD4547 Protects Against Inflammation in Septic Mice. Inflammation 42, 1957–1967 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01056-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01056-4