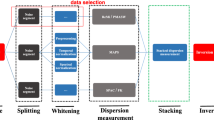
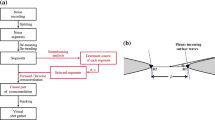
Abstract
Passive surface wave methods have gained much attention from geophysical and civil engineering communities because of the limited application of traditional seismic surveys in highly populated urban areas. Considering that they can provide high-frequency phase velocity information up to several tens of Hz, the active surface wave survey would be omitted and the amount of field work could be dramatically reduced. However, the measured dispersion energy image in the passive surface wave survey would usually be polluted by a type of “crossed” artifacts at high frequencies. It is common in the bidirectional noise distribution case with a linear receiver array deployed along roads or railways. We review several frequently used passive surface wave methods and derive the underlying physics for the existence of the “crossed” artifacts. We prove that the “crossed” artifacts would cross the true surface wave energy at fixed points in the f–v domain and propose a FK-based data selection technique to attenuate the artifacts in order to retrieve the high-frequency information. Numerical tests further demonstrate the existence of the “crossed” artifacts and indicate that the well-known wave field separation method, FK filter, does not work for the selection of directional noise data. Real-world applications manifest the feasibility of the proposed FK-based technique to improve passive surface wave methods by a priori data selection. Finally, we discuss the applicability of our approach.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki K (1957) Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference of strong seismic motion. In: Bolt BA (ed) Strong motion synthetics: computational techniques series. Academic Press, New York
Ali MY, Barkat B, Berteussen KA, Small J (2013) A low-frequency passive seismic array experiment over an onshore oil field in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Geophysics 78:B159–B176
Askari R, Hejazi SH (2015) Estimation of surface-wave group velocity using slant stack in the generalized S-transform domain. Geophysics 80:EN83–EN92
Asten MW (2006a) Site shear velocity profile interpretation from microtremor array data by direct fitting of SPAC curves. In: Proceedings of the third international symposium on the effects of surface geology on seismic motion (ESG2006), Grenoble, France, vol 2, LCPC, Paris, pp 1069–1082
Asten MW (2006b) On bias and noise in passive seismic data from finite circular array data processed using SPAC methods. Geophysics 7:153–162
Asten M, Henstridge J (1984) Array estimators and the use of microseisms for reconnaissance of sedimentary basins. Geophysics 49:1828–1837
Behm M, Snieder R (2013) Love waves from local traffic noise interferometry. Lead Edge 32:628–632
Behm M, Leahy GM, Snieder R (2014) Retrieval of local surface wave velocities from traffic noise—an example from the La Barge basin (Wyoming). Geophys Prospect 62:223–243
Bensen GD, Ritzwoller MH, Barmin MP, Levshin AL, Lin F, Moschetti MP, Shapiro NM, Yang Y (2007) Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophys J Int 169:1239–1260
Bonnefoy-Claudet S, Cornou C, Bard PY, Cotton F, Moczo P, Kristek J, F ̈ah D (2006) H/V ratio: a tool for site effects evaluation. Results from 1-D noise simulations. Geophys J Int 167:827–837
Campillo M, Paul A (2003) Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda. Science 299:547–549
Chapman CH (1978) A new method for computing synthetic seismograms. Geophys J Int 54:481–518
Chaput J, Clerc V, Campillo M, Roux P, Knox H (2016) On the practical convergence of coda-based correlations: a window optimization approach. Geophys J Int 204:736–747
Chávez-García FJ, Rodríguez M, Stephenson WR (2005) An alternative approach to the SPAC analysis of microtremors: exploiting stationarity of noise. Bull Seismol Soc Am 95:277–293
Cheng F, Xia J, Xu Y, Xu Z, Pan Y (2015) A new passive seismic method based on seismic interferometry and multichannel analysis of surface waves. J Appl Geophys 117:126–135
Cheng F, Xia J, Luo Y, Xu Z, Wang L, Shen C, Liu R, Pan Y, Mi B, Hu Y (2016) Multi-channel analysis of passive surface waves based on cross-correlations. Geophysics 81:EN57–EN66
Cheng F, Xia J, Shen C, Hu Y, Xu Z, Mi B (2018) Impose active sources during high-frequency passive surface wave measurement. Engineering (in Press)
Cho I, Tada T, Shinozaki Y (2004) A new method to determine phase velocities of Rayleigh waves from microseisms. Geophysics 69:1535–1551
Cho I, Tada T, Shinozaki Y (2008) Assessing the applicability of the spatial autocorrelation method: a theoretical approach. J Geophys Res 113:1–19
Claerbout JF (1968) Synthesis of a layered medium from its acoustic transmission response. Geophysics 33:264–269
Draganov D, Campman X, Thorbecke J, Verdel A, Wapenaar K (2013) Seismic exploration-scale velocities and structure from ambient seismic noise (> 1 Hz). J Geophys Res Solid Earth 118:4345–4360
Fan Y, Snieder R (2009) Required source distribution for interferometry of waves and diffusive fields. Geophys J Int 179:1232–1244
Foti S (2000) Multistation methods for geotechnical characterization using surface waves. PhD thesis, Politecnico di Torino
Foti S, Parolai S, Albarello D, Picozzi M (2011) Application of surface-wave methods for seismic site characterization. Surv Geophys 32:777–825
Gabàs A, Macau A, Benjumea B, Queralt P, Ledo J, Figueras S, Marcuello A (2016) Joint audio-magnetotelluric and passive seismic imaging of the Cerdanya Basin. Surv Geophys 37:897–921
Galiana-Merino JJ, Rosa-Herranz J, Giner J, Molina S, Botella F (2003) De-noising of short period seismograms by wavelet packet transform. Bull Seismol Soc Am 93:2554–2562
García-Jerez A, Luzón F, Navarro M (2008) An alternative method for calculation of Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocities by using three-component records on a single circular array without a central station. Geophys J Int 173:844–858
Garofalo F, Foti S, Hollender F, Bard PY, Cornou C, Cox BR, Ohrnberger M, Sicilia D, Asten M, Di Giulio G, Forbriger T, Guillier B, Hayashi K, Martin A, Matsushima S, Mercerat D, Poggi V, Yamanaka H (2016) InterPACIFIC project: comparison of invasive and non-invasive methods for seismic site characterization. Part I: Intra-comparison of surface wave methods. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 82:222–240
Groos JC, Bussat S, Ritter JRR (2012) Performance of different processing schemes in seismic noise cross-correlations. Geophys J Int 188:498–512
Haubrich R, McCamy K (1969) Microseisms: coastal and pelagic sources. Rev Geophys 7:539–571
Hayashi K, Craig M, Kita T, Inazaki T (2015) CMP spatial autocorrelation analysis of multichannel passive surface-wave data. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2015, pp 2200–2204
Hayashi K, Cakir R, Walsh TJ, State W (2016) Comparison of dispersion curves and velocity models obtained by active and passive surface wave methods. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2016, pp 4983-4988
Imposa S, Grassi S, De Guidi G, Battaglia F, Lanaia G, Scudero S (2016) 3D subsoil model of the San Biagio “Salinelle” mud volcanoes (Belpasso, Sicily) derived from geophysical surveys. Surv Geophys 37:1117–1138
Le Feuvre M, Joubert A, Leparoux D, Côte P (2015) Passive multi-channel analysis of surface waves with cross-correlations and beamforming. Application to a sea dike. J Appl Geophys 114:36–51
Lin F-C, Moschetti MP, Ritzwoller MH (2008) Surface wave tomography of the western United States from ambient seismic noise: Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocity maps. Geophys J Int 173:281–298
Lobkis OI, Weaver RL (2001) On the emergence of the Green’s function in the correlations of a diffuse field. J Acoust Soc Am 110:3011–3017
Louie JN (2001) Faster, better: shear-wave velocity to 100 meters depth from refraction microtremor arrays. Bull Seismol Soc Am 91:347–364
Luo Y, Xia J, Liu J, Xu Y, Liu Q (2008) Generation of a pseudo-2D shear-wave velocity section by inversion of a series of 1D dispersion curves. J Appl Geophys 64:115–124
Macau A, Benjumea B, Gabàs A, Figueras S, Vilà M (2015) The effect of shallow quaternary deposits on the shape of the H/V spectral ratio. Surv Geophys 36:185–208
McMechan GA, Ottolini R (1980) Direct observation of a p–τ curve in a slant stacked wave field. Bull Seismol Soc Am 70:775–789
McMechan GA, Yedlin MJ (1981) Analysis of dispersive waves by wave field transformation. Geophysics 46:869–874
Nakahara H (2012) Formulation of the spatial autocorrelation (SPAC) method in dissipative media. Geophys J Int 190:1777–1783
Nakata N (2016) Near-surface S-wave velocities estimated from traffic-induced Love waves using seismic interferometry with double beamforming. Interpretation 4:SQ23–SQ31
Nakata N, Snieder R, Tsuji T, Larner K, Matsuoka T (2011) Shear wave imaging from traffic noise using seismic interferometry by cross-coherence. Geophysics 76:SA97–SA106
Okada H (2003) Microtremor survey method (translated by Koya Sato). Geophysical monograph series, vol 12. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Tulsa
Pan Y, Xia J, Xu Y, Xu Z, Cheng F, Xu H, Gao L (2016) Delineating shallow S-wave velocity structure using multiple ambient-noise surface-wave methods: an example from Western Junggar, China. Bull Seismol Soc Am 106:327–336
Park CB, Miller RD, Xia J (1999) Multi-channel analysis of surface waves. Geophysics 64:800–808
Park C, Miller R, Laflen D, Neb C, Ivanov J, Bennett B, Huggins R (2004) Imaging dispersion curves of passive surface waves. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2004, pp 1357–1360
Sabra KG, Gerstoft P, Roux P, Kuperman WA (2005) Surface wave tomography from microseisms in Southern California. Geophys Res Lett 32:L14311
Sacchi MD, Ulrych TJ (1995) High-resolution velocity gathers and offset space reconstruction. Geophysics 60:1169–1177
Savage MK, Lin FC, Townend J (2013) Ambient noise cross-correlation observations of fundamental and higher-mode Rayleigh wave propagation governed by basement resonance. Geophys Res Lett 40:3556–3561
Shapiro NM, Campillo M (2004) Emergence of broadband Rayleigh waves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 31:L07614
Shapiro NM, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller MH (2005) High-resolution surface wave tomography from ambient seismic noise. Science 307:1615–1618
Shen C, Wang A, Wang L, Xu Z, Cheng F (2015) Resolution equivalence of dispersion-imaging methods for noise-free high-frequency surface-wave data. J Appl Geophys 122:167–171
Snieder R (2004) Extracting the Green’s function from the correlation of coda waves: a derivation based on stationary phase. Phys Rev E 69:046610
Snieder R, Larose E (2013) Extracting earth’s elastic wave response from noise measurements. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 41:183–206
Snieder R, Miyazawa M, Slob E, Vasconcelos I, Wapenaar K (2009) A comparison of strategies for seismic interferometry. Surv Geophys 30:503–523
Song YY, Castagna JP, Black RA, Knapp RW (1989) Sensitivity of near-surface shear-wave velocity determination from Rayleigh and Love waves. In: Technical program with biographies, SEG, 59th annual meeting, Dallas, Texas, pp 509–512
Stehly L, Campillo M, Shapiro NM (2006) A study of the seismic noise from its long-range correlation properties. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 111:1–12
Strobbia C, Foti S (2006) Multi-offset phase analysis of surface wave data (MOPA). J Appl Geophys 59:300–313
Stutzmann E, Ardhuin F, Schimmel M, Mangeney A, Patau G (2012) Modelling long-term seismic noise in various environments. Geophys J Int 191:707–722
Tada T, Cho I, Shinozaki Y (2007) Beyond the SPAC method: exploiting the wealth of circular-array methods for microtremor exploration. Bull Seismol Soc Am 97:2080–2095
Tada T, Cho I, Shinozaki Y (2009) New circular-array microtremor techniques to infer love-wave phase velocities. Bull Seismol Soc Am 99:2912–2926
Thorson JR, Claerbout JF (1985) Velocity-stack and slant-stack stochastic inversion. Geophysics 50:2727–2741
Wapenaar K (2004) Retrieving the elastodynamic Green’s function of an arbitrary inhomogeneous medium by cross correlation. Phys Rev Lett 93:254301
Wapenaar K, Fokkema J (2006) Green’s function representations for seismic interferometry. Geophysics 71:SI33–SI46
Weemstra C, Draganov D, Ruigrok EN, Hunziker J, Gomez M, Wapenaar K (2017) Application of seismic interferometry by multidimensional deconvolution to ambient seismic noise recorded in Malargüe, Argentina. Geophys J Int 60(4):802–823
Xia J, Miller RD, Park CB (1999) Estimation of near-surface shear-wave velocity by inversion of Rayleigh wave. Geophysics 64:691–700
Xia J, Miller RD, Park CB, Tian G (2003) Inversion of high frequency surface waves with fundamental and higher modes. J Appl Geophys 52:45–57
Xia J, Miller RD, Park CB, Ivanov J, Tian G, Chen C (2004) Utilization of high-frequency Rayleigh waves in near-surface geophysics. Lead Edge 23:753–759
Xia J, Xu Y, Miller RD, Chen C (2006) Estimation of elastic moduli in a compressible Gibson half-space by inverting Rayleigh wave phase velocity. Surv Geophys 27:1–17
Xia J, Xu Y, Miller RD (2007) Generating an image of dispersive energy by frequency decomposition and slant stacking. Pure Appl Geophys 164:941–956
Xia J, Miller RD, Xu Y (2008) Data-resolution matrix and model-resolution matrix for Rayleigh-wave inversion using a damped least-squares method. Pure Appl Geophys 165:1227–1248
Xia J, Miller RD, Xu Y, Luo Y, Chen C, Liu J, Ivanov J, Zeng C (2009) High-frequency Rayleigh-wave method. J Earth Sci 20:563–579
Xia J, Xu Y, Luo Y, Miller RD, Cakir R, Zeng C (2012) Advantages of using multichannel analysis of Love waves (MALW) to estimate near-surface shear-wave velocity. Surv Geophys 33:841–860
Xia J, Yin X, Xu Y (2013) Feasibility of determining Q of near-surface materials from Love waves. J Appl Geophys 95:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2013.05.007
Xia J, Cheng F, Xu Z, Shen C, Liu R (2017) Advantages of multi-channel analysis of passive surface waves (MAPS). International conference on engineering geophysics, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 9–12 Oct 2017, pp 94–97
Xu Y, Zhang B, Luo Y, Xia J (2013) Surface-wave observations after integrating active and passive source data. Lead Edge 32:634–637
Xu Z, Xia J, Luo Y, Cheng F, Pan Y (2016) Potential misidentification of love-wave phase velocity based on three-component ambient seismic noise. Pure Appl Geophys 173:1115–1124
Xu Z, Mikesell TD, Xia J, Cheng F (2017) A comprehensive comparison between the refraction microtremor and seismic interferometry method for phase velocity estimation. Geophysics 82:1–43
Yang Y, Ritzwoller MH, Levshin AL, Shapiro NM (2007) Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography across Europe. Geophys J Int 168:259–274
Yao H, van der Hilst RD (2009) Analysis of ambient noise energy distribution and phase velocity bias in ambient noise tomography, with application to SE Tibet. Geophys J Int 179:1113–1132
Yilmaz O (1987) Seismic data processing. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Tulsa
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 41774115, the National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant of Institute for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences under Grant No. WHS201306. The authors thank crews of AoCheng Technology for their help in data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, F., Xia, J., Xu, Z. et al. Frequency–Wavenumber (FK)-Based Data Selection in High-Frequency Passive Surface Wave Survey. Surv Geophys 39, 661–682 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-018-9473-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-018-9473-3