Abstract
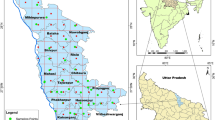
The occurrence of arsenic in drinking water and its detrimental effects have drawn much attention in recent years. Several studies have been conducted in the deltaic plains of River Ganga, NE part of the India, and in other countries, but no systematic study was conducted in South India on occurrence of arsenic in groundwater. The main aim of this study is to determine the level of arsenic in groundwater and to understand the relation with other geochemical parameters of groundwater in the south-eastern coastal aquifer at Kalpakkam region, India. This region is represented by three different lithologies, viz. charnockites, flood plain alluvium and marine alluvium. Twenty-nine representative samples of groundwater were collected and analysed for major ions, metals and isotopes such as 2H and 18O. In addition, geophysical method was also attempted to understand the subsurface condition. The spatial variation in arsenic (As) indicates that higher concentration was observed around the landfill sites and irrigated regions, which was supported by geochemical, statistical and isotopic inferences. The variation in the As with depth, lithology and sources has been clearly brought out. Though the values of As does not exceed the drinking water permissible limit (10 mg/l), it has reached a near permissible level of 8.7 ppb. Hence, it is essential to understand the geochemical behaviour of As for a proper future management of the water resource in the study area.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya, S. K., Chatraborty, P., Lahiri, S., Raymahashay, B. C., Guha, S., & Bhowmik, A. (1999). Arsenic poisoning in the Ganges delta. Nature, 401, 545–546.
Aggarwal, P. K., Basu, A. R., Poreda, R. J., Kulkarni, K. M., Froehlich, K., Tarafdar, S. A., Ali, M., Ahmed, N., Hussian, A., Rahman, M., & Ahmed, S. R. (2000). A report on isotope hydrology of groundwater in Bangladesh: implications for characterization and mitigation of arsenic in groundwater. IAEA: TC Project(BGD/8/016), IAEA, Vienna, 61.
Akan, J. C., Abdulrahman, F. I., Sopido, O. A., & Akandu, P. I. (2009). Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals of six fresh water fishes caught from lake Chad in Doron Buhari, Maiduguri, Borno State, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Sanitation, 4(2), 103–114.
Allison, G. B., Barnes, C. J., Hughes, M. W., Leaney, F. W. J. (1984). Effect of climate and vegetation on oxygen-18 and deuterium profiles in soils. In Isotope Hydrology 1983, IAEA Symposium 270, September 1983, Vienna, (pp. 105–123).
Anshumali & Tripathi, P. (2012). Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the middle Gangetic Plain, India BALWOIS 2012 - Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia - 28 May, 2 June 2012.
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (19th ed.). Washington DC: APHA.
Asadi, A., Huat, B. B. K., Moayedi, H., Shariatmadari, N., & Parsaie, A. (2011). Changes of hydraulic conductivity of silty clayey sand soil under the effects of municipal solid waste leachate. International Journal of the Physical Sciences, 6(12), 2869–2874.
Asaduzzaman, M., Hasanuzzaman, M., Hasan, M. A., & Sultana, S. (2009). Seed germination and seedling growth of some rice varieties under different concentration of added arsenic. International Journal of Sustainable Agriculture Technology, 5, 6–11.
Bagla, P., & Kaiser, J. (1996). India’s spreading health crisis draws global arsenic experts. Science, 274, 174.
Berner, R. A. (1981). A new geochemical classification of sedimentary environments. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 51, 359–365.
BGS, DPHE (2001) Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh (four volumes). British Geological Survey, (www.bgs.ac.uk/Arsenic/Bangladesh).
Bhattacharya, P. (2002). Arsenic contaminated groundwater from the sedimentary aquifers of South-East Asia. In E. Bocanegra , D. Martinez & H. Massone (Eds.), Groundwater and Human Development, Proceedings of the XXXII IAH and VI ALHSUD Congress, (pp. 357–363) Mar del Plata, Argentina, October 21–25, 2002.
Bhattacharya, P., Welch, A. H., Ahmed, K. M., Jacks, G., & Naidu, R. (2004). Arsenic in groundwater of sedimentary aquifers. Applied Geochemistry, 19(2), 163–167.
Bhuiyan, M. A. H., Suruvi, N. I., Dampare, S. B., Islam, M. A., Quraishi, S. B., Ganyaglo, S., & Suzuki, S. (2011). Investigation of the possible sources of heavy metal contamination in lagoon and canal water in the tannery industrial area in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 175(1–4), 633–649.
BIS. (2009). Indian standard drinking water specification ICS 13, 060, 20 Bureau of Indian Standards.
Biswas, B. K., Dhar, R. K., Samanta, G., Mandal, B. K., Chakraborti, D., Faruk, I., et al. (1998). Detailed study report of Samta, one of the arsenic affected villages of Jessore District Bangladesh. Current Science, 74(2), 134–145.
Bhuyan, B. (2010). A study on arsenic and iron contamination of groundwater in three development blocks of Lakhimpur district, Assam, India Report and Opinion 2(6). http://www.sciencepub.net/report.
British Geological Survey. (1999). Groundwater Studies for Arsenic Contamination in Bangladesh. Final Report. London: UK British Geological Survey, Mott MacDonald Ltd., UK.
Buragohaina, M., & Sarma, H. P. (2012). A study on spatial distribution of arsenic in ground Water samples of Dhemaji district of Assam, India by using arc view GIS software. Scientific Reviews and Chemical Communication, 2(1), 7–11.
Chakraborti, D., Biswas, B. K., Chowdhury, T. R., Basu, G. K., Mandal, B. K., Chowdhury, U. K., et al. (1999). Arsenic groundwater contamination and sufferings of people in Rajnandgaon district, Madhya Pradesh India. Current Science, 77, 502–504.
Chakraborti, D., Basu, G. K., Biswas, B. K., Chowdhury, U. K., Rahman, M. M., Paul, K., et al. (2001). Characterization ofarsenic-bearing sediments in the Gangetic delta of West Bengal, India. In W. R. Chappell, C. O. Abernathy, & R. A. Calderon (Eds.), Arsenic exposure and health effects IV (pp. 27–52). Philadelphia: Elsevier Science Ltd.
Chakraborti, D., Mukherjee, S. C., Pati, S., Sengupta, S. K., Rahman, M. M., Chowdhury, U. K., et al. (2003). Arsenic groundwater contamination in Middle Ganga Plain, Bihar, India A Future Danger. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111, 1194–1201.
Chakraborti, D., et al. (2004). Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in the Ganga– Meghna-Brahmaputra plain. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 6, 74N–83N.
Chen, W. L., Sheng-Wei, W., Cheng-Shin, J., & Kao-Hong, L. (2006). Occurrence of arsenic in ground water in the Choushui River alluvial fan, Taiwan. Technical Reports: Heavy metals in the environment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 68–75. doi:10.2134/jeq2005.0129.
Chidambaram, S. (2000). Hydrogeochemical studies of groundwater in Periyar district, Tamilnadu, India. Unpublished Ph.D thesis, Department of Geology, Annamalai University, India.
Chidambaram, S., Karmegam, U., Prasanna, M. V., & Sasidhar, P. (2012). A study on evaluation of probable sources of heavy metal pollution in groundwater of Kalpakkam region, South India. The Environmentalist, 32, 371–382.
Chidambaram, S., Karmegam, U., Prasanna, M. V., Sasidhar, P., & Vasanthavigar, M. (2011). A study on hydrochemical elucidation of coastal groundwater in and around Kalpakkam region, Southern India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64, 1419–1431, ISSN 1866-6280.
Chidambaram, S., Prasanna, M. V., Ramanathan, A. L., Vasu, K., Hameed, S., Warrier, U. K., et al. (2009). A study on the factors affecting the stable isotopic composition in precipitation of Tamil Nadu, India. Hydrological Process, 23(12), 1792–1800.
Chormann, F. H. Jr. (1985). Masters Thesis, Department of Earth Sciences, University of New Hampshire, Durham.
Chouhan, S., & Flora, S. J. S. (2010). Arsenic and fluoride: Two major ground water pollutants. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 48, 666–678.
Chowdhury, U. K., Biswas, B. K., Chowdhury, T. R., Samanta, G., Andal, B. K., Basu, G. C., et al. (2003). Groundwater Arsenic contamination in Bangladesh and West Bengal India. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1081(51), 393.
Chowdhury, T. R., Uchino, T., Tokunaga, H., & Ando, M. (2002). Arsenic and other heavy metals in soils from arsenic-affected area of West Bengal, India. Chemosphere, 49, 605–618.
Cornell, R. M., & Schwertmann, U. (1996). The iron oxides: Structure, properties, reactions, occurrence and uses (p. 570). Weinheim: VCH.
Craig, H. (1961). Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science, 133, 1702–1703.
D’Angelo, D., Norton, S. A., & Loiselle, M. C. (1996). Historical uses and fate of arsenic in Maine: Water Research Institute Completion Report.
Das, D., Chatterjee, A., Samanta, G., Mandal, B., Chowdhury, R. T., Samanta, G., et al. (1994). Arsenic contamination in groundwater in six districts of West Bengal, India: The biggest arsenic calamity in the world. Analyst, 119, 168N–175N.
Davenport, J. R., & Peryea, F. (1991). Phosphate fertilizer influence leaching f lead and arsenic in a soil contaminated with lead and arsenic in a soil contaminated with lead arsenated. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 57–58, 101–110.
Deutsch, W. J. (1997). Groundwater geochemistry: Fundamentals and applications to contamination (p. 221). Boca Raton: Lewis Publ.
Devi, N. L., Chandra, V., & Shihua, Q. (2009). Recent Status of Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater of Northeastern India—A Review Report and Opinion, 1(3), 2009. http://www.sciencepub.net.
Dhār, R. K., Biswas, B. K., Samanta, G., Mandal, B. K., Chakraborti, D., Roy, S., et al. (1997). Groundwater arsenic calamity in Bangladesh. Current Science, 73(1), 48–59.
Diaz, R. V., Aldape, J., & Flores, M. (2002). Identification of airborne particulate sources of samples collected in Ticoma´n, Mexico, using PIXE. Nuclear Instruments Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions Materials and Atoms, 189, 249–253.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, W. (1998). Physical and chemical hydrogeology (2nd ed., p. 506). New York: Wiley.
Dubey, C. S., Mishra, B. K., Shukla, D. P., Singh, R. P., Tajbaksh, M., & Sakhare, P. (2012). Anthropogenic arsenic menace in Delhi Yamuna flood pains. Environmental Earth Sciences, 65, 131–139.
Edet, A. E., & Offiong, O. E. (2002). Trace element hydrochemical assessment of the Calabar Coastal Plain Aquifer, southeastern Nigeria using statistical methods. Environmental Geology, 44, 137–149.
Goodbred ,S. L. Jr., & Kuehl, S. A. (2000). The significance of large sediment supply, active tectonism, and eustasy on margin sequence development: Late quaternary stratigraphy and evolution of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. Sedimentary Geology, 133, 227–248.
Goswami, A. M., Nath, B., Jana, J., Jyothi, S. S., Sarkar, M. J., Jacks, G., et al. (2008). Hydrochemical behaviour of arsenic enriched Groundwater in the Deltaic Environment: Comparison between two study sites in West Bengal. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 99, 22–30.
GuhaMazumder, D. N., Haque, R., Ghosh, N., De, B. K., Santra, A., Chakraborti, D., & Smith, A. H. (1988). Arsenic levels in drinking water and prevalence of skin lesions in West Bengal- India. International Journal of Epidemiology, 27, 871–877.
Gurumoorthy, C., Sasidhar, P., Arumugham, V., & Mathur, R. K. (1994). Sub-surface investigations on deep saline groundwater of Charnockite rock formation, Kalpakkam, India. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 91(1–3), 211–222.
Hem, J. D. (1989). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 2254; 1985.
Hoque, M. A., McArthur, J. M., & Sikdar, P. K. (2012). The palaeosol model of arsenic pollution of groundwater tested along a 32 km traverse across West Bengal. India Science of the Total Environment, 431, 157–165.
Kanchan, R., & Ghosh, T. (2009). Arsenic contaminated groundwater: Human health catastrophe in Nadia District Asia Pacific. Journal of Social sciences, I (2), 123–143.
Kanchan, R., & Roy, M. (2011). Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Groundwater Arsenic Concentration in Thick Unconfined Aquifer of Murshidabad District, West Bengal. Universal Journal of Environmental Research and Technology., 1(3), 311–319.
Karmegam (2012) A study on the hydrogeochemical modeling of coastal aquifers in and around Kalpakkam. Unpublished Ph. D thesis, Department of Earth Sciences, Annamalai University, India.
Karmegam, U., Chidambaram, S., Prasanna, M. V., Sasidhar, P., Manikandan, S., Johnsonbabu, G., et al. (2011). A study on the mixing proportion in groundwater samples by using Piper diagram and Phreeqc model. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 30, 490–495.
Karmegam, U., Chidambaram, S., Sasidhar, P., Manivannan, R., Manikandan, S., & Anandhan, P. (2010). Geochemical Characterization of Groundwater’s of Shallow Coastal Aquifer in and Around Kalpakkam, South India. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 2(4), 170–177, ISSN: 2041-0492.
Keswick, B. H. (1984). Sources of groundwater pollution. In G. Britton & C. P. Gerba (Eds.), 26 Groundwater pollution microbiology (pp. 39–64). New York, NY: Wiley.
Kortatsi, B. K., Anku, Y. A., & Anornu, G. K. (2008). Characterization and appraisal of facets influencing geochemistry of groundwater in the Kulpawn sub-basin of the White Volta Basin, Ghana. Environmental Geology. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1638-9.
Kumar, S. (1997). Widescale arsenic poisoning found in South Asia. Lancet, 349, 1378p.
Lalwani, S., Dogra, T. D., Bhardwaj, D. N., Sharma, R. K., Murty, O. P., & Vij, A. (2004). Study on arsenic level In ground water of delhi using hydride generator accessory coupled with atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 19(2), 135–140.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313, 77–89.
Maharjan, M., Watanabe, C., Ahmad, A., & Ohtsuka, R. (2005). Arsenic contamination in drinking water and skin manifestations in lowland Nepal: the first community-based survey. American Journal of Tropical Medicine Hygiene, 73, 477–479.
Mandal, B. K. (1998). Status of arsenic problem in two blocks out of sixty in eight groundwater arsenic affected districts of West Bengal, India. PhD Thesis, Jadavpur University, Calcutta, India.
McArthur, J. M., et al. (2008). How paleosols influence groundwater flow and arsenic pollution: A model from the Bengal Basin and its worldwide implication. Water Resources Research,. doi:10.1029/2007WR006552.
Miranda, J., Andrade, E., Lo´pez-sua´rez, A., Ledesma, T. R., Cahill, A., & Wakabayashi, P. H. (1996). A receptor model for atmospheric aerosols from a south-western site in Mexico City. Atmospheric Environment, 30(20), 3471–3479.
Molerio León, L. F., & Toujague de la Rosa, R. (2004). Arsenic in a hard rock aquifer: multivariate optimisation of the groundwater monitoring network. In 32nd International Geological Congress Florence, Italy August 20, 2004 to August 28, 2004.
Mukherjee, D. C., Chowdhury, S. B., Paul, A., & Das, P. (2012). A review on arsenic pollution in West Bengal and Bihar : Cause, effects and remedial measures following latest technology. Journal of Indian Chemistry Society, 89, 9–18.
Navada, S. V., & Rao, S. M. (1991). Study of Ganga river—groundwater interaction using environmental oxygen-18. Isotopenpraxis, 27(8), 380–384.
Nickson, R. T., McArthur, J. M., Burgess, W. G., Ahmed, K. M., Ravens croft, P., & Rahaman, M. (1998). Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater. Nature, 395(6700), 338.
Nikolaidis, N. (1998). Oral communication, University of Connecticut.
Oinam, J. D., Ramanathan, A. L., Linda, Anurag, & Singh, Gurmeet. (2011). A study of arsenic, iron and other dissolved ion variations in the groundwater of Bishnupur District, Manipur, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(6), 1183–1195.
Peryea, F. (1991). Phosphate–induced release of arsenic from soil contaminated with lead arsenate. Soil Science America Journal, 55, 1301–1306.
Peryea, F. J., & Kammereck, R. (1997). Phosphate–enhanced movement of arsenic out of lead arsenate–contaminated topsoil and through uncontaminated subsoil. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 93(1–4), 243–254.
Pfeifer, H. R., Giradet, A., Lavanchy, J. C., Reymond, D., Schlegel, C., & Schmidt, V. (2001). Pathways of natural arsenic from rocks and acid soils to groundwaters and plants in Southern Switzerland. In J. Weber et al. (Eds.) Biochemical processes and cycling of elements in the environment (pp. 391–392). Wroclaw, Poland: Polish Society of Humic Substances.
Prasanna, M. V., Chidambaram, S., Shahul Hameed, A., & Srinivasamoorthy, K. (2010). Study of evaluation of groundwater in Gadilam basin using hydrogeochemical and isotope data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 168, 63–90.
Prasanna, M. V., Praveena, S. M., Chidambaram, S., Nagarajan, R., & Elayaraja, A. (2012). Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring: a case study from Curtin Lake, Miri City, East Malaysia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(7), 1987–2001.
Ramanathan, S. (1956). Ultrabasic rocks of Salem and Dodkanya and their relationship with Charnockite, PhD Thesis Unpublished.
Ramesh, R., & Sarin, M. M. (1992). Stable isotope study of the Ganga (Ganges) river system. Journal of Hydrology, 139, 49–62.
Raymahashay, B. C., & Khare, A. S. (2003). The arsenic cycle in late quaternary fluvial sediments: Mineralogical considerations. Special section: Late Cenozoic fluvial deposits. Current Science, 84(8), 25.
Reymond, D., Pfeifer, H. R., Hesterberg, D., & Weiqing Chou, J. (2001). X-ray adsorption spectroscopy of some arsenic-contaminated soils. In J. Weber et al. (Eds.), Biochemical processes and cycling of elements in the environment (pp. 393–394). Wroclaw, Poland: Polish Society of Humic Substances.
Rogers, R. J. (1989). Ground Water, 27, 690–712.
Salameh, E. (2004). Using environmental isotopes in the study of the recharge–discharge mechanisms of the Yarmouk catchment area in Jordan. Hydrogeology Journal, 12, 451–463.
Saikia, K. C., & Gupta, S. (2012). Assessment of surface water quality in an arsenic contaminated village. American Journal of Environmental Science, 8(5), 523–527.
Shah, B. A. (2010). Arsenic-contaminated groundwater in Holocene sediments from parts of Middle Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. Current Science, 98, 10–25.
Shakeri, A., Moore, F., & Modaberi, S. (2009). Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the Shiraz industrial complex zone soil, South Shiraz, Iran. World Applied Science Journal, 6(3), 413–425.
Sharifi, Zahed. (2012). Arsenic and other irrigation water quality Indicators of groundwater in an agricultural area of Qorveh Plain, Kurdistan, American-Eurasian. Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 12(4), 548–555.
Sharma, R. M. (1999). Research study on possible contamination of groundwater with Arsenic in Jhapa, Morang, and Sunsari districts of Eastern Terai of Nepal. Report of the WHO Project, DWSS, Govt of Nepal.
Shih, M. C. (2005). An overview of arsenic removal by pressure-driven membrane processes. Desalination, 172(1), 85–97.
Singh, A. K. (2006). Chemistry of arsenic in ground water of Ganges-Brahmputra river basin, India. Current Science, 91(5), 1–7.
Singh, V. S., & Saxena, V. K. (2004). Assessment of utilization ground water resources in a coastal shallow aquifer. In Proceeding of the 2nd Asia pacific association of hydrology & water resources conference. (Vol. 2, pp. 347–364).
Singh, V. S., Saxena, V. K., Prakash, B. A., Mondal, N. C., & Jain, S. C. (2004). Augmentation of ground water resources in saline ingress coastal deltaic area (pp. 61). NGRI-Tech. Report. No. NGRI-2004-GW-422.
Smith, A. H., Lingas, E. O., & Rahman, M. (2000). Contamination of drinking-water by arsenic in Bangladesh: A public health emergency. Bulletin World Health Organisation, 78, 1093.
Stewart, F. H. (1963). Marine evaporites. In M. Fleischer (Ed.), 1-52 in Data of Geochemistry (6th ed.). Washington: Geological Survey.
Stollenwerk, K. G. (2003). Geochemical processes controlling transport of arsenic in groundwater: a review of adsorption. In Arsenic in ground water: Geochemistry and occurrence (pp. 67-100) . Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Tareq, S. M., Nazrul Islam, S. M., Majibur Rahmam, M., & Chowdhury, Didarul Alam. (2010). Arsenic pollution in groundwater of Southeast Asia: an overview on mobilization process and health effects. Bangladesh Journal of Environmental Research, 8, 47–67.
Tirumalesh K. (2012). Characterization of groundwater in the coastal aquifers of Pondicherry region using chemical, isotopic and geochemical modelling approaches, Published thesis.
Umitsu, M. (1993). Late quaternary sedimentary environments and landforms in the Ganges Delta. Sedimentary Geology, 83, 177–186.
Van Geen, A., Zheng, Y., Versteeg, R., Stute, M., Horneman, A., Dhar, R., et al. (2003). Spatial variability of arsenic in 6000 tube wells in a 25 km (2) area of Bangladesh. Water Resources Research, 39, 1140.
Vengosh, A., Gill, J., Davisson, M. L., & Hudson, G. B. (2002). A multiisotope (B, Sr, O, H, and C) and age dating study of groundwater from Salinas Valley, California: Hydrochemistry, dynamics, and contamination process. Water Resources Research, 38(1), 1–17.
Widory, D., Kloppmann, W., Chery, L., Bonnin, J., Rochdi, H., & Guinamant, J. L. (2004). Nitrate in groundwater: An isotopic multi-tracer approach. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 72, 165–188.
Wilson, J., Schreier, H., & Brown, S. (2008) Arsenic in Groundwater in the Surrey-Langley Area. Institute for Resources & Environment The University of British Columbia For: Fraser Health Authority Environmental Health Services Abbotsford, B.C. and Ministry of Environment Lower Mainland Region Surrey.
Woolsen, E. A., Axley, J. H., & Kearney, P. C. (1973). The chemistry and phytotoxicity of arsenic in soil: II. Effects of time and phosphorous. Soil Science Society America Proceedings, 37(2), 254–259.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2001). United Nations synthesis report on arsenic in drinking water, Geneva.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality recommendations (Vol. 1, p. 515). Geneva: WHO.
Xie, X., Wang, Y., Chunli, S., Li, Junxia, & Li, Mengdi. (2012). Influence of irrigation practices on arsenic mobilization: Evidence from isotope composition and Cl/Br ratios in groundwater from Datong Basin, northern China. Journal of Hydrology, 424–425, 37–47.
Zagana, E., Obeidat, M., Kuells, C., & Udluft, P. (2007). Chloride, hydrochemical and isotope methods of groundwater recharge estimation in eastern Mediterranean areas: a case study in Jordan. Hydrological Processes, 21, 2112–2123.
Zhu, G. F., Li, Z. Z., Su, Y. H., Ma, J. Z., & Zhang, Y. Y. (2007). Hydro geochemical and isotope evidence of groundwater evolution and recharge in Minqin Basin, Northwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 333, 239–251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chidambaram, S., Thilagavathi, R., Thivya, C. et al. A study on the arsenic concentration in groundwater of a coastal aquifer in south-east India: an integrated approach. Environ Dev Sustain 19, 1015–1040 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9786-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9786-7