Abstract
Carbon dioxide emissions have been the primary source of extreme environmental pollution and have detrimental consequences on human life, irrespective of an economy being developed or underdeveloped. For the developing economies, in particular, it is imperative to reduce such emissions in order to sustain the growth of the respective economies. However, for designing appropriate emission reduction policies, it is appropriate to identify the sectors which contribute the most to carbon dioxide emissions and dampen the growth of overall economy. Against this background, the key intention of this study was to examine the influence of carbon dioxide emissions generated from various sources on the economic progress in Pakistan between 1971 and 2017. This study is important for Pakistan to sustain its economic progress and enable the nation to comply with commitments of the Paris Agreement and Sustainable Development Goals. The econometric analysis conducted in this study considers a nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model which is applied to ascertain the short- and long-run economic growth impacts associated with positive and negative shocks to CO2 emissions generated from various sources. The choice of this model is driven by its capacity to perform an asymmetric analysis which is relevant for suitable policy-making purposes. The overall results, in a nutshell, reveal that carbon dioxide emissions from Pakistan’s transportation sector influence the country’s economic progress. Positive shocks to such carbon dioxide emissions are originate to reduce economic progress in the long run while negative shocks are evidenced to boost economic growth both in the short and long run. In contrast, carbon dioxide emissions from other major sectors are found to be ineffective in influencing Pakistan's economic growth both in the short and long run. Hence, keeping into consideration the prospects of attaining sustainable economic growth, the Pakistan government must prioritize the implementation of CO2 emissions-inhibiting policies within the transportation sector. Simultaneously, the traditional fossil fuel dependency within this sector should also be phased out.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
BRICS refers to Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
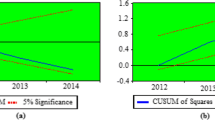
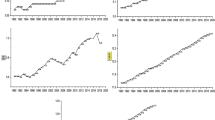
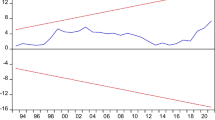
For brevity, the ARDL outputs are not reported but can be made available upon request.
References
Abbasi, K. R., Shahbaz, M., Jiao, Z., & Tufail, M. (2021). How energy consumption, industrial growth, urbanization, and CO2 emissions affect economic growth in Pakistan? A novel dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Energy, 221, 119793
Ahmad, M., Zhao, Z. Y., Irfan, M., Mukeshimana, M. C., Rehman, A., Jabeen, G., & Li, H. (2020). Modeling heterogeneous dynamic interactions among energy investment, SO 2 emissions and economic performance in regional China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(3), 2730–2744
Ahmad, M., Li, H., Anser, M. K., Rehman, A., Fareed, Z., Yan, Q., & Jabeen, G. (2020). Are the intensity of energy use, land agglomeration, CO2 emissions, and economic progress dynamically interlinked across development levels? Energy & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X20949471
Ahmad, M., Chandio, A. A., Solangi, Y. A., Shah, S. A. A., Shahzad, F., Rehman, A., & Jabeen, G. (2021). Dynamic interactive links among sustainable energy investment, air pollution, and sustainable development in regional China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(2), 1502–1518
Alam, M. M., Murad, M. W., Noman, A. H. M., & Ozturk, I. (2016). Relationships among carbon emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and population growth: Testing environmental kuznets Curve hypothesis for Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. Ecological Indicators, 70, 466–479
Alvarado, R., Ponce, P., Criollo, A., Córdova, K., & Khan, M. K. (2018). Environmental degradation and real per capita output: new evidence at the global level grouping countries by income levels. Journal of Cleaner Production, 189, 13–20
Antwi-Agyei, P., Dougill, A. J., Agyekum, T. P., & Stringer, L. C. (2018). Alignment between nationally determined contributions and the sustainable development goals for West Africa. Climate Policy, 18(10), 1296–1312
Attari, M. I. J., Hussain, M., & Javid, A. Y. (2016). Carbon emissions and industrial growth: an ARDL analysis for Pakistan. International Journal of Energy Sector Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJESM-04-2014-0002
Bakhsh, K., Rose, S., Ali, M. F., Ahmad, N., & Shahbaz, M. (2017). Economic growth, CO2 emissions, renewable waste and FDI relation in Pakistan: New evidences from 3SLS. Journal of Environmental Management, 196, 627–632
Baloch, M. A. (2018). Dynamic linkages between road transport energy consumption, economic growth, and environmental quality: evidence from Pakistan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(8), 7541–7552
Bayer, C., & Hanck, C. (2013). Combining non-cointegration tests. Journal of Time series analysis, 34(1), 83–95
Boamah, K. B., Du, J., Bediako, I. A., Boamah, A. J., Abdul-Rasheed, A. A., & Owusu, S. M. (2017). Carbon dioxide emission and economic growth of China—the role of international trade. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(14), 13049–13067
Boontome, P., Therdyothin, A., & Chontanawat, J. (2017). Investigating the causal relationship between non-renewable and renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Thailand. Energy Procedia, 138, 925–930
Chishti, M. Z., Ahmad, M., Rehman, A., & Khan, M. K. (2021). Mitigations pathways towards sustainable development: Assessing the influence of fiscal and monetary policies on carbon emissions in BRICS economies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 292, 126035
Clémençon, R. (2016). The two sides of the paris climate agreement: Dismal failure or historic breakthrough? Journal of Environment & Development, 25(1), 3–24
Davis, S. J., Caldeira, K., & Matthews, H. D. (2010). Future CO2 emissions and climate change from existing energy infrastructure. Science, 329(5997), 1330–1333
Deviren, S. A., & Deviren, B. (2016). The relationship between carbon dioxide emission and economic growth: Hierarchical structure methods. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 451, 429–439
Dickey, D. A., & Fuller, W. A. (1979). Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 74(366a), 427–431
Distefano, T., & Kelly, S. (2017). Are we in deep water? Water scarcity and its limits to economic growth. Ecological Economics, 142, 130–147
Dogaru, L. (2013). The importance of environmental protection and sustainable development. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 93, 1344–1348
Ehigiamusoe, K. U., & Lean, H. H. (2019). Effects of energy consumption, economic growth, and financial development on carbon emissions: evidence from heterogeneous income groups. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(22), 22611–22624
Fankhauser, S., & Tol, R. S. (2005). On climate change and economic growth. Resource and Energy Economics, 27(1), 1–17
Franco, I. B., & Newey, L. (2020). SDG 12 Responsible Consumption and Production. In Isabel B. Franco, Tathagata Chatterji, Ellen Derbyshire, & James Tracey (Eds.), Actioning the Global Goals for Local Impact. (pp. 187–217). Singapore: Springer.
Gao, J., & Zhang, L. (2021). Does biomass energy consumption mitigate CO2 emissions? The role of economic growth and urbanization: evidence from developing Asia. Journal of the Asia Pacific Economy, 26(1), 96–115
Govindaraju, V. C., & Tang, C. F. (2013). The dynamic links between CO2 emissions, economic growth and coal consumption in China and India. Applied Energy, 104, 310–318
Hanif, I. (2018). Impact of economic growth, nonrenewable and renewable energy consumption, and urbanization on carbon emissions in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(15), 15057–15067
Hwang, J. H., & Yoo, S. H. (2014). Energy consumption, CO 2 emissions, and economic growth: evidence from Indonesia. Quality & Quantity, 48(1), 63–73
IEA (2020) CO2 Emissions from fossil fuel combustion: 2020 Edition. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/adc8aaad-432b-443c-8f28-90977789a8c4/WORLDCO2_Documentation.pdf
IPCC. (2014). Climate change 2013: the physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the Fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
IQAir (2019) 2019 World Air Quality Report: Region & City PM2.5 Ranking. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/blog/report-over-90-percent-of-global-population-breathes-dangerously-polluted-air
Johansen, S. (1988). Statistical analysis of cointegration vectors’. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 12(2–3), 231–254
Kahia, M., Jebli, M. B., & Belloumi, M. (2019). Analysis of the impact of renewable energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in 12 MENA countries. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 21(4), 871–885
Karimi, V., Karami, E., & Keshavarz, M. (2018). Climate change and agriculture: Impacts and adaptive responses in Iran. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 17(1), 1–15
Khan, S. A. R. (2019). The nexus between carbon emissions, poverty, economic growth, and logistics operations-empirical evidence from southeast Asian countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(13), 13210–13220
Khan, M. K., Teng, J. Z., Khan, M. I., & Khan, M. O. (2019). Impact of globalization, economic factors and energy consumption on CO2 emissions in Pakistan. Science of the total environment, 688, 424–436
Khan, M. K., Teng, J. Z., & Khan, M. I. (2019). Effect of energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan with dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(23), 23480–23490
Khan, M. I., Teng, J. Z., & Khan, M. K. (2020). The impact of macroeconomic and financial development on carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan: evidence with a novel dynamic simulated ARDL approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(31), 39560–39571
Khan, S., Khan, M. K., & Muhammad, B. (2020). Impact of financial development and energy consumption on environmental degradation in 184 countries using a dynamic panel model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11239-4
Khan, M. K., Khan, M. I., & Rehan, M. (2020). The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan. Financial Innovation, 6(1), 1–13
Kompas, T., Pham, V. H., & Che, T. N. (2018). The effects of climate change on GDP by country and the global economic gains from complying with the Paris climate accord. Earth’s Future, 6(8), 1153–1173
Lee, J., & Strazicich, M. C. (2013). Minimum LM unit root test with one structural break. Economic Bulletin, 33(4), 2483–2492
Li, H., Li, B., & Lu, H. (2017). Carbon dioxide emissions, economic growth, and selected types of fossil energy consumption in China: empirical evidence from 1965 to 2015. Sustainability, 9(5), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050697
Li, L., Hong, X., & Peng, K. (2019). A spatial panel analysis of carbon emissions, economic growth and high-technology industry in China. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 49, 83–92
Li, K., Hu, E., Xu, C., Musah, M., Kong, Y., Mensah, I. A., Zu, J., Jiang, W., & Su, Y. (2020). A heterogeneous analysis of the nexus between energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from the group of twenty (G20) countries. Energy Exploration & Exploitation. https://doi.org/10.1177/0144598720980198
Li, Z. Z., Li, R. Y. M., Malik, M. Y., Murshed, M., Khan, Z., & Umar, M. (2021). Determinants of carbon emission in China: How good is green investment? Sustainable Production and Consumption, 27, 392–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.11.008
Liu, J., Murshed, M., Chen, F., Shahbaz, M., Kirikkaleli, D., & Khan, Z. (2021). An empirical analysis of the household consumption-induced carbon emissions in China. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 26, 943–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.01.006
Lotfalipour, M. R., Falahi, M. A., & Ashena, M. (2010). Economic growth, CO2 emissions, and fossil fuels consumption in Iran. Energy, 35(12), 5115–5120
Marques, A. C., Fuinhas, J. A., & Leal, P. A. (2018). The impact of economic growth on CO 2 emissions in Australia: The environmental Kuznets curve and the decoupling index. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(27), 27283–27296
Mikayilov, J. I., Galeotti, M., & Hasanov, F. J. (2018). The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan. Journal of Cleaner Production, 197, 1558–1572
Mirza, F. M., & Kanwal, A. (2017). Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Pakistan: Dynamic causality analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 1233–1240
Muhammad, B., Khan, M. K., Khan, M. I., & Khan, S. (2020). Impact of foreign direct investment, natural resources, renewable energy consumption, and economic growth on environmental degradation: evidence from BRICS, developing, developed and global countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12084-1
Murshed, M. (2020). An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3
Murshed, M. (2021). Can regional trade integration facilitate renewable energy transition to ensure energy sustainability in South Asia? Energy Reports, 7, 808–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.01.038
Murshed, M., & Dao, N. T. T. (2020). Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: The role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9
Murshed, M., Ali, S. R., & Banerjee, S. (2020). Consumption of liquefied petroleum gas and the EKC hypothesis in South Asia: Evidence from cross-sectionally dependent heterogeneous panel data with structural breaks. Energy, Ecology and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-020-00185-z
Nathaniel, S. P., Murshed, M., & Bassim, M. (2021). The nexus between economic growth, energy use, international trade and ecological footprints: the role of environmental regulations in N11 countries. Energy, Ecology & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-020-00205-y
Ozcan, B. (2013). The nexus between carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Middle East countries: A panel data analysis. Energy Policy, 62, 1138–1147
Pesaran, M. H., Shin, Y., & Smith, R. J. (2001). Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 16(3), 289–326
Phillips, P. C., & Perron, P. (1988). Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika, 75(2), 335–346
Rafindadi, A. A. (2016). Does the need for economic growth influence energy consumption and CO2 emissions in Nigeria? Evidence from the innovation accounting test. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 62, 1209–1225
Rehman, E., Ikram, M., Feng, M. T., & Rehman, S. (2020). Sectoral-based CO 2 emissions of Pakistan: A novel grey relation analysis (GRA) approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 29118–29129
Rehman, A., Ma, H., Ahmad, M., Ozturk, I., & Chishti, M. Z. (2021). How do climatic change, cereal crops and livestock production interact with carbon emissions? Updated evidence from China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12948-0
Shahbaz, M., Khan, S., Ali, A., & Bhattacharya, M. (2017). The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. The Singapore Economic Review, 62(04), 929–957
Shin, Y., Yu, B., & Greenwood-Nimmo, M. (2014). Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. In Robin C. Sickles & William C. Horrace (Eds.), Festschrift in honor of Peter Schmidt. (pp. 281–314). New York, NY: Springer.
Sinha, A., Sengupta, T., & Saha, T. (2020). Technology policy and environmental quality at crossroads: Designing SDG policies for select Asia Pacific countries. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 161, 120317
Sulaiman, C., & Abdul-Rahim, A. S. (2018). Population growth and CO2 emission in Nigeria: A recursive ARDL approach. SAGE Open, 8(2), 2158244018765916
Teng, J. Z., Khan, M. K., Khan, M. I., Chishti, M. Z., & Khan, M. O. (2020). Effect of foreign direct investment on CO 2 emission with the role of globalization, institutional quality with pooled mean group panel ARDL. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 1–12
Toman M (2003) The roles of the environment and natural resources in economic growth analysis (No. 1318–2016–103153).
Uddin, M. G. S., Bidisha, S. H., & Ozturk, I. (2016). Carbon emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth relationship in Sri Lanka. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy, 11(3), 282–287
Vo, D. H., & Le, Q. T. T. (2019). CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth: New evidence in the ASEAN countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 12(3), 145
Watson, R., McCarthy, H., Canziani, P., Nakicenovic, N., & Hisas, L. (2019). The truth behind the climate pledges. The Universal Ecological Fund (Fundación Ecológica Universal FEU-US). Retrieved from https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nFx8UKTyjEteYO87-x06mVEkTs6RSPBi/view
World Bank (2020) World Development Indicators. The World Bank. Retrieved from https://data.worldbank.org/country/PK
Xue, L., Haseeb, M., Mahmood, H., Alkhateeb, T. T. Y., & Murshed, M. (2021). Renewable energy use and ecological footprints mitigation: evidence from selected South Asian economies. Sustainability, 13(4), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041613
Zhang, L., Godil, D. I., Bibi, M., Khan, M. K., Sarwat, S., & Anser, M. K. (2021). Caring for the environment: How human capital, natural resources, and economic growth interact with environmental degradation in Pakistan? A dynamic ARDL approach. Science of The Total Environment, 774, 145553
Funding
This research didn’t receive any financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, A., Ma, H., Ozturk, I. et al. The dynamic impacts of CO2 emissions from different sources on Pakistan’s economic progress: a roadmap to sustainable development. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 17857–17880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01418-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01418-9