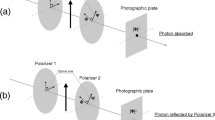
Abstract
An expression of the Lindbladian form is proposed that ensures an unambiguous time-continuous reduction of the initial system-pointer wave-packet to one in which the readings and the observable’s values are aligned, formalized as the transition from an outer product to an inner product of the system’s and apparatus’ density matrices. The jump operators are in the basis of the observables, with uniquely determined parameters derived from the measurement set-up (thereby differing from S. Weinberg’s Lindbladian resolution of wave-packet formalism) and conforming to Born’s probability rules. The novelty lies in formalising the adaptability of the surroundings (including the measuring device) to the mode of observation. Accordingly, the transition is of finite duration (in contrast to its instantaneousness in the von Neumann’s formulation). This duration is estimated for a simple half-spin-like model.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leggett, A.J.: Macroscopic quantum systems and the quantum theory of measurement. Suppl. Progress Theor. Phys. 69, 80 (1980)
Ghirardi, G.C., Pearle, P., Rimini, A.: Markov processes in Hilbert space and continuous spontaneous localization of systems of identical particles. Phys. Rev. A 42, 78 (1990)
Wigner, E.P.: Remarks on the mind-body question. In: Good, I.J. (ed.) The Scientist Speculates. Heinemann, London (1961)
Louisell, W.H.: Quantum Statistical Properties of Radiation. Wiley, New York (1973)
Ghirardi, G.C., Rimini, A., Weber, T.: Unified dynamics for microscopic and macroscopic systems. Phys. Rev. D 34, 470 (1986)
Pearle, P.: Combining stochastic, dynamical state reduction with spontaneous localization. Phys. Rev. A 39, 2277–2289 (1989)
Everett, H.: Relative state formulation of quantum mechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 29, 454–462 (1957)
Byalinicki-Birula, I., Mycielski, J.: Nonlinear wave mechanics. Ann. Phys. 108, 62–83 (1976)
Sewell, G.: On the mathematical structure of quantum measurement theory. Rep. Math. Phys. 56, 271–290 (2005)
Diósi, L.: Models for universal reduction of macroscopic quantum fuctuations. Phys. Rev. A 40, 165 (1989)
Penrose, R.: On gravity’s role in quantum state reduction. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 28, 581 (1996)
Donadi, S., Piscicchia, K., Curceanu, C., Diósi, L., Laubenstein, M., Bassi, A.: Underground test of gravity-related wave function collapse. Nat. Phys. 17, 74 (2021)
Lindblad, G.: On the generators of quantum dynamical semigroups. Commun. Math. Phys. 48, 112–130 (1976)
Gorini, V., Kossakowski, A., Sudarshan, E.C.G.: Completely positive dynamical semigroups of N-level systems. J. Math. Phys. 17, 821–825 (1976)
Weinberg, S.: What happens in a measurement? Phys. Rev. A 93(032124), 1–6 (2016)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Jacobs, K., Steck, D.A.: A straightforward introduction to continuous quantum measurement. Contemp. Phys. 47(5), 279–303 (2006). arXiv:quant-ph/0611067
Bohr, N.: Atomic Physics and Human Knowledge. Wiley, New York (1958)
Bell, J.: Against ‘measurement’. Phys. World 3, 33–4 (1990)
Peres, A.: Quantum Theory: Concepts and Methods. Kluwer Academic, Norwell (1998)
Breuer, H.-P., Petruccione, F.F.: The Theory of Open Quantum Systems. Oxford University Press, New York (2002)
Jäger, S.B., Schmit, T., Morigi, G., Holland, M.J., Betzholz, R.: Lindblad master equations for quantum systems coupled to dissipative bosonic modes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 129(063601), 1–7 (2022)
Leibfried, D., Blatt, R., Monroe, C., Wineland, D.: Quantum dynamics of single trapped ions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75(1), 281–324 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.75.281
Funo, K., Shiraishi, N., Saito, K.: Speed limit for open quantum systems. New J. Phys. 21(0300611), 1–9 (2019)
Horowitz, J.M., Parrondo, J.M.R.: Entropy production along non-equilibrium jump trajectories. New J. Phys. 15(220601), 1–23 (2013)
Mandelshtam, L.I., Tamm, I.E.: The uncertainty relation between energy and time in nonrelativistic quantum mechanics. J. Phys. 9, 249 (1945)
Margulus, N., Levitin, L.B.: The maximum speed of dynamical evolution. Physica D 120, 188 (1998)
Braunstein, S.L., Caves, C.M.: Statistical distance and the geometry of quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 3439–3444 (1994)
Deffner, S., Campbell, S.: Quantum speed limits: from Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle to optimal quantum control. J. Phys. A 50, 453001 (2017)
Anandan, J., Aharonov, Y.: Geometry of quantum evolution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 1697–1701 (1990)
Barnett, S.M.: Quantum Information. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2009)
Manzano, D.: A short introduction to the Lindblad master equation. AIP Adv. 10(2), 1063 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5115323
Korzekwa, K., Lostaglio, M.: Optimizing thermalization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 129(040602), 1–7 (2022)
Lostaglio, M., Korzekwa, K.: Continuous thermomajorizaton and a complete set of Markovian thermal processes. Phys. Rev. A 106(012426), 1–18 (2022)
Kakuyanagi, K., Baba, T., Matsuzaki, Y., Nakano, H., Saito, S., Semba, K.: Observation of quantum Zeno effect in a superconducting flux qubit. New J. Phys. 17(063035), 1–10 (2015)
Keyl, M.: Fundamentals of quantum information theory. Phys. Rep. 369(5), 431–58 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the referee for meticulous reading and insightful questioning of a previous version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Englman, R., Yahalom, A. Lindbladian-Induced Alignment in Quantum Measurements. Found Phys 53, 19 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10701-022-00659-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10701-022-00659-6