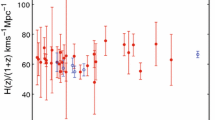
Abstract
In this paper we summarise the constraints that low-redshift data—such as supernovae Ia (SN Ia), baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) and cosmic chronometers (CC)—are able to set on the concordance model and its extensions, as well as on inhomogeneous but isotropic models. We provide a broad overlook into these cosmological scenarios and several aspects of data analysis. In particular, we review a number of systematic issues of SN Ia analysis that include magnitude correction techniques, selection bias and their influence on the inferred cosmological constraints. Furthermore, we examine the isotropic and anisotropic components of the BAO data and their individual relevance for cosmological model-fitting. We extend the discussion presented in earlier works regarding the inferred dynamics of cosmic expansion and its present rate from the low-redshift data. Specifically, we discuss the cosmological constraints on the accelerated expansion and related model-selections. In addition, we extensively talk about the Hubble constant problem, then focus on the low-redshift data constraint on \(H_0\) that is based on CC. Finally, we present the way in which this result compares to the high-redshift \(H_0\) estimate and local (redshift zero) measurements that are in tension.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, B.P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T.D., et al.: A gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant. Nature 551, 85 (2017a)
Abbott, B.P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T.D., et al.: GW170814: a three-detector observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 141101 (2017b)
Abbott, B.P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T.D., et al.: GW170817: observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 161101 (2017c)
Addison, G.E., Watts, D.J., Bennett, C.L., et al.: Elucidating \(\varLambda \)CDM: impact of baryon acoustic oscillation measurements on the hubble constant discrepancy. (2017). arXiv:1707.06547
Akaike, H.: A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19, 716 (1974)
Alam, S., Ata, M., Bailey, S., et al.: The clustering of galaxies in the completed SDSS-III Baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey: cosmological analysis of the DR12 galaxy sample. MNRAS 470, 2617 (2017)
Alam, U., Sahni, V., Deep Saini, T., Starobinsky, A.A.: Exploring the expanding Universe and dark energy using the statefinder diagnostic. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1057 (2003)
Alcock, C., Paczyński, B.: An evolution free test for non-zero cosmological constant. Nature 281, 358 (1979)
Alnes, H., Amarzguioui, M.: CMB anisotropies seen by an off-center observer in a spherically symmetric inhomogeneous universe. Phys. Rev. D 74, 103520 (2006)
Alnes, H., Amarzguioui, M., Grøn, Ø.: Inhomogeneous alternative to dark energy? Phys. Rev. D 73, 083519 (2006)
Alonso, D., García-Bellido, J., Haugbølle, T., Vicente, J.: Large scale structure simulations of inhomogeneous Lemaître-Tolman-Bondi void models. Phys. Rev. D 82, 123530 (2010)
Amati, L., Frontera, F., Guidorzi, C.: Extremely energetic Fermi gamma-ray bursts obey spectral energy correlations. Astron. Astrophys. 508, 173 (2009)
Amati, L., Frontera, F., Tavani, M., et al.: Intrinsic spectra and energetics of BeppoSAX gamma-ray bursts with known redshifts. Astron. Astrophys. 390, 81 (2002)
Amati, L., Guidorzi, C., Frontera, F., et al.: Measuring the cosmological parameters with the Ep, i-Eiso correlation of Gamma-Ray bursts. MNRAS 391, 577 (2008)
Amendola, L.: Coupled quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 62, 043511 (2000)
Amendola, L., Eggers Bjæ lde, O., Valkenburg, W., Wong, Y.Y.Y.: How real-time cosmology can distinguish between different anisotropic models. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 12, 042 (2013)
Anderson, R.I., Riess, A.G.: On Cepheid distance scale bias due to stellar companions and cluster populations. (2017). arXiv:1712.01065
Andres Vallejo, S., Enea Romano, A.: Reconstructing the metric of the local universe from number counts observations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 023 (2017)
Armendariz-Picon, C., Mukhanov, V., Steinhardt, P.J.: Dynamical solution to the problem of a small cosmological constant and late-time cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4438 (2000)
Armendariz-Picon, C., Mukhanov, V., Steinhardt, P.J.: Essentials of k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 63, 103510 (2001)
Ata, M., Baumgarten, F., Bautista, J., et al.: The clustering of the SDSS-IV extended baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey DR14 quasar sample: first measurement of baryon acoustic oscillations between redshift 0.8 and 2.2. MNRAS 473, 4773 (2017)
Aubourg, É., Bailey, S., Bautista, J.E., et al.: Cosmological implications of baryon acoustic oscillation measurements. Phys. Rev. D 92, 123516 (2015)
Bagla, J.S., Jassal, H.K., Padmanabhan, T.: Cosmology with tachyon field as dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 67, 063504 (2003)
Bahamonde, S., Boehmer, C.G., Carloni, S., et al.: Dynamical systems applied to cosmology: dark energy and modified gravity. (2017) arXiv:1712.03107
Bahcall, N.A., Cen, R.: Galaxy clusters and cold dark matter—a low-density unbiased universe? Astrophys. J. 398, L81 (1992)
Bardeen, J.M., Bond, J.R., Efstathiou, G.: Cosmic fluctuation spectra with large-scale power. Astrophys. J. 321, 28 (1987)
Bautista, J.E., Busca, N.G., Guy, J., et al.: Measurement of baryon acoustic oscillation correlations at z = 2.3 with SDSS DR12 Ly\(\alpha \)-forests. Astron. Astrophys. 603, A12 (2017)
Beaton, R.L., Freedman, W.L., Madore, B.F., et al.: The Carnegie-Chicago hubble program. I. An independent approach to the extragalactic distance scale using only population II distance indicators. Astron. Astrophys. 832, 210 (2016)
Bernal, J.L., Verde, L., Riess, A.G.: The trouble with H\(_{0}\). J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 019 (2016)
Bessel, F.W.: Über Veränderlichkeit der eigenen Bewegungen der Fixterne Von Herrn Geh-Rath Bessel. Astron. Nachr. 22, 145 (1844)
Betoule, M., Kessler, R., Guy, J., et al.: Improved cosmological constraints from a joint analysis of the SDSS-II and SNLS supernova samples. Astron. Astrophys. 568, A22 (2014)
Bilicki, M., Seikel, M.: We do not live in the R\(_{h}\) = ct universe. MNRAS 425, 1664 (2012)
Blondin, S., Mandel, K.S., Kirshner, R.P.: Do spectra improve distance measurements of Type Ia supernovae? Astron. Astrophys. 526, A81 (2011)
Böhringer, H., Chon, G., Bristow, M., Collins, C .A.: The extended ROSAT-ESO flux-limited X-ray galaxy cluster survey (REFLEX II). V. Exploring a local underdensity in the southern sky. Astron. Astrophys. 574, A26 (2015)
Bonamente, M., Joy, M.K., LaRoque, S.J., et al.: Determination of the cosmic distance scale from Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect and Chandra X-ray measurements of high-redshift galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. 647, 25 (2006)
Bondi, H.: Spherically symmetrical models in general relativity. MNRAS 107, 410 (1947)
Bono, G., Stetson, P.B., VandenBerg, D.A., et al.: On a new near-infrared method to estimate the absolute ages of star clusters: NGC 3201 as a first test case. Astrophys. J. 708, L74 (2010)
Bonvin, V., Courbin, F., Suyu, S.H., et al.: H0LiCOW - V. New COSMOGRAIL time delays of HE 0435–1223: H\(_{0}\) to 3.8 per cent precision from strong lensing in a flat \(\varLambda \)CDM model. MNRAS 465, 4914 (2017)
Bourdin, H., Mazzotta, P., Kozmanyan, A., Jones, C., Vikhlinin, A.: Pressure profiles of distant galaxy clusters in the Planck catalogue. Astrophys. J. 843, 72 (2017)
Bronder, T.J., Hook, I.M., Astier, P., et al.: SNLS spectroscopy: testing for evolution in type Ia supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 477, 717 (2008)
Bull, P., Clifton, T., Ferreira, P.G.: Kinematic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect as a test of general radial inhomogeneity in Lemaître-Tolman-Bondi cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 85, 024002 (2012)
Cai, R.-G., Wang, A.: Cosmology with interaction between phantom dark energy and dark matter and the coincidence problem. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 3, 002 (2005)
Caldwell, R.R.: A phantom menace? Cosmological consequences of a dark energy component with super-negative equation of state. Phys. Lett. B 545, 23 (2002)
Caldwell, R.R., Dave, R., Steinhardt, P.J.: Cosmological imprint of an energy component with general equation of state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1582 (1998)
Caldwell, R.R., Kamionkowski, M., Weinberg, N.N.: Phantom energy: dark energy with w\(<\)-1 causes a cosmic doomsday. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 071301 (2003)
Carroll, S.M., Hoffman, M., Trodden, M.: Can the dark energy equation-of-state parameter w be less than -1? Phys. Rev. D 68, 023509 (2003)
Célérier, M.-N.: Do we really see a cosmological constant in the supernovae data? Astron. Astrophys. 353, 63 (2000)
Chen, Y., Kumar, S., Ratra, B.: Determining the hubble constant from hubble parameter measurements. Astrophys. J. 835, 86 (2017)
Cheng, C., Huang, Q.: An accurate determination of the Hubble constant from baryon acoustic oscillation datasets. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 095684 (2015)
Chevallier, M., Polarski, D.: Accelerating universes with scaling dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 10, 213 (2001)
Chiba, T., Okabe, T., Yamaguchi, M.: Kinetically driven quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 62, 023511 (2000)
Clarkson, C.: Establishing homogeneity of the universe in the shadow of dark energy. C.R. Phys. 13, 682 (2012)
Clarkson, C., Clifton, T., February, S.: Perturbation theory in Lemaître-Tolman-Bondi cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 6, 25 (2009)
Clifton, T., Ferreira, P.G., Padilla, A., Skordis, C.: Modified gravity and cosmology. Phys. Rep. 513, 1 (2012)
Cohen, A.G., Kaplan, D.B., Nelson, A.E.: Effective field theory, black holes, and the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4971 (1999)
Conley, A., Guy, J., Sullivan, M., et al.: Supernova constraints and systematic uncertainties from the first three years of the supernova legacy survey. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 192, 1 (2011)
Copeland, E.J., Garousi, M.R., Sami, M., Tsujikawa, S.: What is needed of a tachyon if it is to be the dark energy? Phys. Rev. D 71, 043003 (2005)
Copeland, E.J., Sami, M., Tsujikawa, S.: Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 15, 1753 (2006)
Coulter, D.A., Foley, R.J., Kilpatrick, C.D., et al.: Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the optical counterpart to a gravitational wave source. Science 358, 1556–1558 (2017)
Dai, M., Wang, Y.: Sampling the probability distribution of type Ia supernova lightcurve parameters in cosmological analysis. MNRAS 459, 1819 (2016)
de Grijs, R., Wicker, J.E., Bono, G.: Clustering of local group distances: publication bias or correlated measurements? I the large magellanic cloud. Astron. J. 147, 122 (2014)
Delabrouille, J., de Bernardis, P., Bouchet, F.R., et al.: Exploring cosmic origins with CORE: survey requirements and mission design. (2017). arXiv:1706.04516
Delubac, T., Bautista, J.E., Busca, N.G., et al.: Baryon acoustic oscillations in the Ly\(\alpha \) forest of BOSS DR11 quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 574, A59 (2015)
Deng, X.-M.: A modified generalized chaplygin gas as the unified dark matter-dark energy revisited. Braz. J. Phys. 41, 333 (2011)
Deser, S.: Introduction to Jebsen’s paper. Gen. Rel. Grav. 37, 2251 (2005)
DESI Collaboration; Aghamousa, A., Aguilar, J., et al.: The DESI experiment part I: science, targeting, and survey design. (2016). arXiv:1611.00036
Dev, A., Jain, D., Lohiya, D.: Power law cosmology—a viable alternative. (2008). arXiv:0804.3491
Dev, A., Safonova, M., Jain, D., Lohiya, D.: Cosmological tests for a linear coasting cosmology. Phys. Lett. B 548, 12 (2002)
Dhawan, S., Jha, S.W., Leibundgut, B.: Measuring the hubble constant with type Ia supernovae as near-infrared standard candles. Astron. Astrophys. 609, A72 (2018)
Di Valentino, E., Melchiorri, A., Silk, J.: Reconciling Planck with the local value of H\(_{0}\) in extended parameter space. Phys. Lett. B 761, 242 (2016)
Ding, X., Biesiada, M., Cao, S., Li, Z., Zhu, Z.-H.: Is there evidence for dark energy evolution? Astrophys. J. 803, L22 (2015)
Dolgov, A., Halenka, V., Tkachev, I.: Power-law cosmology, SN Ia, and BAO. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 047 (2014)
Dolgov, A.D.: Higher spin fields and the problem of the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 55, 5881 (1997)
Doran, M., Schwindt, J.-M., Wetterich, C.: Structure formation and the time dependence of quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 64, 123520 (2001)
du Mas des Bourboux, H., Le Goff, J.-M., Blomqvist, M., et al.: Baryon acoustic oscillations from the complete SDSS-III Ly\(\alpha \)-quasar cross-correlation function at z = 2.4. Astron. Astrophys. 608, A130 (2017)
Efstathiou, G.: H\(_{0}\) revisited. MNRAS 440, 1138 (2014)
Efstathiou, G., Sutherland, W.J., Maddox, S.J.: The cosmological constant and cold dark matter. Nature 348, 705 (1990)
Einstein, A.: Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation, pp. 844–847. Sitzungsberichte der Königlich Preußischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Berlin (1915)
Einstein, A.: Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur Allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie, pp. 142–152. Sitzungsberichte der Königlich Preußischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Berlin (1917)
Eisenstein, D.J., Hu, W.: Baryonic features in the matter transfer function. Astrophys. J. 496, 605 (1998)
Eisenstein, D.J., Zehavi, I., Hogg, D.W., et al.: Detection of the baryon acoustic peak in the large-scale correlation function of SDSS luminous red galaxies. Astrophys. J. 633, 560 (2005)
Ellis, G.F.R.: On the definition of distance in general relativity: I. M. H. Etherington (Philosophical Magazine ser. 7, vol. 15, 761 (1933)). Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 39, 1047 (2007)
Enea Romano, A.: Hubble trouble or Hubble bubble? (2016). arXiv:1609.04081
Enqvist, K., Mattsson, T.: The effect of inhomogeneous expansion on the supernova observations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2, 19 (2007)
February, S., Larena, J., Smith, M., Clarkson, C.: Rendering dark energy void. MNRAS 405, 2231 (2010)
Feeney, S.M., Mortlock, D.J., Dalmasso, N.: Clarifying the Hubble constant tension with a Bayesian hierarchical model of the local distance ladder. (2017). arXiv:1707.00007
Feng, C.-J., Shen, X.-Y., Li, P., Li, X.-Z.: A new class of parametrization for dark energy without divergence. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 9, 023 (2012)
Fernández Arenas, D., Terlevich, E., Terlevich, R., et al.: An independent determination of the local Hubble constant. MNRAS 474, 1250 (2018)
Filippenko, A.V.: Type Ia supernovae and cosmology. In: Sion, E.M., Vennes, S., Shipman, H.I. (eds.) White Dwarfs: Cosmological and Galactic Probes. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, pp. 97–133. Springer, New York (2005)
Follin, B., Knox, L.: Insensitivity of the distance ladder hubble constant determination to Cepheid calibration modeling choices. (2017). arXiv:1707.01175
Font-Ribera, A., McDonald, P., Mostek, N., et al.: DESI and other dark energy experiments in the era of neutrino mass measurements. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 5, 023 (2014)
Freedman, W.L.: Correction: cosmology at a crossroads. Nat. Astron. 1, 0169 (2017)
Freedman, W.L., Madore, B.F.: The hubble constant. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 48, 673 (2010)
Freedman, W.L., Madore, B.F., Gibson, B.K., et al.: Final results from the hubble space telescope key project to measure the hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 553, 47 (2001)
Freedman, W.L., Madore, B.F., Scowcroft, V., et al.: Carnegie hubble program: a mid-infrared calibration of the hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 758, 24 (2012)
Friedmann, A.: Über die Krümmung des Raumes. Z. Angew. Phys. 10, 377 (1922)
Friedmann, A.: Über die Möglichkeit einer welt mit konstanter negativer Krümmung des Raumes. Z. Angew. Phys. 21, 326 (1924)
Collaboration, Gaia, Prusti, T., de Bruijne, J.H.J., et al.: The Gaia mission. Astron. Astrophys. 595, A1 (2016)
Gao, F., Braatz, J.A., Reid, M.J., et al.: The megamaser cosmology project. IX. Black hole masses for three maser galaxies, the megamaser cosmology project. Astrophys. J. 834, 52 (2017)
Garcia-Bellido, J., Haugbølle, T.: Confronting Lemaitre Tolman Bondi models with observational cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 4, 3 (2008)
Gaztañaga, E., Cabré, A., Hui, L.: Clustering of luminous red galaxies—IV. Baryon acoustic peak in the line-of-sight direction and a direct measurement of H(z). MNRAS 399, 1663 (2009)
Gehlaut, S., Kumar, P., Geetanjali, Lohiya, D.: A concordant “freely coasting cosmology”. (2003). arXiv:astro-ph/0306448
Goldhaber, G., Groom, D.E., Kim, A., et al.: Timescale stretch parameterization of type Ia supernova B-band light curves. Astrophys. J. 558, 359 (2001)
Goldstein, A., Veres, P., Burns, E., et al.: An ordinary short gamma-ray burst with extraordinary implications: fermi-GBM detection of GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 848, L14 (2017)
Goobar, A.: Low R\(_{V}\) from circumstellar dust around supernovae. Astrophys. J. 686, L103 (2008)
Guth, A.H.: Inflationary universe: a possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. D 23, 347 (1981)
Guy, J., Astier, P., Baumont, S., et al.: SALT2: using distant supernovae to improve the use of type Ia supernovae as distance indicators. Astron. Astrophys. 466, 11 (2007)
Guy, J., Astier, P., Nobili, S., Regnault, N., Pain, R.: SALT: a spectral adaptive light curve template for type Ia supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 443, 781 (2005)
Haridasu, B.S., Luković, V.V., D’Agostino, R., Vittorio, N.: Strong evidence for an accelerating universe. Astron. Astrophys. 600, L1 (2017a)
Haridasu, B.S., Luković, V.V., Vittorio, N.: Isotropic vs. anisotropic components of BAO data: a tool for model selection. (2017b). arXiv:1711.03929
Harvey, A.: How Einstein discovered dark energy. (2012). arXiv:1211.6338
Hayden, B.T., Gupta, R.R., Garnavich, P.M., et al.: The fundamental metallicity relation reduces type Ia SN hubble residuals more than host mass alone. Astrophys. J. 764, 191 (2013)
Hicken, M., Wood-Vasey, W.M., Blondin, S., et al.: Improved dark energy constraints from \(\sim \)100 new CfA supernova type Ia light curves. Astrophys. J. 700, 1097 (2009)
Hillebrandt, W., Niemeyer, J.C.: Type IA supernova explosion models. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 38, 191 (2000)
Hinshaw, G., Larson, D., Komatsu, E.: Nine-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: cosmological parameter results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 208, 19 (2013)
Hinton, S.R., Kim, A., Davis, T.M.: Accounting for sample selection in Bayesian analyses. (2017). arXiv:1706.03856
Holwerda, B.W., Reynolds, A., Smith, M., Kraan-Korteweg, R.C.: SN Ia host galaxy properties and the dust extinction distribution. MNRAS 446, 3768 (2015)
Hoscheit, B.L., Barger, A.J.: Large local void, supernovae type Ia, and the kinematic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect in a lambda-LTB model. In: American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts, Vol. 230 (2017)
Hubble, E.: A relation between distance and radial velocity among extra-galactic nebulae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 15, 168 (1929)
Huchra, J.P.: The hubble constant. Science 256, 321 (1992)
Jackson, N.: The hubble constant. Living Rev. Relat. 10, 4 (2007)
Jang, I.S., Lee, M.G.: The tip of the red giant branch distances to typa Ia supernova host galaxies. V. NGC 3021, NGC 3370, and NGC 1309 and the value of the hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 836, 74 (2017)
Jassal, H.K., Bagla, J.S., Padmanabhan, T.: WMAP constraints on low redshift evolution of dark energy. MNRAS 356, L11 (2005)
Jimenez, R., Loeb, A.: Constraining cosmological parameters based on relative galaxy ages. Astrophys. J. 573, 37 (2002)
Johansson, J., Thomas, D., Pforr, J., et al.: SN Ia host galaxy properties from Sloan digital sky survey-II spectroscopy. MNRAS 435, 1680 (2013)
John, M.V., Joseph, K.B.: Generalized Chen-Wu type cosmological model. Phys. Rev. D 61, 087304 (2000)
Jones, D.O., Scolnic, D.M., Riess, A.G., et al.: Measuring dark energy properties with photometrically classified pan-STARRS supernovae. II. Cosmological parameters. (2017). arXiv:1710.00846
Joudaki, S., Mead, A., Blake, C., et al.: KiDS-450: testing extensions to the standard cosmological model. MNRAS 471, 1259 (2017)
Joyce, A., Jain, B., Khoury, J., Trodden, M.: Beyond the cosmological standard model. Phys. Rep. 568, 1 (2015)
Joyce, A., Lombriser, L., Schmidt, F.: Dark energy versus modified gravity. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 66, 95 (2016)
Kamenshchik, A., Moschella, U., Pasquier, V.: An alternative to quintessence. Phys. Lett. B 511, 265 (2001)
Kasen, D.: Secondary maximum in the near-infrared light curves of type Ia supernovae. Astrophys. J. 649, 939 (2006)
Kattner, S., Leonard, D.C., Burns, C.R., et al.: The standardizability of type Ia supernovae in the near-infrared: evidence for a peak-luminosity versus decline-rate relation in the near-infrared. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 124, 114 (2012)
Keenan, R.C., Barger, A.J., Cowie, L.L.: Evidence for a \(\sim \)300 megaparsec scale under-density in the local galaxy distribution. Astrophys. J. 775, 62 (2013)
Kelly, P.L., Hicken, M., Burke, D.L., Mandel, K.S., Kirshner, R.P.: Hubble residuals of nearby type Ia supernovae are correlated with host galaxy masses. Astrophys. J. 715, 743 (2010)
Kessler, R., Becker, A.C., Cinabro, D., et al.: First-year sloan digital sky survey-II supernova results: hubble diagram and cosmological parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 185, 32 (2009)
Kessler, R., Scolnic, D.: Correcting type Ia supernova distances for selection biases and contamination in photometrically identified samples. Astrophys. J. 836, 56 (2017)
Kim, A.G.: Type Ia supernova intrinsic magnitude dispersion and the fitting of cosmological parameters. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 123, 230 (2011)
Kim, A.G., Aldering, G., Antilogus, P., et al.: Type Ia supernova hubble residuals and host-galaxy properties. Astrophys. J. 784, 51 (2014)
Kirshner, R.P.: Hubble’s diagram and cosmic expansion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101, 8 (2003)
Komatsu, E., Dunkley, J., Nolta, M.R., et al.: Five-year wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe observations: cosmological interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 180, 330 (2009)
Komatsu, E., Smith, K.M., Dunkley, J., et al.: Seven-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: cosmological interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 192, 18 (2011)
Kowalski, M., Rubin, D., Aldering, G., et al.: Improved cosmological constraints from new, old, and combined supernova data sets. Astrophys. J. 686, 749 (2008)
Krasiński, A.: Inhomogeneous Cosmological Models. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Kristian, J., Sachs, R.K.: Observations in cosmology. Astrophys. J. 143, 379 (1966)
Kuo, C.Y., Braatz, J.A., Lo, K.Y., et al.: The megamaser cosmology project. VI. Observations of NGC 6323. Astrophys. J. 800, 26 (2015)
Kuo, C.Y., Braatz, J.A., Reid, M.J., et al.: The megamaser cosmology project. V. An angular-diameter distance to NGC 6264 at 140 Mpc. Astrophys. J. 767, 155 (2013)
Laureijs, R., Amiaux, J., Arduini, S., et al.: Euclid definition study report. (2011). arXiv:1110.3193
Leavitt, H.S.: 1777 variables in the Magellanic clouds. Ann. Harv. Coll. Observ. 60, 87 (1908)
Lemaître, G.: Un univers homogène de masse constant et de rayon croissant, rendant compte de la vitesse radiale des nébeleuses extra-galactiques. Ann. Soc. Sci. Brux 47, 49 (1927)
Lemaître, G.: L’Univers en expansion. Ann. Soc. Sci. Brux. 53, 51 (1933)
Lewis, G.F., Barnes, L.A., Kaushik, R.: Primordial nucleosynthesis in the R\(_{h}\) = ct cosmology: pouring cold water on the simmering Universe. MNRAS 460, 291 (2016)
Li, M., Li, N., Wang, S., Lanjun, Z.: More evidence for the redshift dependence of color from the JLA supernova sample using redshift tomography. MNRAS 460, 2586–2592 (2016)
Li, M., Li, X.-D., Wang, S., Wang, Y.: Dark energy. Commun. Theor. Phys. 56, 525 (2011)
Liao, K., Fan, X.-L., Ding, X., Biesiada, M., Zhu, Z.-H.: Precision cosmology from future lensed gravitational wave and electromagnetic signals. Nat. Commun. 8, 1148 (2017)
Lin, W., Ishak, M.: Cosmological discordances: a new measure, marginalization effects, and application to geometry versus growth current data sets. Phys. Rev. D 96, 023532 (2017)
Linder, E.V.: Exploring the expansion history of the universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 091301 (2003)
Linder, E.V., Huterer, D.: How many dark energy parameters? Phys. Rev. D 72, 043509 (2005)
Linder, E.V., Jenkins, A.: Cosmic structure growth and dark energy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 346, 573 (2003)
Lonappan, A.I., Kumar, S., Ruchika, Dinda, B.R., Sen, A.A.: Bayesian evidences for dark energy models in light of current observational data. (2017). arXiv:1707.00603
Lovelock, D.: The Einstein tensor and its generalizations. J. Math. Phys. 12, 498 (1971)
Lovelock, D.: The four-dimensionality of space and the Einstein tensor. J. Math. Phys. 13, 874 (1972)
Luković, V., Cabella, P., Vittorio, N.: Dark matter in cosmology. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 29, 1443001 (2014)
Luković, V.V., D’Agostino, R., Vittorio, N.: Is there a concordance value for H\(_{0}\)? Astron. Astrophys. 595, A109 (2016)
Maartens, R.: Is the universe homogeneous? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 369, 5115 (2011)
Malmquist, K.G.: On some relations in stellar statistics. Medd. Fran Lunds Astron. Observ. Ser. I 100, 1 (1922)
March, M.C., Trotta, R., Berkes, P., Starkman, G.D., Vaudrevange, P.M.: Improved constraints on cosmological parameters from type Ia supernova data. MNRAS 418, 2308 (2011)
Marra, V., Amendola, L., Sawicki, I., Valkenburg, W.: Cosmic variance and the measurement of the local hubble parameter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 241305 (2013)
Marriner, J., Bernstein, J.P., Kessler, R., et al.: A more general model for the intrinsic scatter in type Ia supernova distance moduli. Astrophys. J. 740, 72 (2011)
McCrea, W.H.: The cosmical constant. Q. J. R. Astron. Soc. 12, 140 (1971)
Melia, F.: On recent claims concerning the R\(_{h}\) = ct universe. MNRAS 446, 1191 (2015)
Melia, F.: The linear growth of structure in the R\(_{h}\) = ct universe. MNRAS 464, 1966 (2017)
Melia, F., Shevchuk, A.S.H.: The R\(_{h}\)=ct universe. MNRAS 419, 2579 (2012)
Milne, E.A.: Relativity, Gravitation and World-Structure. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1935)
Mitra, A.: Why the big bang model does not allow inflationary and cyclic cosmologies though mathematically one can obtain any model with favourable assumptions. New A 30, 46 (2014)
Moffat, J.W.: Inhomogeneous cosmology Redux. (2016). arXiv:1608.00534
Monelli, M., Testa, V., Bono, G., et al.: The absolute age of the globular cluster M15 using near-infrared adaptive optics images from PISCES/LBT. Astrophys. J. 812, 25 (2015)
Moreno-Raya, M.E., Mollá, M., López-Sánchez, Á.R., et al.: On the dependence of type Ia SNe luminosities on the metallicity of their host galaxies. Astrophys. J. 818, L19 (2016)
Moresco, M.: Raising the bar: new constraints on the Hubble parameter with cosmic chronometers at z \(\sim \) 2. MNRAS 450, L16 (2015)
Moresco, M., Cimatti, A., Jimenez, R., et al.: Improved constraints on the expansion rate of the universe up to z \(\sim \) 1.1 from the spectroscopic evolution of cosmic chronometers. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 8, 006 (2012)
Moresco, M., Pozzetti, L., Cimatti, A., et al.: A 6% measurement of the Hubble parameter at \(z\sim 0.45\): direct evidence of the epoch of cosmic re-acceleration. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys 2016, 014 (2016)
Mukherjee, P., Parkinson, D., Corasaniti, P.S., Liddle, A.R., Kunz, M.: Model selection as a science driver for dark energy surveys. MNRAS 369, 1725 (2006)
Nadathur, S., Sarkar, S.: Reconciling the local void with the CMB. Phys. Rev. D 83, 063506 (2011)
Nielsen, J.T., Guffanti, A., Sarkar, S.: Marginal evidence for cosmic acceleration from type Ia supernovae. Sci. Rep. 6, 35596 (2016)
Nobili, S., Goobar, A.: The colour-lightcurve shape relation of type Ia supernovae and the reddening law. Astron. Astrophys. 487, 19 (2008)
Ooba, J., Ratra, B., Sugiyama, N.: Planck 2015 constraints on the non-flat \(\phi \)CDM inflation model. (2017). arXiv:1712.08617
O’Raifeartaigh, C., O’Keeffe, M., Nahm, W., Mitton, S.: One hundred years of the cosmological constant: from ’superfluous stunt’ to dark energy. (2017). arXiv:1711.06890
Padmanabhan, T., Choudhury, T.R.: Can the clustered dark matter and the smooth dark energy arise from the same scalar field? Phys. Rev. D 66, 081301 (2002)
Park, C.-G., Ratra, B.: Using the tilted flat-\(\varLambda \)CDM and the non-flat \(\varLambda \)CDM inflation models to measure cosmological parameters from a compilation of observational data. (2018). arXiv:1801.00213
Peebles, P.J.E., Ratra, B.: Cosmology with a time variable cosmological constant. Astrophys. J. 325, L17 (1988)
Perlmutter, S., Aldering, G., Goldhaber, G., et al.: Measurements of \(\varOmega \) and \(\varLambda \) from 42 high-redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 517, 565 (1999)
Phillips, M.M.: The absolute magnitudes of type IA supernovae. Astrophys. J. 413, L105 (1993)
Planck Collaboration; Ade, P.A.R., Aghanim, N., et al.: Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 571, A16 (2014)
Planck Collaboration; Ade, P.A.R., Aghanim, N., et al.: Planck 2015 results. XXVII. The second Planck catalogue of Sunyaev-Zeldovich sources. Astron. Astrophys. 594, A27 (2016a)
Planck Collaboration; Ade, P.A.R., Aghanim, N., et al.: Planck 2015 results. XXVII. The second Planck catalogue of Sunyaev-Zeldovich sources. Astron. Astrophys. 594, A13 (2016b)
Planck Collaboration; Aghanim, N., Ashdown, M., et al.: Planck intermediate results. XLVI. Reduction of large-scale systematic effects in HFI polarization maps and estimation of the reionization optical depth. Astron. Astrophys. 596, A107 (2016c)
Pourhassan, B., Kahya, E.O.: FRW cosmology with the extended Chaplygin gas. Adv. High Energy. (2014). arXiv:1405.0667
Pskovskii, I.P.: Light curves, color curves, and expansion velocity of type I supernovae as functions of the rate of brightness decline. Sov. Ast. 21, 675 (1977)
Pun, C.S.J., Gergely, L., Mak, M.K., et al.: Viscous dissipative Chaplygin gas dominated homogenous and isotropic cosmological models. Phys. Rev. D 77, 063528 (2008)
Rani, S., Altaibayeva, A., Shahalam, M., Singh, J.K., Myrzakulov, R.: Constraints on cosmological parameters in power-law cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 3, 031 (2015)
Ratra, B., Peebles, P.J.E.: Cosmological consequences of a rolling homogeneous scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 37, 3406 (1988)
Ratsimbazafy, A.L., Loubser, S.I., Crawford, S.M., et al.: Age-dating luminous red galaxies observed with the Southern African large telescope. MNRAS 467, 3239 (2017)
Reid, M.J., Braatz, J.A., Condon, J.J., et al.: The megamaser cosmology project. I. Very long baseline interferometric observations of UGC 3789. Astrophys. J. 695, 287 (2009)
Reid, M.J., Braatz, J.A., Condon, J .J., et al.: The Megamaser cosmology project. IV. A direct measurement of the hubble constant from UGC 3789. Astrophys. J. 767, 154 (2013)
Richardson, D., Jenkins III, R.L., Wright, J., Maddox, L.: Absolute-magnitude distributions of supernovae. Astron. J. 147, 118 (2014)
Riess, A.G., Casertano, S., Yuan, W., et al.: New parallaxes of galactic Cepheids from spatially scanning the hubble space telescope: implications for the hubble constant. (2018). arXiv:1801.01120
Riess, A.G., Filippenko, A.V., Challis, P., et al.: Nine-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: cosmological parameter results. Astron. J. 116, 1009 (1998)
Riess, A.G., Li, W., Stetson, P.B., et al.: Cepheid calibrations from the hubble space telescope of the luminosity of two recent type Ia supernovae and a redetermination of the hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 627, 579 (2005)
Riess, A.G., Macri, L., Casertano, S., et al.: A 3% solution: determination of the hubble constant with the hubble space telescope and wide field camera 3. Astrophys. J. 730, 119 (2011)
Riess, A.G., Macri, L., Casertano, S., et al.: A redetermination of the hubble constant with the hubble space telescope from a differential distance ladder. Astrophys. J. 699, 539 (2009)
Riess, A .G., Macri, L .M., Hoffmann, S .L., et al.: A 2.4% determination of the local value of the hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 826, 56 (2016)
Robertson, H.P.: Kinematics and world-structure. Astrophys. J. 82, 284 (1935)
Rowan-Robinson, M.: The Cosmological Distance Ladder: Distance and Time in the Universe. W.H. Freeman, New York (1985)
Rubin, D., Aldering, G., Barbary, K., et al.: UNITY: confronting supernova cosmology’s statistical and systematic uncertainties in a unified Bayesian framework. Astrophys. J. 813, 137 (2015)
Rubin, D., Hayden, B.: Is the expansion of the universe accelerating? All signs point to yes. Astrophys. J. 833, L30 (2016)
Saha, A., Thim, F., Tammann, G.A., Reindl, B., Sandage, A.: Cepheid distances to SNe Ia host galaxies based on a revised photometric zero point of the HST WFPC2 and new PL relations and metallicity corrections. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 165, 108 (2006)
Sahni, V., Shafieloo, A., Starobinsky, A.A.: Model-independent evidence for dark energy evolution from Baryon acoustic oscillations. Astrophys. J. 793, L40 (2014)
Sandage, A., Tammann, G.A., Saha, A., et al.: The hubble constant: a summary of the hubble space telescope program for the luminosity calibration of type Ia supernovae by means of cepheids. Astrophys. J. 653, 843 (2006)
Sarkar, S.: Is the evidence for dark energy secure? Gen. Rel. Grav. 40, 269 (2008)
Savchenko, V., Ferrigno, C., Kuulkers, E., et al.: INTEGRAL detection of the first prompt gamma-ray signal coincident with the gravitational-wave event GW170817. Astrophys. J. 848, L15 (2017)
Schrödinger, E.: Über ein Lösungssystem der allgemein kovarianten. Phys. Z. 19, 20–22 (1918)
Schwarz, G., et al.: Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 6, 461 (1978)
Scolnic, D.M., Jones, D.O., Rest, A., et al.: The complete light-curve sample of spectroscopically confirmed type Ia supernovae from Pan-STARRS1 and cosmological constraints from the combined pantheon sample. (2017). arXiv:1710.00845
Shafer, D.L.: Robust model comparison disfavors power law cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 91, 103516 (2015)
Shafieloo, A.: Crossing statistic: Bayesian interpretation, model selection and resolving dark energy parametrization problem. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 5, 024 (2012)
Shariff, H., Jiao, X., Trotta, R., van Dyk, D.A.: BAHAMAS: new analysis of type Ia supernovae reveals inconsistencies with standard cosmology. Astrophys. J. 827, 1 (2016)
Sievers, J.L., Hlozek, R.A., Nolta, M.R., et al.: The Atacama cosmology telescope: cosmological parameters from three seasons of data. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 060 (2013)
Simon, J., Verde, L., Jimenez, R.: Constraints on the redshift dependence of the dark energy potential. Phys. Rev. D 71, 123001 (2005)
Sotiriou, T.P., Faraoni, V.: f(R) theories of gravity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 451 (2010)
Spergel, D.N., Bean, R., Doré, O., et al.: Three-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: implications for cosmology. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 170, 377 (2007)
Spergel, D.N., Verde, L., Peiris, H.V., et al.: First-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: determination of cosmological parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 148, 175 (2003)
Steinhardt, P .J., Wang, L.: Cosmological tracking solutions. Phys. Rev. D 59, 123504 (1999)
Stern, D., Jimenez, R., Verde, L., Stanford, S.A., Kamionkowski, M.: Cosmic chronometers: constraining the equation of state of dark energy. II. A spectroscopic catalog of red galaxiesin galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 188, 280 (2010)
Sundell, P., Mörtsell, E., Vilja, I.: Can a void mimic the \(\varLambda \) in \(\varLambda \)CDM? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 8, 037 (2015)
Suzuki, N., Rubin, D., Lidman, C., et al.: The hubble space telescope cluster supernova survey. V. Improving the dark-energy constraints above z\(>\)1 and building an early-type-hosted supernova sample. Astrophys. J. 746, 85 (2012)
Tammann, G.A., Reindl, B.: The luminosity of supernovae of type Ia from tip of the red-giant branch distances and the value of H\(_{0}\). Astron. Astrophys. 549, A136 (2013)
Terlevich, R., Melnick, J.: The dynamics and chemical composition of giant extragalactic H II regions. MNRAS 195, 839 (1981)
Tokutake, M., Ichiki, K., Yoo, C.-M.: Observational constraint on spherical inhomogeneity with CMB and local hubble parameter. (2017). arXiv:1712.04229
Tolman, R.C.: Effect of inhomogeneity on cosmological models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 20, 169 (1934)
Tripp, R.: A two-parameter luminosity correction for Type IA supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 331, 815 (1998)
Tsujikawa, S.: Quintessence: a review. Class. Quant. Gravity 30, 214003 (2013)
Tutusaus, I., Lamine, B., Blanchard, A., et al.: Power law cosmology model comparison with CMB scale information. Phys. Rev. D 94, 103511 (2016)
Tutusaus, I., Lamine, B., Dupays, A., Blanchard, A.: Is cosmic acceleration proven by local cosmological probes? Astron. Astrophys. 602, A73 (2017)
Uemura, M., Kawabata, K.S., Ikeda, S., Maeda, K.: Variable selection for modeling the absolute magnitude at maximum of type Ia supernovae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 67, 55 (2015)
Vargas, C.Z., Falciano, F.T., Reis, R.R.R.: Discrepancy in parameter constraints for LTB models using BAO and SNIa. Class. Quant. Gravity 34, 025002 (2017)
Verde, L., Protopapas, P., Jimenez, R.: Planck and the local universe: quantifying the tension. Phys. Dark Univ. 2, 166 (2013)
Walker, A.G.: On Milne’s theory of world-structure. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. s2–42, 90 (1937)
Wang, B., Han, Z.: Progenitors of type Ia supernovae. New A Rev. 56, 122 (2012)
Wang, Y., Xu, L., Zhao, G.-B.: A measurement of the hubble constant using galaxy redshift surveys. Astrophys. J. 849, 84 (2017)
Wei, H.: Observational constraints on cosmological models with the updated long gamma-ray bursts. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1008, 020 (2010)
Wen, S., Wang, S., Luo, X.: Comparing dark energy models with current observational data. (2017). arXiv:1708.03143
Wetterich, C.: Cosmology and the fate of dilatation symmetry. Nucl. Phys. B 302, 668 (1988)
Weyant, A., Wood-Vasey, W.M., Joyce, R., et al.: The first data release from SweetSpot: 74 supernovae in 36 nights on WIYN+WHIRC. (2017). arXiv:1703.02402
Whitbourn, J.R., Shanks, T.: The local hole revealed by galaxy counts and redshifts. MNRAS 437, 2146 (2014)
Willick, J.A., Batra, P.: A determination of the hubble constant from cepheid distances and a model of the local peculiar velocity field. Astrophys. J. 548, 564 (2001)
Wojtak, R., Prada, F.: Redshift remapping and cosmic acceleration in dark-matter-dominated cosmological models. MNRAS 470, 4493 (2017)
Wood-Vasey, W.M., Miknaitis, G., Stubbs, C.W., et al.: Observational constraints on the nature of dark energy: first cosmological results from the ESSENCE supernova survey. Astrophys. J. 666, 694 (2007)
Yang, W., Pan, S., Paliathanasis, A.: Latest astronomical constraints on some nonlinear parametric dark energy models. MNRAS 475(2), 2605–2613 (2018)
Zeldovich, Y.B.: Cosmological constant and elementary particles. JETP Lett. 6, 316 (1967)
Zhang, B.R., Childress, M.J., Davis, T.M., et al.: A blinded determination of H\(_{0}\) from low-redshift type Ia supernovae, calibrated by Cepheid variables. MNRAS 471, 2254 (2017)
Zhang, C., Zhang, H., Yuan, S., et al.: Four new observational H(z) data from luminous red galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky survey data release seven. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 14, 1221 (2014)
Zhang, Z.-S., Zhang, T.-J., Wang, H., Ma, C.: Testing the Copernican principle with the Hubble parameter. Phys. Rev. D 91, 063506 (2015)
Zhao, G.-B., Raveri, M., Pogosian, L., et al.: Dynamical dark energy in light of the latest observations. Nat. Astron. 1, 627 (2017)
Zhu, Z.-H., Hu, M., Alcaniz, J.S., Liu, Y.-X.: Testing power-law cosmology with galaxy clusters. Astron. Astrophys. 483, 15 (2008)
Zibin, J.P.: Scalar perturbations on Lemaître-Tolman-Bondi spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 78, 043504 (2008)
Zibin, J.P.: Can decaying modes save void models for acceleration? Phys. Rev. D 84, 123508 (2011)
Zlatev, I., Wang, L., Steinhardt, P.J.: Quintessence, cosmic coincidence, and the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 896 (1999)
Zumalacárregui, M., García-Bellido, J., Ruiz-Lapuente, P.: Tension in the void: cosmic rulers strain inhomogeneous cosmologies. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 009 (2012)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support by ASI Grant No. 2016-24-H.0. We thank Giuseppe Bono for his constructive comments and helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luković, V.V., Haridasu, B.S. & Vittorio, N. Cosmological Constraints from Low-Redshift Data. Found Phys 48, 1446–1485 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10701-018-0202-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10701-018-0202-z