Abstract
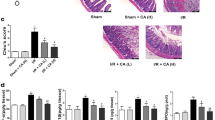
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the role of curcumin on oxidative stress, cell proliferation and apoptosis in the rat intestinal mucosa after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R). A total of 30 male Wistar albino rats were divided into three groups: sham, I/R and I/R+ curcumin; each group contain 10 animals. Sham group animals underwent laparotomy without I/R injury. After I/R groups animals underwent laparotomy, 1 h of superior mesenteric artery ligation were followed by 1 h of reperfusion. In the curcumin group, 3 days before I/R, curcumin (100 mg/kg) was administered by gastric gavage. All animals were sacrificed at the end of reperfusion and intestinal tissues samples were obtained for biochemical and histopathological investigation in all groups. Curcumin treatment significantly decreased the elevated tissue malondialdehyde levels and increased of reduced superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase enzyme activities in intestinal tissues samples. I/R caused severe histopathological injury including mucosal erosions and villous congestion and hemorrhage. Curcumin treatment significantly attenuated the severity of intestinal I/R injury, with inhibiting of I/R-induced apoptosis and cell proliferation. These results suggest that curcumin treatment has a protective effect against intestinal damage induced by intestinal I/R. This protective effect is possibly due to its ability to inhibit I/R-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and cell proliferation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud B, Daher R, Boujaoude J (2008) Acute mesenteric ischemia after cardio-pulmonary bypass surgery. World J Gastroenterol 14:5361–5370
Berland T, Oldenburg WA (2008) Acute mesenteric ischemia. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10:341–346
Bruin RWF, Heineman E, Marquet RL (1994) Small bowel transplantation: an overview. Transpl Int 7:47–61
Cai J, Jones DP (1998) Superoxide in apoptosis: mitochondrial generation triggered by cytochrome c loss. J Biol Chem 273:11401–11404
Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X, Shi Y (2000) Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 406:855–862
Chen Y, Lui VCH, Rooijen NV, Tam PKH (2004) Depletion of intestinal resident macrophages prevents ischaemia reperfusion injury in gut. Gut 53:1772–1780
Chen W, Fu XB, Ge SL, Sun TZ, Li WJ, Sheng ZY (2005) Acid fibroblast growth factor reduces rat intestinal mucosal damage caused by ischemia/reperfusion insult. World J Gastroenterol 11:6477–6482
Chiu CJ, Mcardle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ, Gurd FN (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. A morphologic, hemodynamic and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg 101:478–483
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102:33–42
Fujimoto K, Hosotani R, Wada M, Lee JU, Koshiba T, Miyamoto Y, Doi R, Imamura M (1997) Ischemia-reperfusion injury on the pancreas in rats: identification of acinar cell apoptosis. J Surg Res 71:127–136
Fukuyama K, Iwakiri R, Noda T, Kojima M, Utsumi H, Tsunada S, Sakata H, Ootani A, Fujimoto K (2001) Apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion and fasting in gastric mucosa compared to small intestine in rats. Dig Dis Sci 46:545–549
Granger DN, Hollwarth ME, Parks DA (1986) Ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of oxygen-derived free radicals. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 548:47–63
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Itoh H, Yagi M, Fushida S, Tani T, Hashimoto T, Shimizu K, Miwa K (2000) Activation of immediate early gene, c-fos, and c-jun in the rat small intestine after ischemia/reperfusion. Transplantation 69:598
Iwakiri R, Gotoh Y, Noda H, Sugihara K, Fujimoto K, Fuseler J, Aw TY (2001) Programmed cell death in rat intestine: effect of feeding and fasting. Scand J Gastroenterol 36:39–47
Kalpana C, Menon VP (2004) Curcumin ameliorates oxidative stres during nicotine induced lung toxicity in Wistar rats. Ital J Biochem 53:82–86
Karatepe O, Gulcicek OB, Ugurlucan M, Adas G, Battal M, Kemik A, Kamali G, Altug T, Karahan S (2009) Curcumin Nutrition for the prevention of mesenteric ischemia–reperfusion injury: an experimental rodent model. Transplant Proc 41:3611–3616
Koçogullari CU, Becit N, Erkut B, Keleş MS, Ceviz M, Ates A, Gündoğdu C, Kaygin MA, Koçak H (2008) Prevention of reperfusion injury of the spinal cord in aortic surgery: an experimental study. Surg Today 38:237–244
Kong SE, Blennerhassett LR, Heel KA, McCauley RD, Hall JC (1998) Ischaemia-reperfusion injury to the intestine. Aust N Z J Surg 68:554–561
Linfert D, Chowdhry T, Rabb H (2009) Lymphocytes and ischemia-reperfusion. Transplant Rev 23:1–10
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AC, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol regent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maclellan WR, Schneider MD (1997) Death by design. Programmed cell death in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ Res 81:137–144
Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC, Seifalian AM (2004) Ischemia reperfusion injury of the intestine and protective strategies against injury. Dig Dis Sci 49:1359–1377
Mao YF, Zheng XF, Cai JM, You XM, Deng XM, Zhang JH, Jiang L, Sun XJ (2009) Hydrogen-rich saline reduces lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381:602–605
Noda T, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Matsuo S, Aw TY (1998) Programmed cell death induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rat intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol 274:G270
Ohkawa H, Oshishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay of lipid peroxidation in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterisation of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Polasa K, Naidu NA, Ravindranath I, Krishanaswamy K (2004) Inhibition of B(a)P induced strand breaks in presence of curcumin. Mutat Res 557:203–213
Quaedackers JSLT, Beuk RJ, Bennet L, Charlton A, Egbrink MGA, Gunn AJ, Heineman E (2000) An evaluation of methods for grading histologic injury ischemia/reperfusion of the small bowel. Transplant Proc 32:1307–1310
Schoenberg MH, Beger HG (1993) Reperfusion injury after intestinal ischemia. Crit Care Med 21:1376
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Tagami M, Ikeda K, Nara Y, Fujino H, Kubota A, Numano F, Yamori Y (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-1 attenuates apoptosis in hippocampal neurons caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Lab Invest 76:613–617
Takeshita M, Tani T, Harada S, Hayashi H, Itoh H, Tajima H, Ohnishi I, Takamura H, Fushida S, Kayahara M (2010) Role of transcription factors in small intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury and tolerance induced by ischemic preconditioning. Transplant Proc 42:3406–3413
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462
Yadav S, Sindram D, Perry DK, Clavien PA (1999) Ischemic preconditioning protects the mouse liver by inhibition of apoptosis through a caspase-dependant pathway. Hepatology 30:1223–1231
Yin T, Sandhu G, Wolfgang CD, Burrier A, Webb RL, Rigel DF, Hai T, Whelan J (1997) Tissue-specific pattern of stress kinase activation in ischemia/reperfused heart and kidney. J Biol Chem 272:19943–19950
Yoshida T, Iwakiri R, Noda T, Okamoto K, Kojima M, Fukuyama K, Fujimoto K (2000) Histaminergic effect on apoptosis of rat small intestinal mucosa after ischemia-reperfusion. Dig Dis Sci 45:1138–1144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yucel, A.F., Kanter, M., Pergel, A. et al. The role of curcumin on intestinal oxidative stress, cell proliferation and apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Mol Hist 42, 579–587 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9364-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9364-0