Abstract
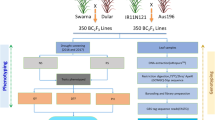
Grain weight and grain length are the most stable components of rice yield and important indicators of consumer preference. Considering the potentials of wild rice and to enhance the rice yields to meet the increasing demands, 185 Backcross Inbred Lines (BILs) in the background of O. sativa ssp. indica cv. PR114, including 63 rufi-BILs derived from O. rufipogon IRGC104433 and 122 glumae-BILs from O. glumaepatula IRGC104387 were evaluated for mapping QTLs for yield and yield component traits using Genotyping by Sequencing (GBS). Phenotypic evaluation of BILs in three seasons spanning two locations revealed significant differences compared with recurrent parent. BILs which did not show significant differences for any trait under investigation, or similar based on pedigree, were excluded from GBS. Some glumae-BILs had to be excluded from mapping QTLs due to less sequence information. A custom designed approach for GBS data analysis identified 3322 informative SNPs in 55 rufi-BILs and 3437 informative SNPs in 79 glumae-BILs. QTL mapping identified one QTL for thousand grain weight (qtgw5.1), two for grain width (qgw5.1, qgw5.2) and one for grain length (qgl7.1) in rufi-BILs. In the glumae-BILs, three QTL for thousand grain weight (qtgw2.1, qtgw3.1, qtgw6.1) and two for grain length (qgl3.1, qgl7.1) were identified. Most of the grain weight and width QTL showed positive additive effect contributed by wild species allele, whereas the grain length QTL showed positive additive effect contributed by recurrent parent allele. Based on their physical position, none of the QTLs were found similar to previously cloned QTLs. QTLs for grain traits identified from low yielding wild relatives of rice reveals their significance in improving further the rice yields and widen the genetic base of cultivated rice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatia D, Wing RA, Singh K (2013) Genotyping by sequencing, its implications and benefits. Crop improv 40:101–111
Bhatia D, Joshi S, Das A, Vikal Y, Sahi GK, Neelam K, Kaur K, Singh K (2017) Introgression of yield component traits in rice (Oryza sativa ssp indica) through interspecific hybridization. Crop Sci 57:1–17
Brar D, Singh K (2011) Oryza. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomics and breeding resources: cereals. Springer, Berlin, pp 321–365
Brondani C, Rangel P, Brondani R, Ferreira M (2002) QTL mapping and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1192–1203
Buso GSC, Rangel PH, Ferreira ME (1998) Analysis of genetic variability of South American wild rice populations (Oryza glumaepatula) with isozymes and RAPD markers. Mol Ecol 7:107–117
Chauhan JS (1998) Inheritance of grain weight, size and shape in rainfed rice (Oryza sativa). Indian J Agric Sci 68(1), http://epubs.icar.org.in/ejournal/index.php/IJAgS/article/view/27174
Cheema K, Bains N, Mangat G, Das A, Brar D, Khush G, Singh K (2008) Introgression of quantitative trait loci for improved productivity from Oryza rufipogon into O. sativa. Euphytica 160:401–409
Davey JW, Hohenlohe PA, Etter PD, Boone JQ, Catchen JM, Blaxter ML (2011) Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 12:499–510
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1995) An introgression line population of Lycopersicon pennellii in the cultivated tomato enables the identification and fine mapping of yield-associated QTL. Genetics 141:1147–1162
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Fukuoka S, Nonoue Y, Yano M (2010) Germplasm enhancement by developing advanced plant materials from diverse rice accessions. Breed Sci 60:509–517
Gao Z-Y, Zhao S-C, He W-M, Guo L-B, Peng Y-L, Wang J-J, Guo X-S, Zhang X-M, Rao Y-C, Zhang C (2013) Dissecting yield-associated loci in super hybrid rice by resequencing recombinant inbred lines and improving parental genome sequences. Proc Nat Acad Sci 110:14492–14497
Harlan JR (1992) Crops and man, 2nd edition, Madison. Am Soc Agron, WI
Huang R, Jiang L, Zheng J, Wang T, Wang H, Huang Y, Hong Z (2013) Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci 18:218–226
Imai I, Kimball JA, Conway B, Yeater KM, McCouch SR, McClung A (2013) Validation of yield-enhancing quantitative trait loci from a low-yielding wild ancestor of rice. Mol Breed 32:101–120
Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, B-i Shimizu, Onishi A (2013) Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet 45:707–711
Jacquemin J, Bhatia D, Singh K, Wing RA (2013) The International Oryza Map Alignment Project: development of a genus-wide comparative genomics platform to help solve the 9 billion-people question. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:147–156
Jeuken MJW, Lindhout P (2004) The development of lettuce backcross inbred lines (BILs) for exploitation of the Lactuca saligna (wild lettuce) germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 109:394–401
Jin F-X, Kim D-M, Ju H-G, Ahn S-N (2009) Mapping quantitative trait loci for awnness and yield component traits in isogenic lines derived from an Oryza sativa/O. rufipogon cross. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 12:9–15
Khush GS (2013) Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: case of rice as an example. Plant Breed 132:433–436
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Li J, Thomson M, McCouch SR (2004) Fine mapping of a grain-weight quantitative trait locus in the pericentromeric region of rice chromosome 3. Genetics 168:2187–2195
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079
Li Y, Fan C, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1266–1269
McCouch SR, Sweeney M, Li J, Jiang H, Thomson M, Septiningsih E, Edwards J, Moncada P, Xiao J, Garris A (2007) Through the genetic bottleneck: O. rufipogon as a source of trait-enhancing alleles for O. sativa. Euphytica 154:317–339
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2015) QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3:269–283
Moncada P, Martinez CP, Borrero J, Châtel M, Jr Gauch H, Guimaraes E, Tohme J, McCouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa x Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Poland JA, Rife TW (2012) Genotyping-by-sequencing for plant breeding and genetics. Plant Genome 5:92–102
Poland JA, Brown PJ, Sorrells ME, Jannink J-L (2012) Development of high-density genetic maps for barley and wheat using a novel two-enzyme genotyping-by-sequencing approach. PLoS ONE 7:e32253
Qiu X, Gong R, Tan Y, Yu S (2012) Mapping and characterization of the major quantitative trait locus qSS7 associated with increased length and decreased width of rice seeds. Theor Appl Genet 125:1717–1726
Rosyara UR, Gonzalez-Hernandez JL, Glover KD, Gedye KR, Stein JM (2009) Family-based mapping of quantitative trait loci in plant breeding populations with resistance to Fusarium head blight in wheat as an illustration. Theor Appl Genet 118:1617–1631
Septiningsih EM, Prasetiyono J, Lubis E, Tai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M (2008) Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet 40:1023–1028
Song X-J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M-Z, Lin H-X (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Spindel J, Wright M, Chen C, Cobb J, Gage J, Harrington S, Lorieux M, Ahmadi N, McCouch S (2013) Bridging the genotyping gap: using genotyping by sequencing (GBS) to add high-density SNP markers and new value to traditional bi-parental mapping and breeding populations. Theor Appl Genet 126:2699–2716
Tan L, Liu F, Xue W, Wang G, Ye S, Zhu Z, Fu Y, Wang X, Sun C (2007) Development of Oryza rufipogon and O. sativa introgression lines and assessment for yield related quantitative trait loci. J Integr Plant Biol 49:871–884
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Thomson MJ, Zhao K, Wright M, McNally KL, Rey J, Tung C-W, Reynolds A, Scheffler B, Eizenga G, McClung A (2012) High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping for breeding applications in rice using the BeadXpress platform. Mol Breed 29:875–886
Vaughan DA, Morishima H, Kadowaki K (2003) Diversity in the Oryza genus. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:139–146
Wickneswari R, Bhuiyan MAR, Lim LS, Thomson MJ, Narimah MK, Abdullah MZ (2012) Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for agronomic traits in advanced backcross breeding lines derived from Oryza rufipogon x Oryza sativa cultivar MR219. Plant Mol Biol Report 30:929–939
Xiao J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD, JiMing L, LongPing Y (1996) Genes from wild rice improve yield. Nat (Lond) 384:223–224
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Xie X, Song M-H, Jin F, Ahn S-N, Suh J-P, Hwang H-G, McCouch SR (2006) Fine mapping of a grain weight quantitative trait locus on rice chromosome 8 using near-isogenic lines derived from a cross between Oryza sativa and Oryza rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 113:885–894
Xie X, Jin F, Song M-H, Suh J-P, Hwang H-G, Kim Y-G, McCouch SR, Ahn S-N (2008) Fine mapping of a yield-enhancing QTL cluster associated with transgressive variation in an Oryza sativa x O. rufipogon cross. Theor Appl Genet 116:613–622
Zhao Q, Huang X, Lin Z, Han B (2010) SEG-Map: A novel software for genotype calling and genetic map construction from next-generation sequencing. Rice 3:98–102
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Monsanto Beachell Borlaug International Scholarship Programme (MBBISP) to DB, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DB, KS, RAW, AR designed and conducted the study, DB did field evaluation; DB, YY, DK prepared GBS library; SL, YY sequenced the GBS library; DB, KC analysed GBS data; DB did QTL mapping; DB, KS, RAW wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10681_2018_2119_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 619 kb). Fig. S1. Custom designed GBS data analysis workflow used for SNP identification and mapping of target traits in both rufi-BILs and glumae-BILs
10681_2018_2119_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2 (TIFF 362 kb). Fig. S2. Graphical plots of phenotypic variation in DF, PH, PS and PY in BILs. Plotted values are the adjusted means of square lattice design. SI, SII, SIII represent three different seasons. Arrow indicates where the recurrent parent PR114 falls
10681_2018_2119_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 3 (TIFF 1045 kb). Fig. S3. Graphical representation of read alignment statistics of (a) rufi-BILs; (b) glumae-BILs aligned to PR114 fake pseudomolecule
10681_2018_2119_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 4 (TIFF 2839 kb). Fig. S4. Distribution of (a) 3322 informative SNPs of rufi-BILs and (b) 3437 informative SNPs of glumae-BILs on twelve chromosomes of rice based on their physical distance. Red lines in the bars indicate the SNP
10681_2018_2119_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 5 (TIFF 6245 kb). Fig. S5. Graphical genotypes of (a) rufi-BILs based on 3322 informative SNPs (b) glumae-BILs based on 3437 informative markers. Red colour indicates the recurrent parent, purple colour indicates the introgressions from donor parent and white colour indicates missing data points
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, D., Wing, R.A., Yu, Y. et al. Genotyping by sequencing of rice interspecific backcross inbred lines identifies QTLs for grain weight and grain length. Euphytica 214, 41 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2119-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2119-1